Korean automotive manufacturer “moving beyond land, sea, and air mobility to expand into space”.
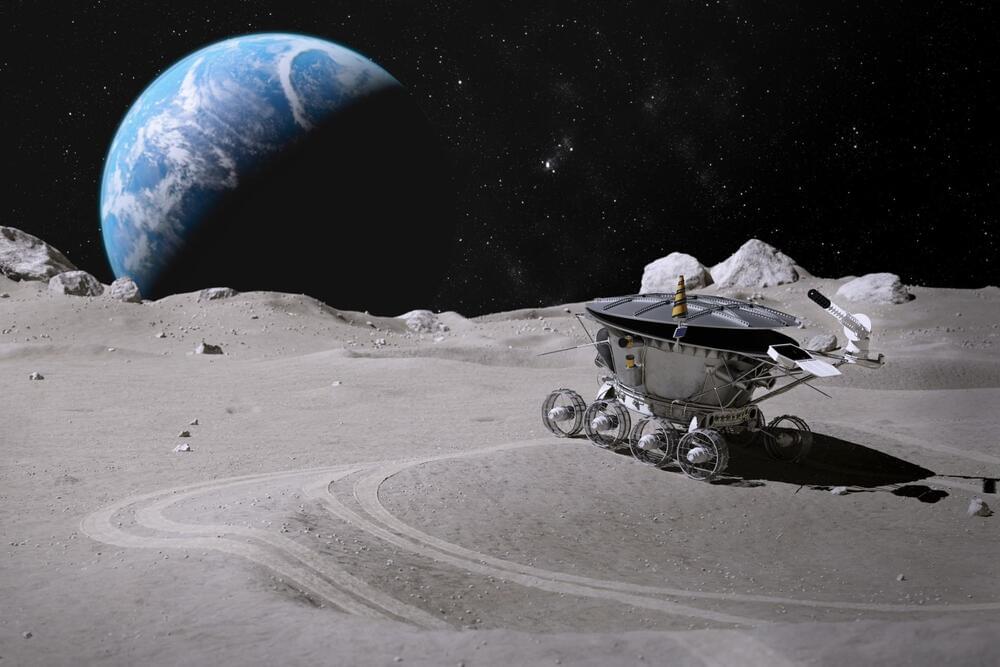
Hyundai Motor Group, a leading South Korean automotive manufacturer, has announced its entry into the space exploration industry. On April 20, 2023, the company unveiled plans to build a lunar exploration rover development model, in collaboration with several Korean research institutions in the aerospace sector.
The ambitious project aims to create a versatile mobility platform capable of handling various payloads, with cutting-edge autonomous driving technology, solar charging, thermal management, and radiation shielding features. The rover is designed to carry various pieces of equipment on top of it, with a maximum weight of 70 kg.