From Kasparov’s chess career to Steve Jobs’ bicycle, we already know how to approach these new AI tools. The real question: Will you master them before your competition does?




The secret mode, which the hacker nicknamed “Elon Mode,” allows for completely hands-free driving during Full Self-Driving mode.


The above considerations have to be carefully factored in while selecting the approach to model different subsystems and modules, hardware or physics-based twins in the digital twin.
Data recording and logging are crucial components of any digital twin project. This data not only serves as the basis for simulation and testing but also facilitates debugging, system optimization and performance analysis. Effective data recording strategies can also assist in the validation of model assumptions, further enhancing system accuracy and reliability.
Digital twins are not merely simulation tools; they represent a fundamental shift in the way we can plan, design, deploy and optimize robotic automation systems in warehouses. A well-designed digital twin, factoring in the aspects outlined in this article, empowers reliable, predictable and efficient order fulfillment, catalyzing innovation and progress in customer satisfaction.
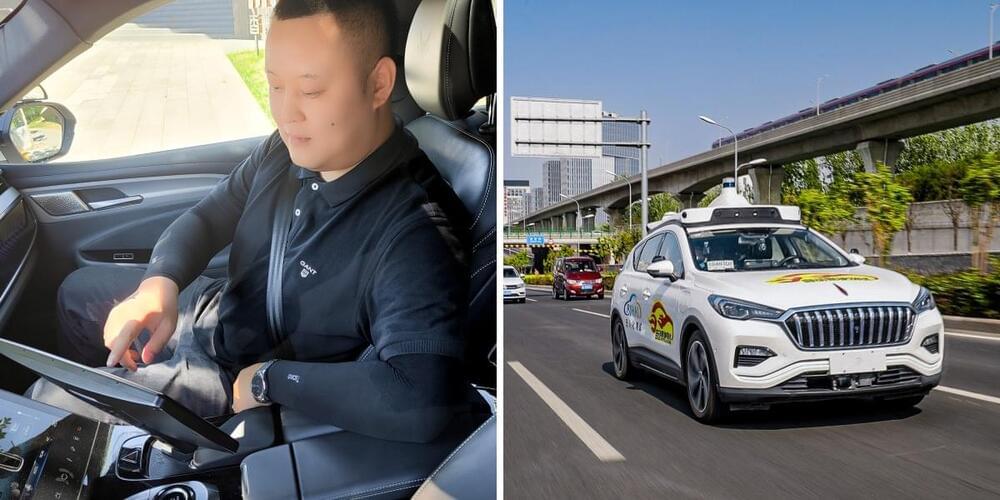

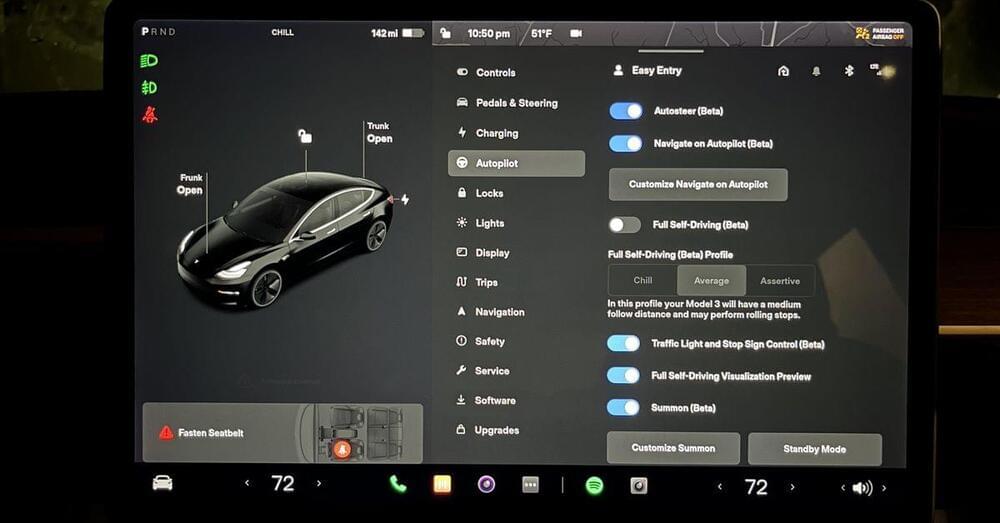
A Tesla software hacker has found an ‘Elon Mode’ driving feature that seems to allow Tesla vehicles with Full Self-Driving to operate without any driver monitoring.
Tesla CEO Elon Musk might have his very own supersecret driver mode that enables hands-free driving in Tesla vehicles.
The hidden feature, aptly named “Elon Mode,” was discovered by a Tesla software hacker known online as @greentheonly. The anonymous hacker has dug deep into the vehicle code for years and uncovered things like how Tesla can lock you out of using your power seats or the center camera in the Model 3 before it was officially activated.
After finding and enabling Elon Mode, greentheonly ventured out to test the system… More.
Elon Musk might be driving FSD hands-free.
A new model will allow robots to mimic human actions fast. Scientists are using this model to train robots so that they could do daily chores just like the way we do.
Are you among those who often dream of a day when a robot will do all the everyday household chores for you? A team of researchers from Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) has figured out how to turn your dream into reality.
In their latest study, they proposed a model that allowed them to train robots to do household tasks by showing them videos of people doing ordinary activities in their homes, like picking up the phone, opening a drawer, etc.
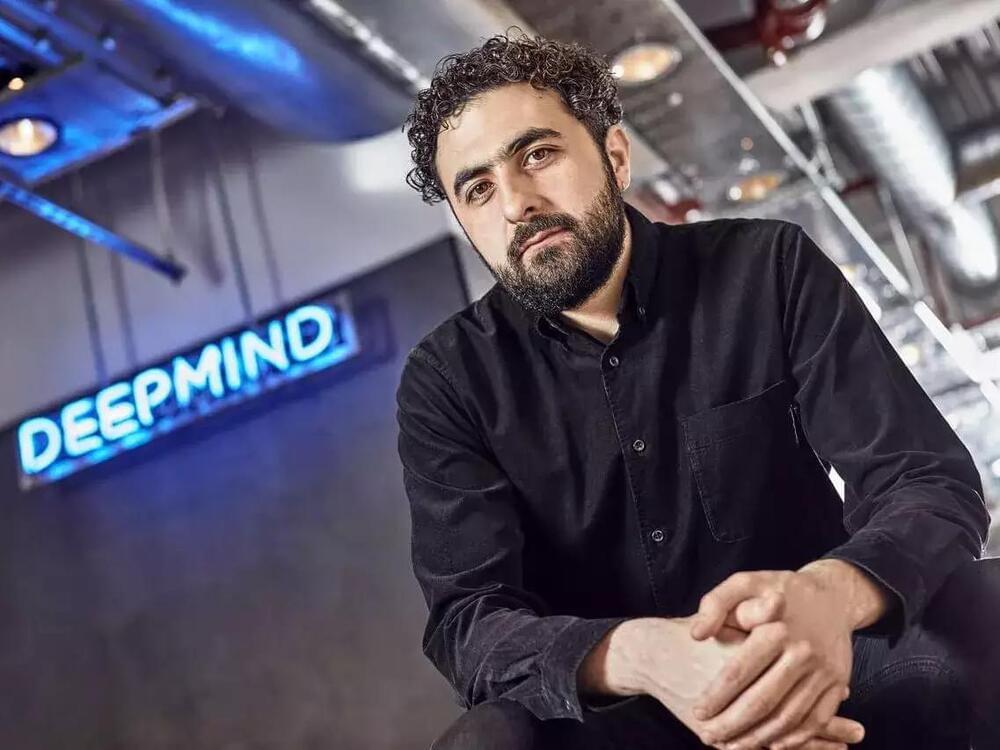

DeepMind’s co-founder believes the Turing test is an outdated method to test AI intelligence. In his book, he suggests a new idea in which AI chatbots have to turn $100,000 into $1 million.
A co-founder of Google’s AI research lab DeepMind thinks AI chatbots like ChatGPT should be tested on their ability to turn $100,000 into $1 million in a “modern Turing test” that measures human-like intelligence.
Mustafa Suleyman, formerly head of applied AI at DeepMind and now CEO and co-founder of Inflection AI, is releasing a new book called “The Coming Wave: Technology, Power, and the Twenty-first Century’s Greatest Dilemma.”
Mustafa Suleyman said the original Turing Test is outdated because it’s “unclear” whether it’s a “meaningful milestone” for AI intelligence anymore.