Today’s rechargeable batteries are a wonder, but far from perfect. Eventually, they all wear out, begetting expensive replacements and recycling.
“But what if batteries were indestructible?” asks William Chueh, an associate professor of materials science and engineering at Stanford University and senior author of a new paper detailing a first-of-its-kind analytical approach to building better batteries that could help speed that day. The study appears in the journal Nature Materials.
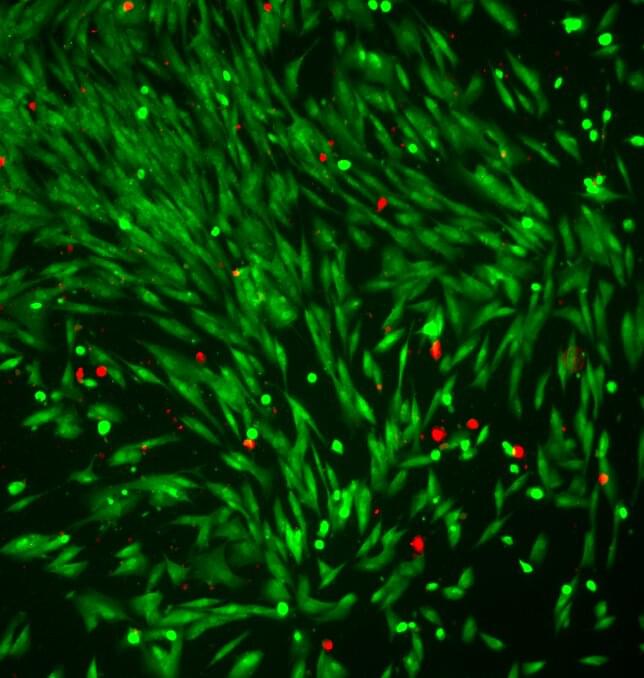
Chueh, lead author Haitao “Dean” Deng, Ph.D. ‘21, and collaborators at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, MIT and other research institutions used artificial intelligence to analyze new kinds of atomic-scale microscopic images to understand exactly why batteries wear out. Eventually, they say, the revelations could lead to batteries that last much longer than today’s. Specifically, they looked at a particular type of lithium-ion batteries based on so-called LFP materials, which could lead to mass-market electric vehicles because it does not use chemicals with constrained supply chains.