Plus: Official ChatGPT iPhone app debuts; Debt collectors using chatbots to chase debtors.


ChatGPT has changed the world since it emerged a few short months ago. Where will future advancements in generative AI take us?
Welcome back Katie Brenneman, a regular contributor to 21st Century Tech Blog. Several weeks ago when ChatGPT entered the headlines I suggested to Katie that she consider writing about Large Language Modelling (LLM) and the technological and societal implications in terms of its capabilities. Were we witnessing the birth of consciousness in this new artificial intelligence (AI) discipline, or were we coming to terms with what defines our sentience?
By definition, sentience is about feelings and sensations and not thinking. Consciousness, on the other hand, is about our awareness of self and our place in the world around us. And thinking is about the ability to reason, consider a problem, come up with an idea or solution, or have an opinion.
So from what we know about ChatGPT in its various iterations, does it meet the definition of any of these terms? Is it sentient? Is it conscious? Is it thinking?

Join top executives in San Francisco on July 11–12, to hear how leaders are integrating and optimizing AI investments for success. Learn More
When Microsoft-funded lab OpenAI launched ChatGPT in February, millions of people realized almost overnight what tech professionals have understood for a long time: Today’s AI tools are advanced enough to transform daily life as well as an incredibly broad range of industries. Microsoft’s Bing leaped from a distant second place in search to a much higher-profile level. Concepts like large language models (LLMs) and natural language processing are now part of mainstream discussion.
However, with the spotlight also comes scrutiny. Regulators around the world are taking note of AI’s risks to user privacy. The Elon Musk-backed Future of Life Institute amassed 1,000 signatures from tech leaders asking for a six-month pause on training AI tools that are more advanced than GPT-4, which powers ChatGPT.
Rapid progress in AI is arousing fear as well as excitement. How worried should you be?


Increasingly, social robots are being used for support in educational contexts. But does the sound of a social robot affect how well they perform, especially when dealing with teams of humans? Teamwork is a key factor in human creativity, boosting collaboration and new ideas. Danish scientists set out to understand whether robots using a voice designed to sound charismatic would be more successful as team creativity facilitators.
“We had a robot instruct teams of students in a creativity task. The robot either used a confident, passionate—ie charismatic—tone of voice or a normal, matter-of-fact tone of voice,” said Dr. Kerstin Fischer of the University of Southern Denmark, corresponding author of the study in Frontiers in Communication. “We found that when the robot spoke in a charismatic speaking style, students’ ideas were more original and more elaborate.”
We know that social robots acting as facilitators can boost creativity, and that the success of facilitators is at least partly dependent on charisma: people respond to charismatic speech by becoming more confident and engaged. Fischer and her colleagues aimed to see if this effect could be reproduced with the voices of social robots by using a text-to-speech function engineered for characteristics associated with charismatic speaking, such as a specific pitch range and way of stressing words. Two voices were developed, one charismatic and one less expressive, based on a range of parameters which correlate with perceived speaker charisma.
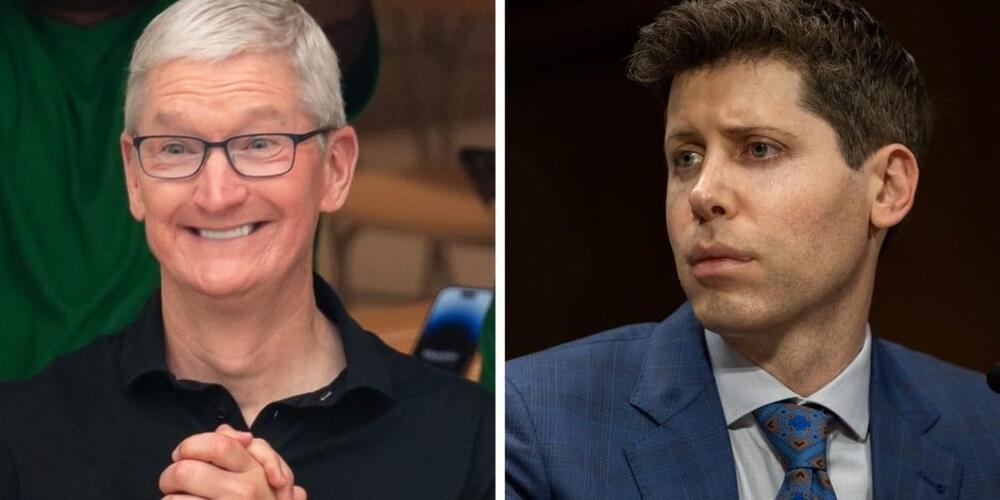

In the company’s quarterly earnings call earlier this month, CEO Tim Cook said Apple is planning to “weave” AI into its products, per The Independent. But he also cautioned about the future of the technology.
“I do think it’s very important to be deliberate and thoughtful in how you approach these things,” he said, per Inc. “And there’s a number of issues that need to be sorted as is being talked about in a number of different places, but the potential is certainly very interesting.”
Apple is also telling some employees to limit their use of ChatGPT and other external AI tools, according to an internal document seen by the Journal. That includes the automated coding tool Copilot, from the Microsoft-owned GitHub.

A team of researchers from Stanford University and Google let 25 AI-powered bots loose inside a virtual town — and they acted a lot more like humans than you might expect.
As detailed in a recent, yet-to-be-peer-reviewed study, the researchers trained 25 different “generative agents,” using OpenAI’s GPT-3.5 large language model, to “simulate believable human behavior” such as cooking up breakfast, going to work, or practicing a specific profession like painting or writing.
A virtual town called “Smallville” allowed these agents to hop from school to a cafe, or head to a bar after work.
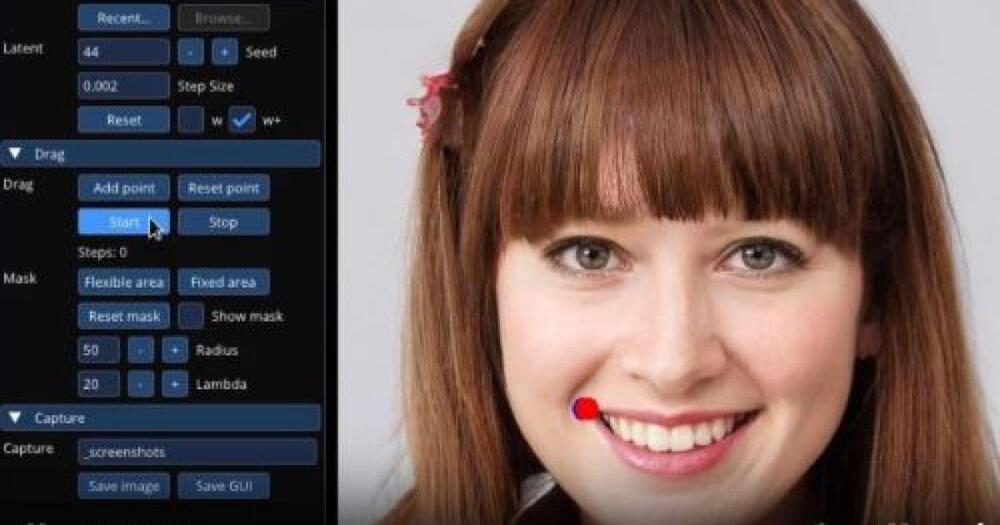
AI powered photo editing tool.
The research team noted in its paper that new details can be added within the regeneration of the edited aspects of images that are beneficial to the update. “Our approach can hallucinate occluded content, like the teeth inside a lion’s mouth, and can deform following the object’s rigidity, like the bending of a horse leg.”
There are many brands that are attempting to offer editing options for generative AI content. However, most do not go as far as allowing for the actual editing of images, but rather for aspects such as editing around images. For example, Microsoft’s Designer app allows you to generate AI images from a text prompt, and you can select your favorite from three results, then take it to the design studio where you can create a host of creativity and productivity-based projects, such as social media posts, invitations, digital postcards, or graphics with the image as the focal point. However, you cannot edit the AI-generated image.
With the DragGAN tool still being a demo for now, there is no telling what the quality of a readily available technology would be, or if it would even be possible, especially since the demos are based on low-resolution videos. However, it is an interesting example of how quickly AI continues to develop.