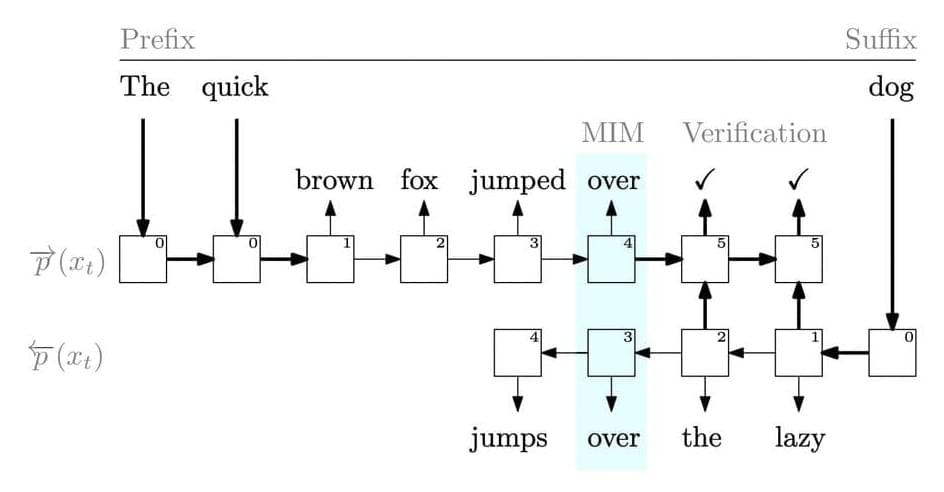
Language models (LMs) have been extensively utilized for various aided writing activities, including text summarization, code completion, and paraphrasing. LMs are effective tools for creating both natural and programming languages. Most LMs must be able to develop the next token from the sequence of earlier tokens to be useful in a wide range of applications. Due to the significance of this operation, pretraining has concentrated on improving the model’s perplexity in predicting the next token given the last tokens. However, they do have extra information that they are not using during pretraining.
For instance, they entirely disregard the following tokens while training the model to predict one token and only condition on the prefix (prior tokens) (suffix). There are alternative approaches to include the suffix in pretraining that have yet to be discussed in the literature, even though it cannot be utilized as an input to the model. They want to increase the pretraining data’s usefulness while maintaining the underlying LM’s autoregressive properties. Their strategy calls for more modeling, which at first glance could appear useless. After all, an autoregressive left-to-right LM is a primary artifact created during pretraining, and the pretraining aim closely resembles how the LM is used.
Yet, there are two reasons to explore different training objectives. Data efficiency is discussed in the first. The LM is trained using a sparse, inexpensive signal that generates a probability distribution over all potential next-token selections. However, it is only supervised using the actual next token from the training set. What if a more intense kind of supervision was used during training, where the probability distribution for the next tokens was compared to a different probability distribution? The second justification relates to other connected responsibilities. For instance, the user may prefer to fill in or edit an existing sequence of tokens in many real-world settings rather than creating text entirely from scratch.