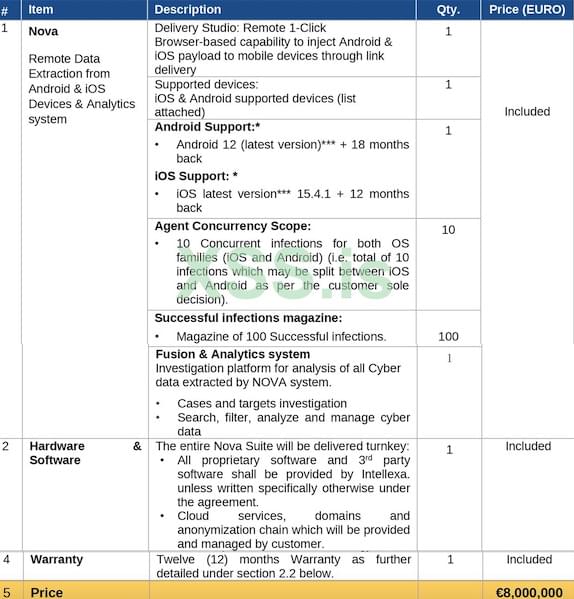
Are you ready to put mini robots in your mouth?
Do you get lazy about brushing your teeth? Well, soon microbots could do the whole thing for you. A multidisciplinary team at the University of Pennsylvania has created a novel automated way to perform brushing and flossing through robotics, according to a press release published by the institution last month.
The development could be particularly useful for those who lack the manual dexterity to clean their teeth effectively themselves.
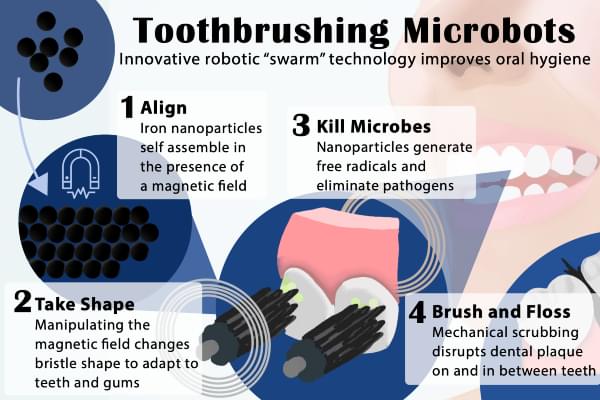
A shapeshifting robotic microswarm may one day act as a toothbrush, rinse, and dental floss in one.
The technology, developed by a multidisciplinary team at the University of Pennsylvania, is poised to offer a new and automated way to perform the mundane but critical daily tasks of brushing and flossing. It’s a system that could be particularly valuable for those who lack the manual dexterity to clean their teeth effectively themselves.
The building blocks of these microrobots are iron oxide nanoparticles that have both catalytic and magnetic activity. Using a magnetic field, researchers could direct their motion and configuration to form either bristlelike structures that sweep away dental plaque from the broad surfaces of teeth, or elongated strings that can slip between teeth like a length of floss. In both instances, a catalytic reaction drives the nanoparticles to produce antimicrobials that kill harmful oral bacteria on site.