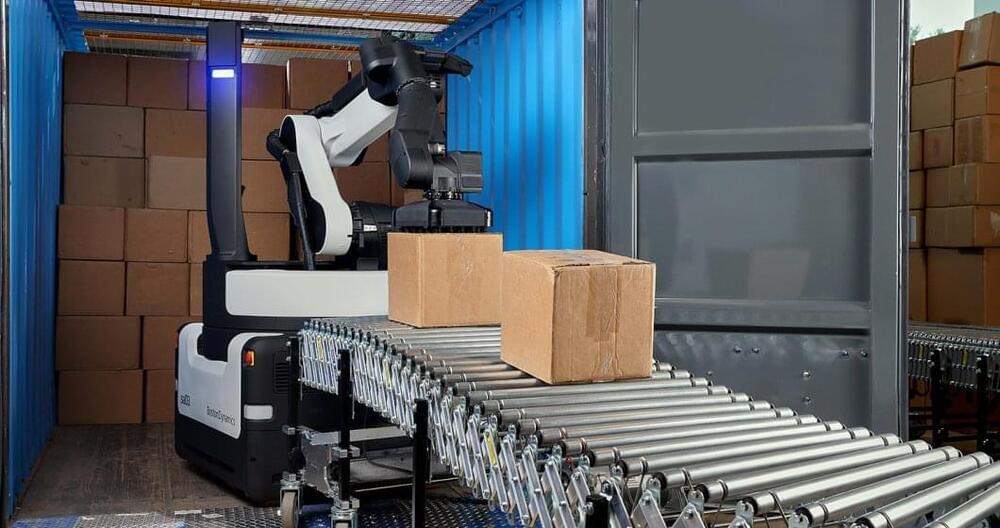
CAMDEN, N.J., August 30, 2022 – NFI, a leading supply chain solutions provider, today announced it has signed a $10 million agreement to deploy Boston Dynamics’ newest robot, Stretch, across its U.S. warehousing operations. The mobile robot will begin unloading trucks and containers as a pilot program at NFI’s Savannah, GA facility in 2023, with plans to outfit additional warehouse locations across North America over the next few years.
Supply chain demand remains near all-time highs. To support the flow of goods and increase operational capacity, NFI continues to invest in technology that supports a people-led, technology-enabled approach. The investment also falls in line with NFI’s Applied Innovation focus, which pilots new technologies to demonstrate a real-world application within operations before scaling across its North American network.
“At a time when companies need to evolve to meet consumer expectations, NFI has stepped in as the innovative logistics partner, contributing to our customers’ competitive edge,” said Sid Brown, CEO of NFI. “Our innovation portfolio emphasizes productivity and safety in NFI’s operations. With Stretch, we will enhance the movement of freight through our facilities while providing a safer environment for our employees.”
 עברית (Hebrew)
עברית (Hebrew)