In June 2022, Amazon re: MARS, the company’s in-person event that explores advancements and practical applications within machine learning, automation, robotics, and space (MARS), took place in Las Vegas. The event brought together thought leaders and technical experts building the future of artificial intelligence and machine learning, and included keynote talks, innovation spotlights, and a series of breakout-session talks.
Now, in our re: MARS revisited series, Amazon Science is taking a look back at some of the keynotes, and breakout session talks from the conference. We’ve asked presenters three questions about their talks, and provide the full video of their presentation.
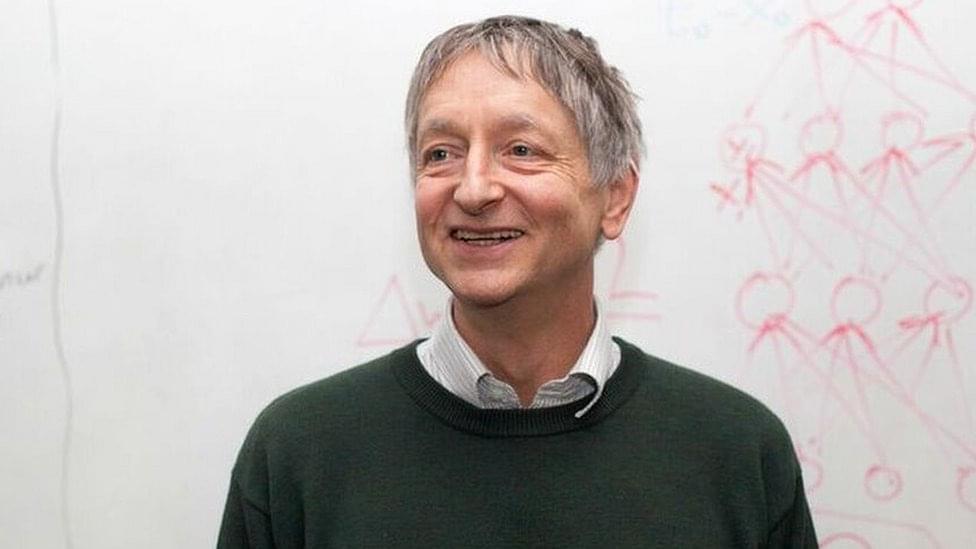
On June 24, Alexa AI-Natural Understanding employees Craig Saunders, director of machine learning, and Devesh Pandey, principal product manager, presented their talk, “Human-like reasoning for an AI”. Their presentation focused on how Amazon is developing human-like reasoning for Alexa, including how Alexa can automatically recover from errors such as recognizing “turn on lights” in a noisy environment (instead of “turn off lights”) when the lights are already on.