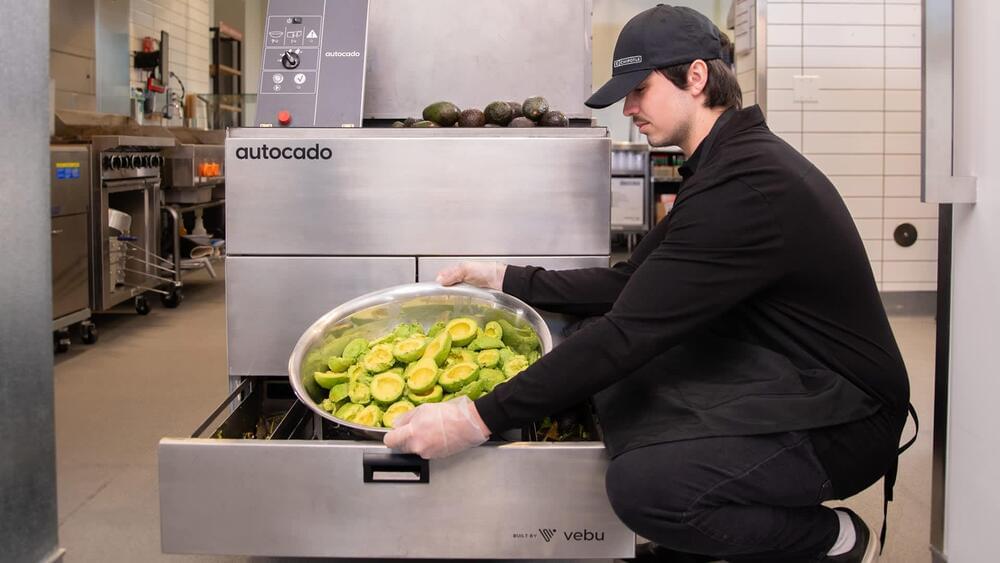
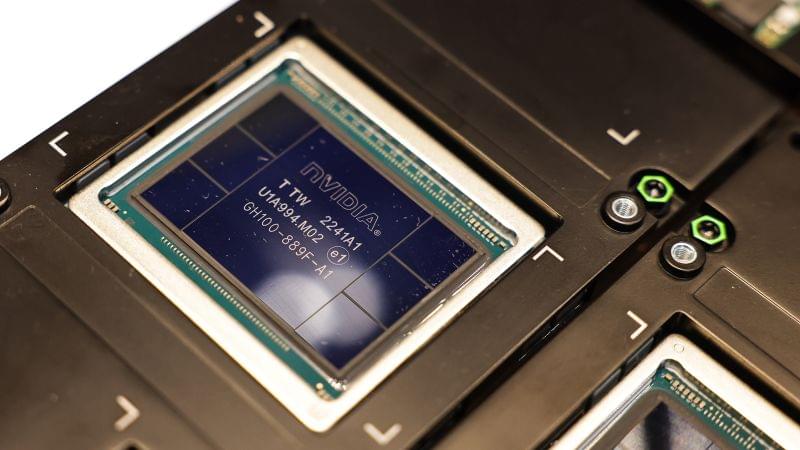
Generative AI, in particular, is placing new demands on IT teams across nearly every industry. The GPUs required for generative AI are expensive and power-hungry, and you may need many. Aligning storage to keep those data-hungry GPUs fed requires adopting new technologies, such as NVIDIA’s GPUDirect, that enable applications to transfer data from primary storage directly into the GPU’s memory. The software stack looks unlike nearly anything else in enterprise IT. The list goes on and on.
Dell Technologies and NVIDIA are working together to reduce the complexity of building and deploying infrastructure for Generative AI. The two companies announced Project Helix earlier this year at Dell Technologies World, which Dell described as delivering full-stack solutions with technical expertise and pre-built tools based on Dell and NVIDIA infrastructure and software.