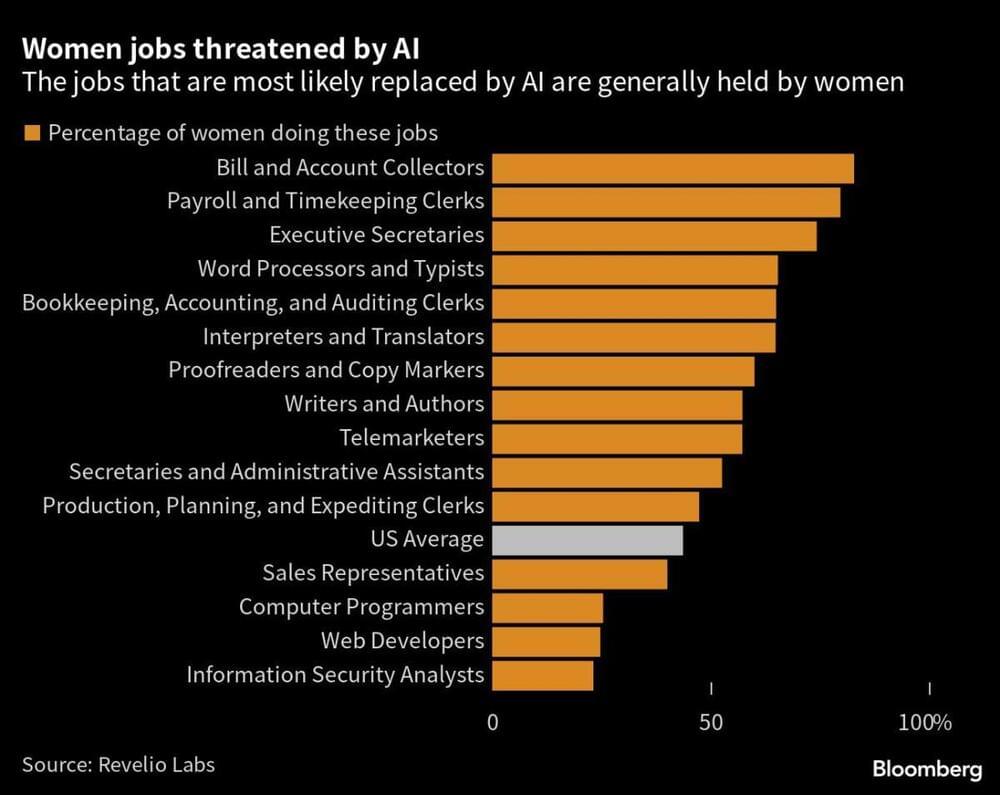
How do you decide whether a pedestrian needs to wait or it’s safe to cross the road in front of a car? In today’s world, drivers and pedestrians simply exchange a brief eye contact or small hand gestures to express their intentions to one another. But how will future autonomous cars communicate? Researchers involved in the MaMeK project are seeking to answer this question. They will present their findings at the LASER World of PHOTONICS trade fair in Munich from June 27 to 30 (Booth 415, Hall A2).
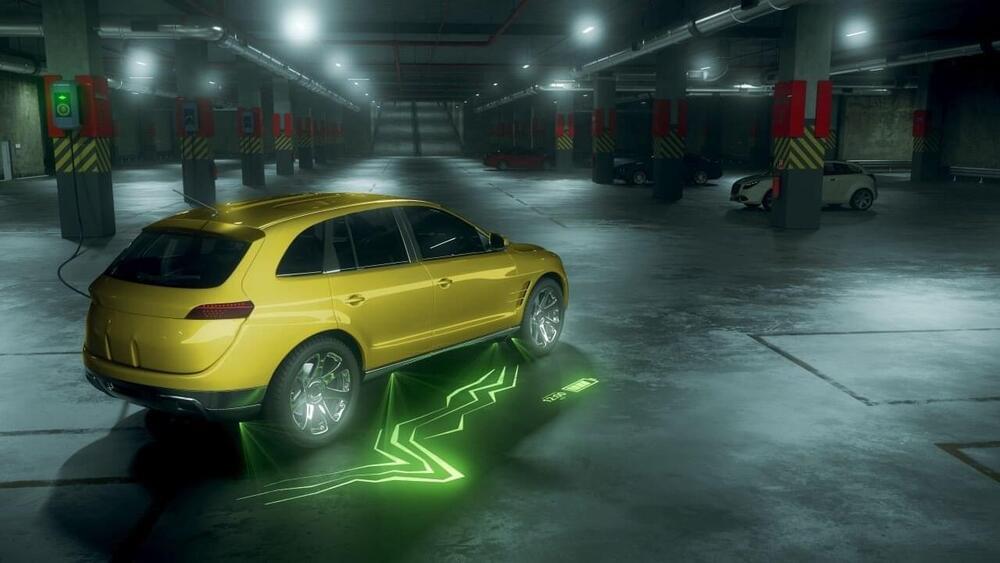
Imagine a situation in which a cyclist isn’t sure whether an approaching car giving him way or not—but then a bright projection appears in front of the vehicle, indicating that it has detected the bike and is waiting for it. This is one example of how cars and humans might communicate with one another on the streets of the future.
Together with his team at the Fraunhofer Institute for Applied Optics and Precision Engineering IOF in Jena, Norbert Danz is looking at scenarios of this kind within the MaMeK joint project, which is focusing on projection systems for human-machine communication and involves partners including Audi AG. Two technological approaches are being pursued as part of this: displays shown directly on the car itself and holographic projections on the ground surrounding the vehicle. Fraunhofer IOF is responsible for the technology on which the latter of these cases is based.