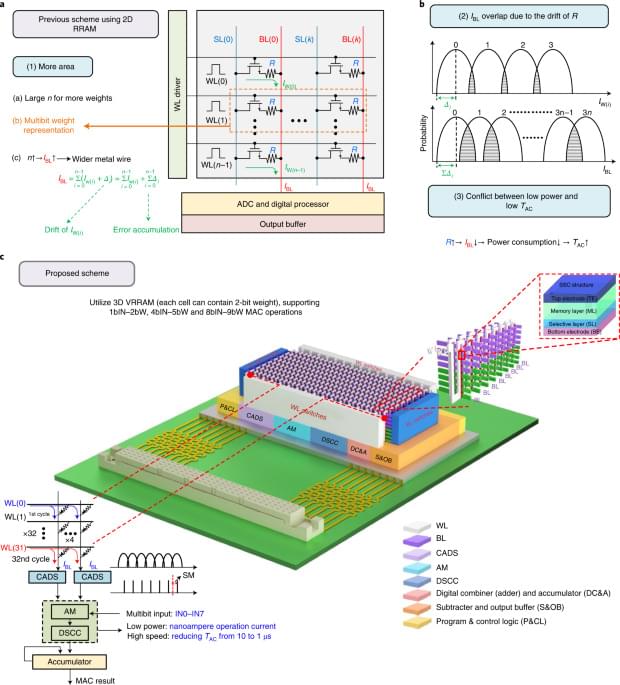
Three-dimensional computing-in-memory circuits based on vertical resistive random-access memory and complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor technologies can be used to create efficient hardware for artificial neural networks.

A team of researchers at Google’s Deep Mind London project, has taught animated players how to play a realistic version of soccer on a computer screen. In their paper published in the journal Science Robotics, the group describes teaching the animated players to play as solo players and also in teams.
For several years, robot engineers have been working diligently to create robots capable of playing soccer. Such work has resulted in competition between various groups to see who can devise the best robot players. And that has led to the creation of RoboCup, which has several leagues, both in the real world and simulated. In this new effort, the researchers applied a new degree of artificial intelligence programming and learning networks to teach simulated robots how to play soccer without ever giving them the rules.
The idea behind the new approach is to get simulated soccer players to learn to play the game the same way humans do—by watching how others do it. It also involved starting from pretty much ground zero. The simulated players first had to learn how to walk, then to run and kick a ball around. At each new level, the AI systems were shown video of real-world soccer players, which allowed them to learn not just the basics of soccer playing, but to mimic the way professional athletes move as they engage in high level sporting events.

Two of America’s top chipmakers have been ordered to stop selling some of their technology to China that can be used for artificial intelligence.
Nvidia (NVDA) and AMD (AMD) said Wednesday that they had been told by the US government to halt exports of certain high-performance chips to the world’s second largest economy.
In a regulatory filing, Nvidia said that it had been told by US officials that the requirement was due to a potential risk of the products being used by, or diverted to, a “military end user.”
North American robot sales continued to set records for year-over-year growth, according to the Association for Advancing Automation. FANUC also saw strong demand.

By Thomas Frey | Sep 1, 2022 | Artificial Intelligence
When Steve Jobs unveiled the iPhone in 2007, no one understood at the time how disruptive that device would be to existing technology. Now with rumors of Apple launching their augmented reality (AR) smart glasses products next year, people are speculating about how disruptive this technology will be.
Since iPhones are one of Apple’s primary revenue streams, they may be cautious about releasing a product that may encroach on their own turf. However, as we’ll suggest below, it may not be an either/or situation for users.
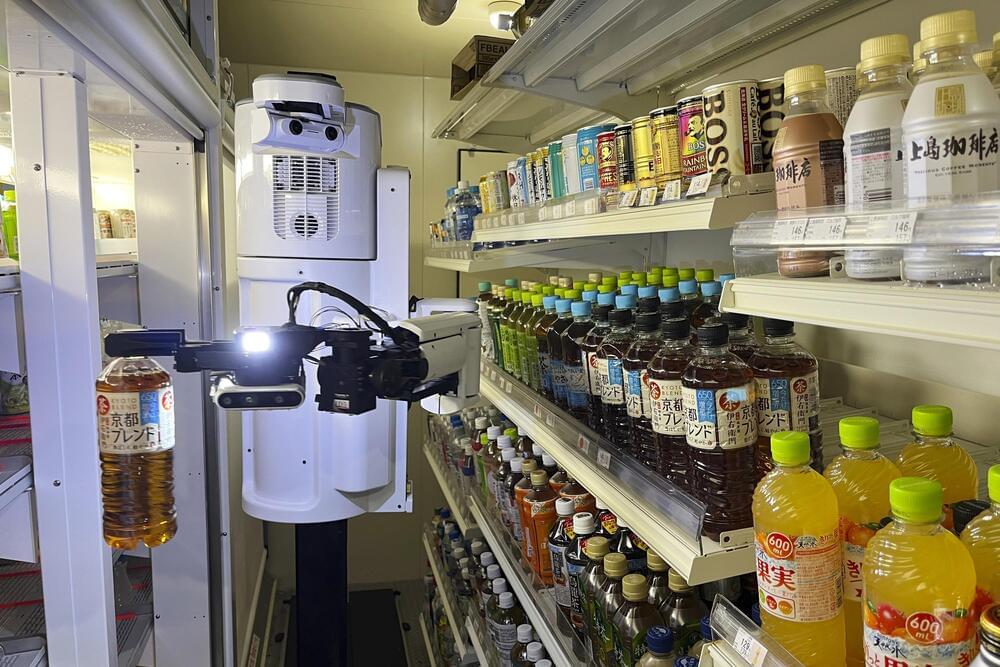

TOKYO (AP) — A small robot with a clip-like hand and enough smarts to know which drinks are popular is part of an effort to make convenience stores even more convenient.
On a recent day in Tokyo, the robot named TX SCARA slid back and forth behind the refrigerated shelves in the back of a FamilyMart store.
The hand on the end of its mechanical arm grasped a bottle or can from the stacks to the side, then the robot slithered to the right spot and placed the drink on the shelf — in a place chosen after its artificial intelligence and tiny cameras matched the kind of beverage to what’s running short.
Text-to-video generators are already creating award-winning short films. Are AI-generated blockbusters coming next?

Conversational AI platform Jio Haptik has tied up with Microsoft Azure to improve its existing hindi language chatbots | Photo Credit: Getty Images.
He claimed that using the data from Haptik and cognitive models from Microsoft, the team could come up with a highly accurate solution for Hindi — not only written in Devanagari but also Hindi written in Roman script.

Every year, more than 69 million people around the world suffer traumatic brain injury, which leaves many of them unable to communicate through speech, typing, or gestures. These people’s lives could dramatically improve if researchers developed a technology to decode language directly from noninvasive brain recordings. Today, we’re sharing research that takes a step toward this goal. We’ve developed an AI model that can decode speech from noninvasive recordings of brain activity.
From three seconds of brain activity, our results show that our model can decode the corresponding speech segments with up to 73 percent top-10 accuracy from a vocabulary of 793 words, i.e., a large portion of the words we typically use on a day-to-day basis.
Decoding speech from brain activity has been a long-standing goal of neuroscientists and clinicians, but most of the progress has relied on invasive brain-recording techniques, such as stereotactic electroencephalography and electrocorticography. These devices provide clearer signals than noninvasive methods but require neurosurgical interventions. While results from that work suggest that decoding speech from recordings of brain activity is feasible, decoding speech with noninvasive approaches would provide a safer, more scalable solution that could ultimately benefit many more people. This is very challenging, however, since noninvasive recordings are notoriously noisy and can greatly vary across recording sessions and individuals for a variety of reasons, including differences in each person’s brain and where the sensors are placed.
