An artificial intelligence system developed in John Dabiri’s lab could one day swim and navigate autonomously underwater even more effectively than living creat… See more.
New AI uses reinforcement learning to efficiently navigate oceans.
An artificial intelligence system developed in John Dabiri’s lab could one day swim and navigate autonomously underwater even more effectively than living creat… See more.
New AI uses reinforcement learning to efficiently navigate oceans.

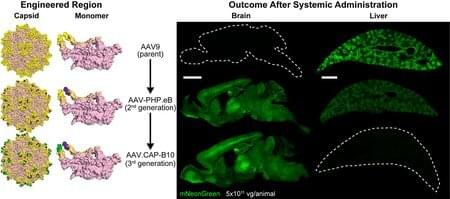
Gene therapy is a powerful developing technology that has the potential to address myriad diseases. For example, Huntington’s disease, a neurodegenerative disorder, is caused by a mutation in a single gene, and if researchers could go into specific cells and correct that defect, theoretically those cells could regain normal function.
A major challenge, however, has been creating the right “delivery vehicles” that can carry genes and molecules into the cells that need treatment, while avoiding the cells that do not.
Now, a team led by Caltech researchers has developed a gene-delivery system that can specifically target brain cells while avoiding the liver. This is important because a gene therapy intended to treat a disorder in the brain, for example, could also have the side effect of creating a toxic immune response in the liver, hence the desire to find delivery vehicles that only go to their intended target. The findings were shown in both mouse and marmoset models, an important step towards translating the technology into humans.
😃
In a paper published today in the scientific journal Science, DeepMind demonstrates how neural networks can be used to describe electron interactions in chemical systems more accurately than existing methods.
Density Functional Theory, established in the 1960s, describes the mapping between electron density and interaction energy. For more than 50 years, the exact nature of mapping between electron density and interaction energy—the so-called density functional—has remained unknown. In a significant advancement for the field, DeepMind has shown that neural networks can be used to build a more accurate map of the density and interaction between electrons than was previously attainable.
By expressing the functional as a neural network and incorporating exact properties into the training data, DeepMind was able to train the model to learn functionals free from two important systematic errors—the delocalisation error and spin symmetry breaking—resulting in a better description of a broad class of chemical reactions.
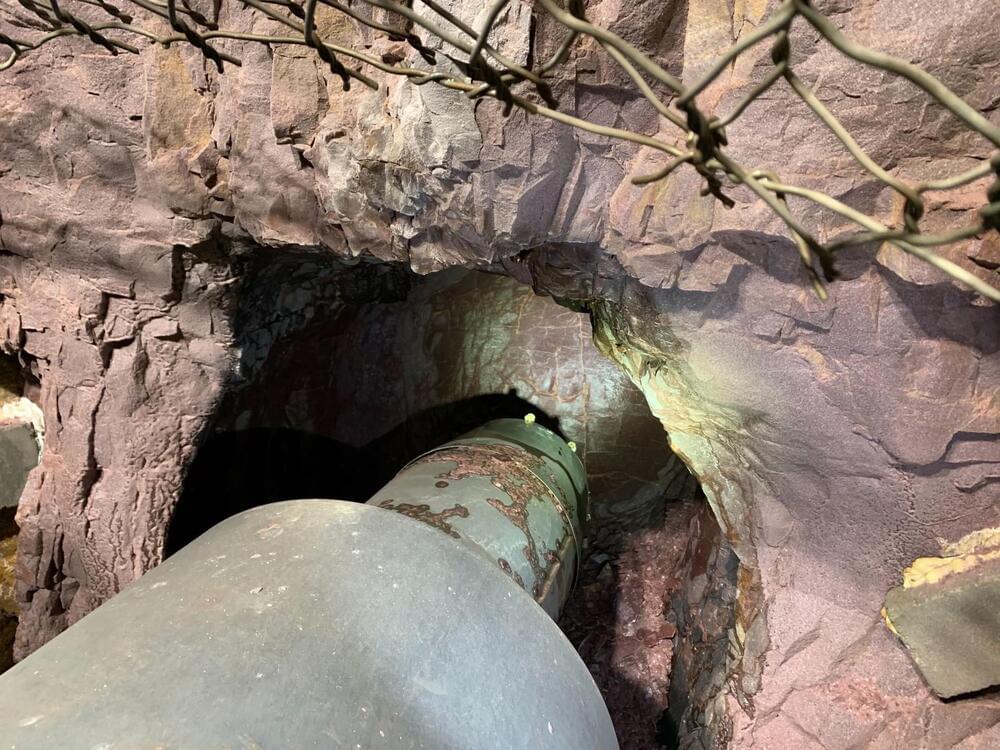

Petra emerged from stealth this week, announcing a $30 million Series A. The round, led by DCVC, brings the robotics company’s funding up to $33 million, with additional participation from ACME Capital Congruent Ventures, 8VC, Real Ventures, Elementum Ventures and Mac Venture Capital.
“We’ve invented a completely new way to excavate rock and this will have profound implications on the future of tunneling,” co-founder and CEO Kim Abrams said in release tied to the news. “By delivering a boring solution that affordably undergrounds utilities through high-grade rock, we can finally protect communities from exposure to wildfires and ensure the safety of critical infrastructure in disaster-prone areas, especially in places like the Sierra Nevada mountains, Rocky Mountains, and coastal regions.”
The news arrives as the company is announcing a successful pilot of its robot, Swifty. According to the firm, the robot successfully bored a 20-foot tunnel through Sioux Quartzite at a rate of one inch-per-minute. The metamorphic rock is notoriously hard, making it a popular choice for buildings in the upper Midwest region in which it is found. That strength, however, also makes it a formidable challenge from infrastructure and other projects that require tunneling.
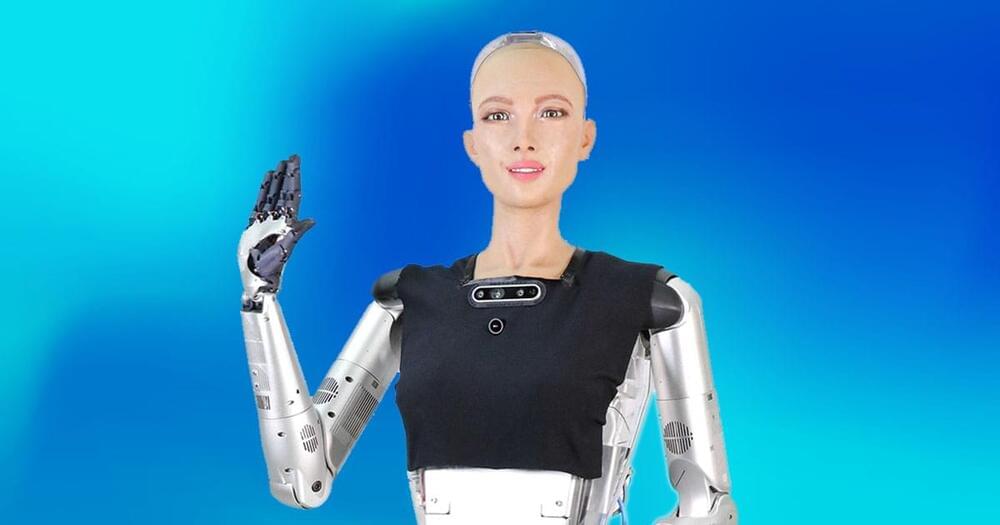

Since then, Sophia has spoken to audiences across the globe (in multiple languages), been interviewed on countless TV shows, and even earned a United Nations title (a first for a non-human).
Today, she’s arguably the most famous robot in the world, but she’s isn’t going to be unique for much longer. Her maker, Hanson Robotics, has announced plans to begin mass-producing Sophia the robot this year — so that she can help the world cope with the pandemic.

As Russia ramps up preparations for a possible assault on Ukraine, President Biden has ruled out sending U.S. troops, but an invasion would still face serious resistance and Ukraine’s defense minister promising a ‘bloody massacre’ if Russia invades. While Ukraine is heavily outmatched by Russian forces, the threat of heavy casualties is one which Russian cannot ignore. This is why uncrewed systems – remote-controlled robot warriors – could play an important part where the fighting is heaviest.
Soviet Russia shrugged off mass casualties, with Stalin remarking, “One death is a tragedy; a million deaths is a statistic.” During World War II – the Great Patriotic War to Russians – the Soviet Union lost more than 8 million members of its armed forces, 20 times as many as the United States. Names like Stalingrad became legendary for bloody battles and tough resistance regardless of casualties.
Modern Russia is very different. Unlike Stalin, President Putin cannot ignore public opinion, and his media machine will hide or deny Russian casualties in foreign operations. Mercenaries are increasingly used to keep conflict at arm’s length, as the loss of contractors does not play so badly in the motherland.
And it looks a little creepy.
Roboticists at the Italian Institute of Technology (IIT) strapped a fully functioning jetpack onto their humanoid robot, called iRonCub, a report from IEEE Spectrum reveals.
While several outlets have unsurprisingly drawn comparisons to Iron Man, the truth looks far scarier, and like something out of an as-yet unmade horror movie.
In the same configuration as Gravity Industries’ famous Iron Man-like jetpack design, the iRonCub robot was equipped with four jet engines, giving it the ability to fly. Tests are ongoing, but let’s just say, the team at IIT have struggled at times to keep their robot from igniting, and even exploding, due to the exhaust from the engines.
Full Story:
Become smarter in 5 minutes by signing up for free today: https://cen.yt/mbcoldfusion12
Previous GPT-3 Episode: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Te5rOTcE4J4
Podcast: https://open.spotify.com/show/3dj6YGjgK3eA4Ti6G2Il8H?si=a233e860cd3c4334
— About ColdFusion –
ColdFusion is an Australian based online media company independently run by Dagogo Altraide since 2009. Topics cover anything in science, technology, history and business in a calm and relaxed environment.
ColdFusion Discord: https://discord.gg/coldfusion.
ColdFusion Music Channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCGkpFfEMF0eMJlh9xXj2lMw.