The Pope said artificial intelligence should be used “in service of humanity.”




The Impact of chatGPT and other large language models on physics research and education (2023)
Event organizers: Kevin Burdge, Joshua Borrow, Mark Vogelsberger.
Session 1: The computer science underlying large language models.
“Keeping AI under control through mechanistic interpretability“
Speaker: Prof. Max Tegmark (MIT)
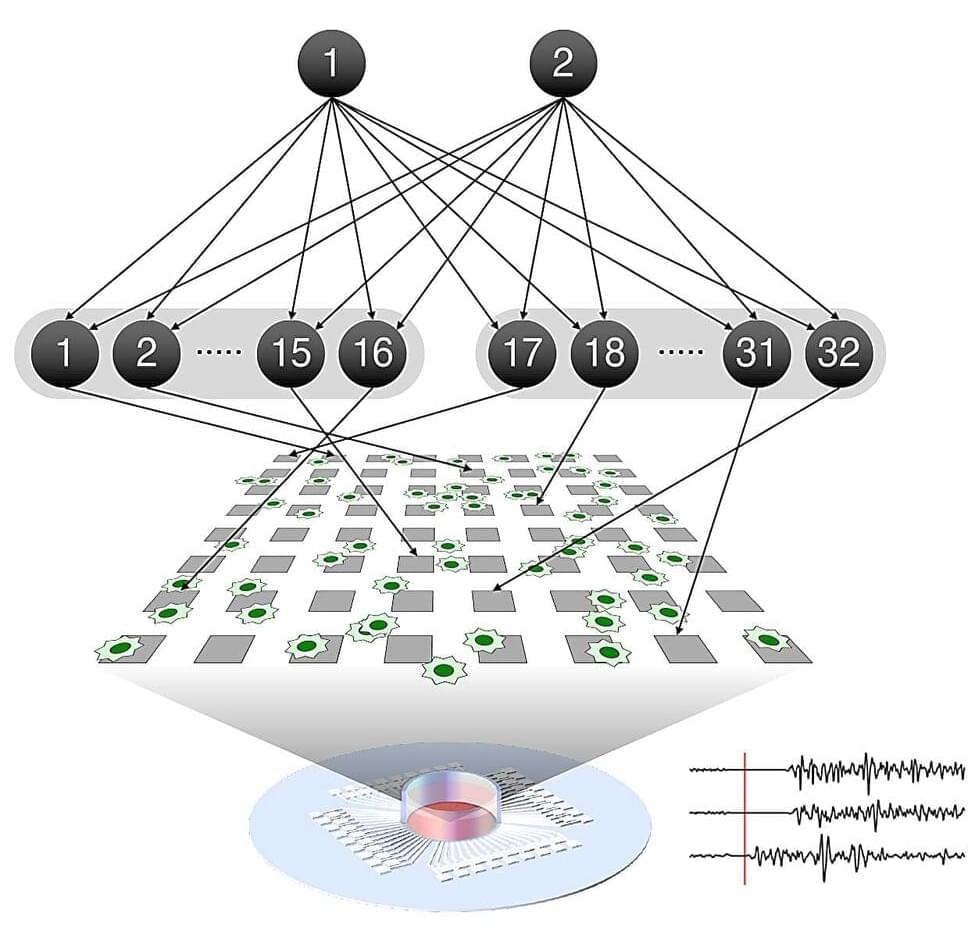
An international collaboration between researchers at the RIKEN Center for Brain Science (CBS) in Japan, the University of Tokyo, and University College London has demonstrated that self-organization of neurons as they learn follows a mathematical theory called the free energy principle.
The principle accurately predicted how real neural networks spontaneously reorganize to distinguish incoming information, as well as how altering neural excitability can disrupt the process. The findings thus have implications for building animal-like artificial intelligences and for understanding cases of impaired learning. The study was published August 7 in Nature Communications.
When we learn to tell the difference between voices, faces, or smells, networks of neurons in our brains automatically organize themselves so that they can distinguish between the different sources of incoming information. This process involves changing the strength of connections between neurons, and is the basis of all learning in the brain.


Jeff Tao is the founder, CEO and core developer of TDengine.
The emergence of ChatGPT in the public eye has brought new life to the field of artificial intelligence (AI). As AI technology enters all industries, it becomes a part of our work and lives, ushering in a new industrial revolution. While jobs will be lost, new opportunities will be created for those who work with AI.
Traditional industries, such as energy and manufacturing, are even more anxious about the AI-oriented future than those in the IT sector. They want to know how they can use AI technologies to reduce costs and increase efficiency in their industries.

Head over to our on-demand library to view sessions from VB Transform 2023. Register Here
There’s a lot of angst about software developers “losing their jobs” to AI, being replaced by a more intelligent version of ChatGPT, GitHub’s Copilot, Google’s foundation model Codey, or something similar.
AI startup founder Matt Welsh has been talking and writing about the end of programming. He’s asking whether large language models (LLMs) eliminate programming as we know it, and he’s excited that the answer is “yes”: Eventually, if not in the immediate future.

On any given day, Dallas motorists traveling along I-20 or I-45 are likely to be sharing the road with a self-driving truck that has the equivalent of a learner’s permit.
Why it matters: Dallas is the hub of autonomous truck testing and development, thanks to its vital freight corridors, business-friendly policies and generally favorable weather.

Through a scattering medium such as ground glass? Traditionally, this would be considered impossible. When light passes through an opaque substance, the information carried within the light becomes “jumbled up”, almost as if undergoes complex encryption.
Recently, a remarkable scientific breakthrough by Professor Choi Wonshik’s team from the IBS Center for Molecular Spectroscopy and Dynamics (IBS CMSD) has unveiled a method to leverage this phenomenon in the fields of optical computing and machine learning.
Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence (AI) that deals with the development of algorithms and statistical models that enable computers to learn from data and make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed to do so. Machine learning is used to identify patterns in data, classify data into different categories, or make predictions about future events. It can be categorized into three main types of learning: supervised, unsupervised and reinforcement learning.