
Category: robotics/AI – Page 1,162




New Senolytics from Artificial Intelligence
Recent research published in Nature Communications has used machine learning algorithms to find new compounds that can eliminate senescent cells [1].
Senolytics are molecules that destroy senescent cells. Only a small number of such molecules have been identified, and only two have shown efficacy in clinical trials: dasatinib and quercetin in combination [2]. One of the biggest challenges is that senolytics often only work against specific types of cells. Additionally, some senolytics may work well for one cell type while being toxic to other, non-senescent cell types [3].
There is also a group of senolytics that are used in cancer therapies. However, most of them target pathways that are mutated in cancer. Therefore, they cannot be used as therapeutic agents in different contexts.

Scientists develop AI system to alert us of next pandemic
Using machine learning, the system could warn us about the emergence of dangerous virus variants in the future and allow us to prepare in advance.
We all know how devastating the COVID-19 pandemic has been – and it could have been even worse if not for the efforts of scientists and health workers around the world. But what if we could get a heads-up on the next most dangerous variants of a virus before they become a global threat?
Well, a new AI system can just do that. It can warn us about the emergence of dangerous virus variants in future pandemics, according to a study by scientists from Scripps Research and Northwestern University in the US.

AI.com flips from ChatGPT to Elon Musk’s X.ai
There was a bit of a hubbub in February as it emerged that OpenAI had seemingly purchased AI.com in order to redirect it to the ChatGPT web interface. But now erstwhile backer, Twitter haver and X lover Elon Musk appears to have taken the valuable domain off their hands, or else someone has done it for him: AI.com now redirects to X.ai, the billionaire’s embryonic machine learning research outfit.
Of course domains are bought and sold every day. But two-letter.com domains are rare and highly expensive, especially those that form words or familiar abbreviations. When AI.com started redirecting to OpenAI’s site, Mashable pointed out that the domain could hardly have sold for less than IT.com’s $3.8 million the previous year, and likely attained a far higher price given the hype around artificial intelligence in general.
No doubt OpenAI hoped that the purchase of AI.com would turn confused URL bar typers into lifetime users. Or perhaps it intended to eventually move its consumer-facing operations (like ChatGPT’s web client) over to the shorter domain. It seems we’ll never know, because now the domain goes to X.ai.
This Sea Slug Can Chop Off Its Head and Grow an Entire New Body—Twice
Year 2021 This bit of dna could be synthesized to essentially regrow humans if they had critical injury much like wolverine from the marvel movies.
Two species of sea slugs can pop off their heads and regrow their entire bodies from the noggin down, scientists in Japan recently discovered. This incredible feat of regeneration can be achieved in just a couple of weeks and is absolutely mind-blowing.
Most cases of animal regeneration — replacing damaged or lost body parts with an identical replacement — occur when arms, legs or tails are lost to predators and must be regrown. But these sea slugs, which belong to a group called sacoglossans, can take it to the next level by regrowing an entirely new body from just their heads, which they seem to be able to detach from their original bodies on purpose.
If that wasn’t strange enough, the slugs’ heads can survive autonomously for weeks thanks in part to their unusual ability to photosynthesize like plants, which they hijack from the algae they eat. And if that’s still not enough in the bizarro realm, the original decapitated body can also go on living for days or even months without their heads.

Big Tech Agrees to AI Pledges With White House. There’s a Big Omission
The Biden administration said Friday it struck a deal with some of the biggest U.S. technology companies to manage risks posed by artificial intelligence. However, the agreement didn’t directly address how AI systems are trained, a crucial issue as AI companies face lawsuits over alleged copyright violations.

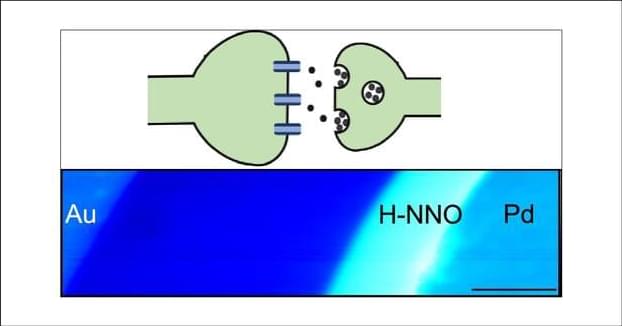
Spatial Interactions in Hydrogenated Perovskite Nickelate Synaptic Networks
A key aspect of how the brain learns and enables decision-making processes is through synaptic interactions. Electrical transmission and communication in a network of synapses are modulated by extracellular fields generated by ionic chemical gradients. Emulating such spatial interactions in synthetic networks can be of potential use for neuromorphic learning and the hardware implementation of artificial intelligence. Here, we demonstrate that in a network of hydrogen-doped perovskite nickelate devices, electric bias across a single junction can tune the coupling strength between the neighboring cells. Electrical transport measurements and spatially resolved diffraction and nanoprobe X-ray and scanning microwave impedance spectroscopic studies suggest that graded proton distribution in the inhomogeneous medium of hydrogen-doped nickelate film enables this behavior.