A mix of quantum processors and standard GPUs can speed up the machine learning process, Nvidia and Orca have discovered.

GM’s Cruise aims to turn self-driving into a billion-dollar business.

Missed the GamesBeat Summit excitement? Don’t worry! Tune in now to catch all of the live and virtual sessions here.
3DFY.ai announced the launch of 3DFY Prompt, a generative AI that lets developers and creators build 3D models based on text prompts.
The Tel Aviv, Israel-based company said the tech democratizes professional-quality 3D model creation, enabling anyone to use text prompts to create high-quality models that can be used in gaming, design or virtual environments.
Robots are nothing new. They build our cars, vacuum our floors, prepare our e-commerce orders, and even help carry out surgeries. But now the sci-fi vision of a general-purpose humanoid robot seems to be edging closer.
While disembodied artificial intelligence has seen rapid improvements in performance in recent years, most robots are still relatively dumb. For the most part, they are used for highly specialized purposes, the environments they operate in are carefully controlled, and they are not particularly autonomous.
That’s because operating in the messy uncertainty of the real world remains difficult for current AI approaches. As impressive as the recent feats of large language models have been, they are dealing with a fairly limited palette of data types that are fed to them in predictable ways.

Like death and taxes, there seem to be few things more predictable than artificial intelligence going off the rails.
Case in point, remember that influencer who created a virtual version of herself to rent out as an “AI girlfriend”? In a new interview with Insider, Snapchat influencer Caryn Marjorie admitted that the voice-based chatbot she made to mimic her speech and be a paid virtual companion has gotten much hornier than intended.
“The AI was not programmed to do this and has seemed to go rogue,” she told Insider. “My team and I are working around the clock to prevent this from happening again.”

Stockholm-based learning platform Sana has announced a suite of generative AI tools along with an extension to its Series B round, bringing its total funding to $80 million.
Inside companies, information is often scattered across silos, buried in systems and locked in different formats, making it inaccessible to employees when they need it most, says Swedish entrepreneur Joel Hellermark. The 26-year-old hopes to help companies tackle this problem through his learning platform Sana, which uses AI to create an index for companies’ information, allowing employees to query and search it and perform tasks like creating training courses and summarizing and translating information.
Workplace collaboration tools are supposed to make things easier. I think they just make everything more complicated.
From my personal experience, these tools require quite a bit of manual input from users and are limited in their scopes of functionality. Strategy documents, proposals, roadmaps, meetings and notes may be found living in separate apps.
Notion hopes that AI can help cut down on the fragmentation within this space with its new product, Notion Projects. Projects aims to connect all aspects of collaboration in one place, making it easier for teams to plan, manage, and execute work, with the help of AI LLMs from OpenAI and Anthropic.
Join top executives in San Francisco on July 11–12, to hear how leaders are integrating and optimizing AI investments for success. Learn More
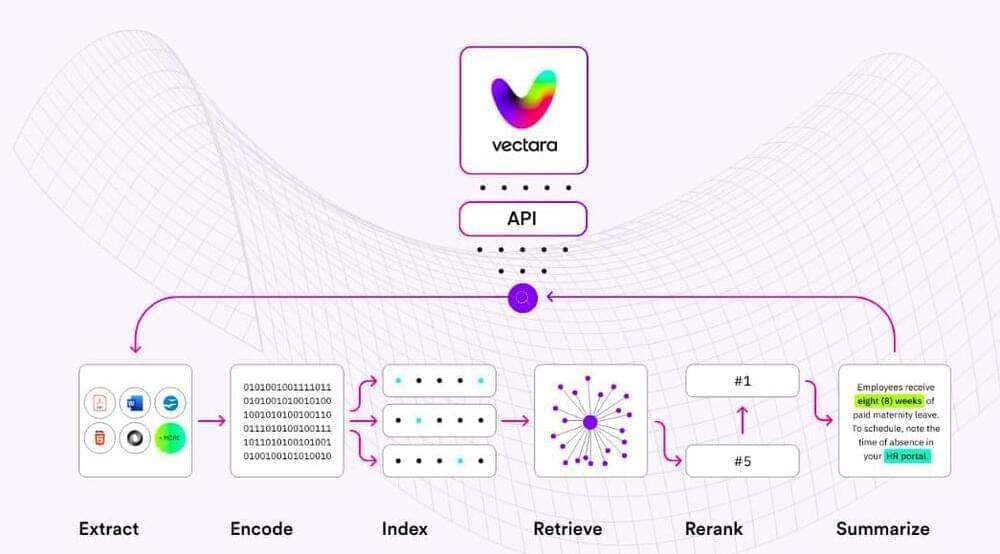
Vectara is continuing to grow as an AI powered conversational search platform with new capabilities announced today that aim to improve generative AI for business data.
The Santa Clara, Calif.- based startup emerged from stealth in Oct. 2022, led by the former CTO and founder of big data vendor Cloudera. Vectara originally branded its platform as a neural search-as-a-service technology. This approach combines AI-based large language models (LLMs), natural language processing (NLP), data integration pipelines and vector techniques to create a neural network that can be optimized for search.


Cybersecurity researchers are warning about CAPTCHA-breaking services that are being offered for sale to bypass systems designed to distinguish legitimate users from bot traffic.
“Because cybercriminals are keen on breaking CAPTCHAs accurately, several services that are primarily geared toward this market demand have been created,” Trend Micro said in a report published last week.
“These CAPTCHA-solving services don’t use [optical character recognition] techniques or advanced machine learning methods; instead, they break CAPTCHAs by farming out CAPTCHA-breaking tasks to actual human solvers.”