Introducing Nvidia’s most recently announced major advancements in the Omniverse platform to collaborations with giants like Adobe and Wonder Dynamics. Also, Dive into the revolutionary GH200 Grace Hopper AI Superchip platform, boasting unparalleled memory technology and a collaboration with Hugging-Face. Finally, explore the collaboration between Nvidia and Shutterstock, unveiling tools that redefine 3D scene development, all powered by Nvidia’s Picasso and generative AI.
Deep Learning AI Specialization: https://imp.i384100.net/GET-STARTED
AI Marketplace: https://taimine.com/
AI News timestamps:
0:00 Intro.
0:28 OpenUSD
1:12 Omniverse Kit.
1:24 Audio2Face.
1:44 Modular App Building (over 600 core extensions)
1:58 Resource Rich Developer Environment (Templates for Developer)
2:08 Opitimized User Experience (DLSS 3)
2:28 Spatial Integration (External Reality Tools)
2:43 Adobe Firefly Integration.
2:52 Wonder Dynamics Integration.
3:08 ChatUSD
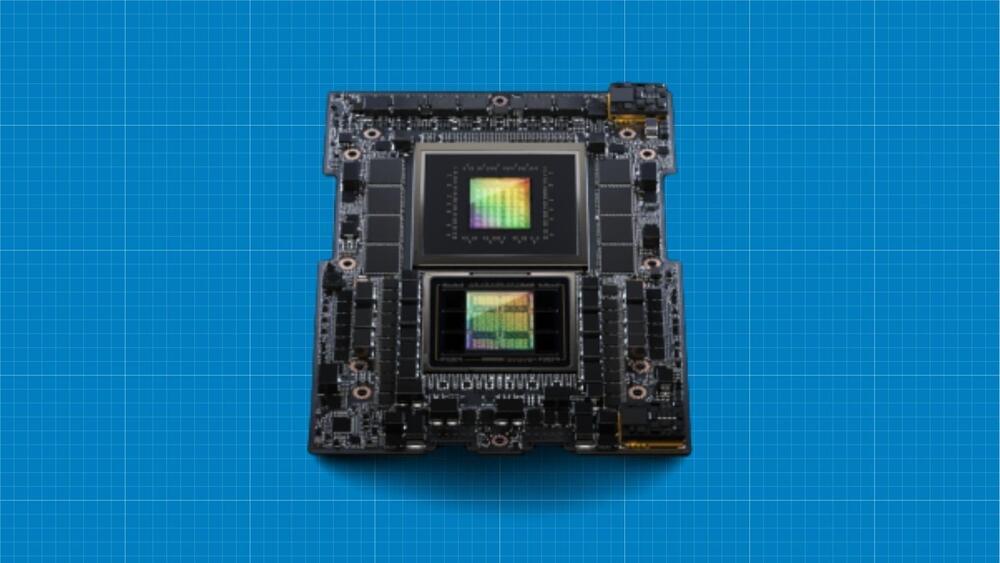
3:42 GH200 AI Superchip.
4:15 Configuration of GH200
5:15 NVLink.
6:00 Hugging Face Alliance.
6:29 Shutterstock Using NVIDIA Picasso.
#new #ai #technology