Using artificial intellgence to find possibilities while humans gauge their significance is proving to be a powerful new form of scientific discovery.



Elon Musk Reveals Secret DOJO Computer at Tesla AI Day.
#teslanews #teslaai #elonmusk.
During AI Day, the Tesla CEO was the first person to confirm the existence of the ‘Dojo’ program: “We do have a major program at Tesla which we don’t have enough time to talk about today called ” Dojo”. That’s a super powerful training computer. The goal of Dojo will be to be able to take in vast amounts of data and train at a video level and do massive unsupervised training of vast amounts of video with the Dojo program – or Dojo computer.”
In June 2020, Elon Musk tweeted, “Dojo, our training supercomputer, will be able to process vast amounts of video training data & efficiently run hyperspace arrays with an enormous number of parameters, plenty of memory & ultra-high bandwidth between cores.
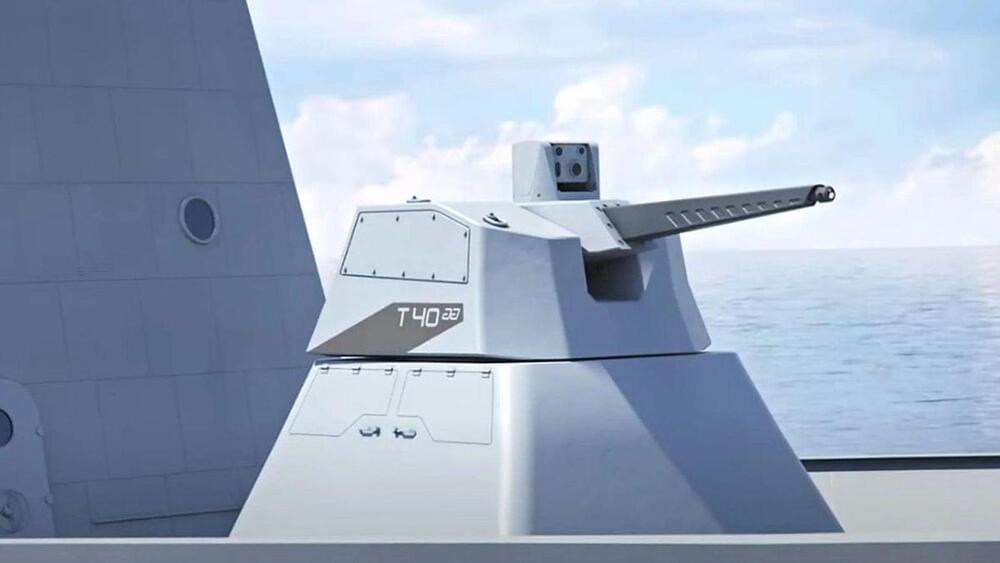

The system autonomously ensures high interception accuracy while retaining a non-penetrating turret design.
US and French defense companies have unveiled the latest version of the RAPIDFire autonomous gun turret at the Euronaval 2022, a naval defense exhibition, in Paris.
The gun turret which is a joint effort of Nexter and Thales, is claimed to counter growing low-level, close-quarters surface and aerial threats, as per a press release published by the defense company Nexter on Wednesday.
The only way we can safeguard against this terrifying future is if nations collectively take action.
You might suppose Hollywood is good at predicting the future. Indeed, Robert Wallace, head of the CIA’s Office of Technical Service and the US equivalent of MI6’s fictional Q, has recounted how Russian spies would watch the latest Bond movie to see what technologies might be coming their way.
Hollywood’s continuing obsession with killer robots might therefore be of significant concern. The newest such movie is Apple TV’s forthcoming sex robot courtroom drama Dolly.
I never thought I’d write the phrase “sex robot courtroom drama”, but there you go.
Mikkelwilliam/iStock.
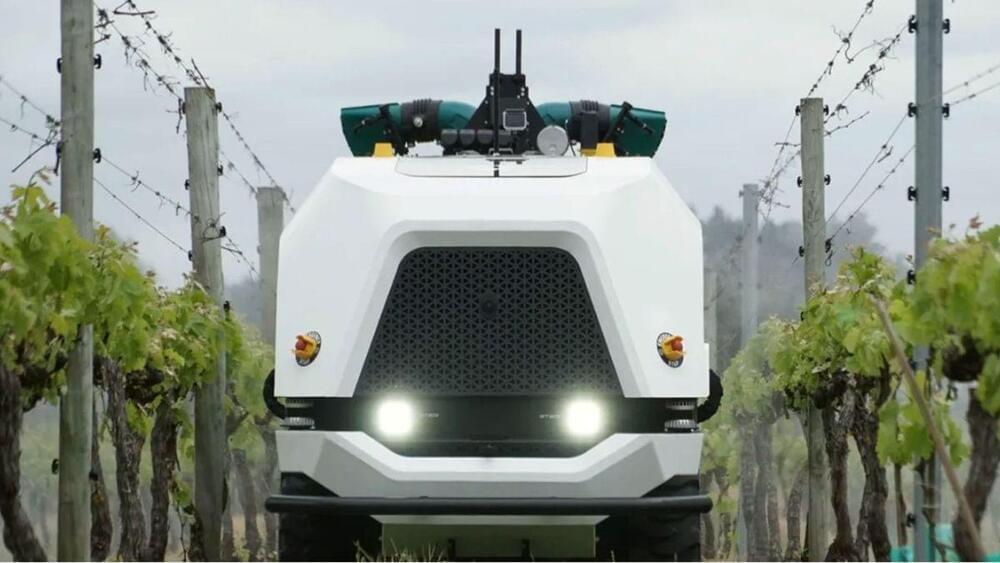

New Zealand-based agritech company Robotics Plus has launched an autonomous multi-use, modular vehicle for agriculture that could revolutionize the industry by alleviating ongoing labor shortages and simplifying agricultural tasks, according to a press release by the firm published on Thursday.
Optimizing tasks
The robot can be supervised in a fleet of vehicles by a single human operator, using a combination of vision systems and other technologies to sense its environment. This empowers it to optimize tasks and allow intelligent and targeted application of inputs such as sprays. It is suitable for a variety of jobs including spraying, weed control, mulching, mowing and crop analysis.
Many modern science fiction movies tend to use the veneer of science fiction as a way to plug potholes or feature elaborate explosions and action. There’s always a time-travel portal to stand in as the deus ex machina, and some advanced robot or alien who only seems interested in killing everyone.
I like those movies as much as the next fella. But some filmmakers do make a sincere effort to imagine other realities and technologies that inspire in the way classic science fiction does. It doesn’t mean the films have to be the on-screen equivalent of reading an MIT paper on quantum entanglement or something, just that they spin a decent yarn inspired by actual science.
The below are a few slightly less commercial selections, instead of obvious choices like Interstellar or 2001 or Chef, that science fiction movie where Jon Favreau dates both Scarlett Johnasson and Sofia Vergara. That’s the future I want.
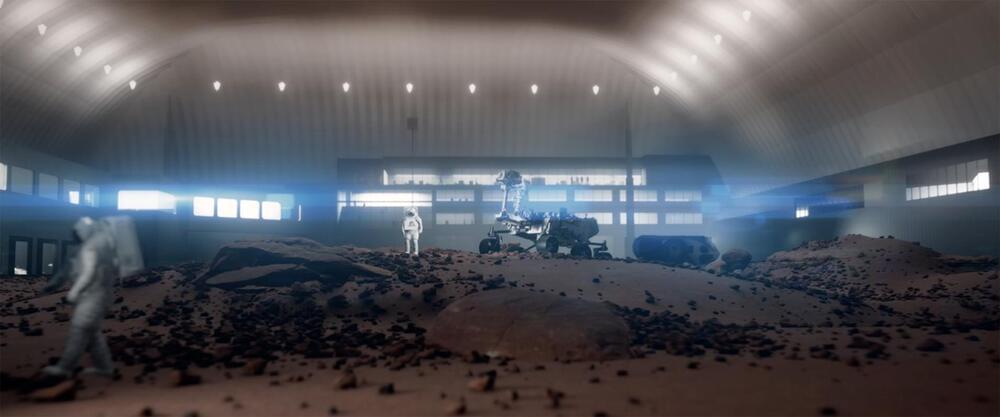


HOUSTON, Oct. 18, 2022 – The nonprofit Space Center Houston is advancing a Facilities Master Plan to support the growing need for space exploration learning and training in two massive structures that will also give the public a front row seat into the development of robotics, rovers, lunar landers and reduced gravity systems. Today, the center offered a glimpse of the facility that will include two enclosed simulated cosmic terrains of the Moon and Mars, as well as modular surface labs and STEM learning centers. An elevated exhibit hall over the two surfaces will offer the public immersive experiences to observe astronaut training first-hand while experiencing the future of space exploration as humans return to the Moon and eventually on to Mars.
Space Center Houston is responding to the opportunities and challenges in a rapidly evolving space sector, including the need for facilities built for current and future missions, while sharing this excitement with the public and addressing critical gaps in the development of the STEM workforce through its education programs. The facility will bring together guests, NASA, commercial space partners, colleges, universities and global space agencies to collaborate on new technologies that are propelling present and future human spaceflight.
For 30 years, Space Center Houston has chronicled the journey of human spaceflight while empowering and inspiring people to pursue careers in science, technology, engineering and mathematics. “Space is expanding once again and a new space age is upon us,” said William T. Harris, President and CEO Space Center Houston. “With new ambitions, new players and new challenges, we will shift our focus from being a curator of past achievements to also facilitating new feats in space.”