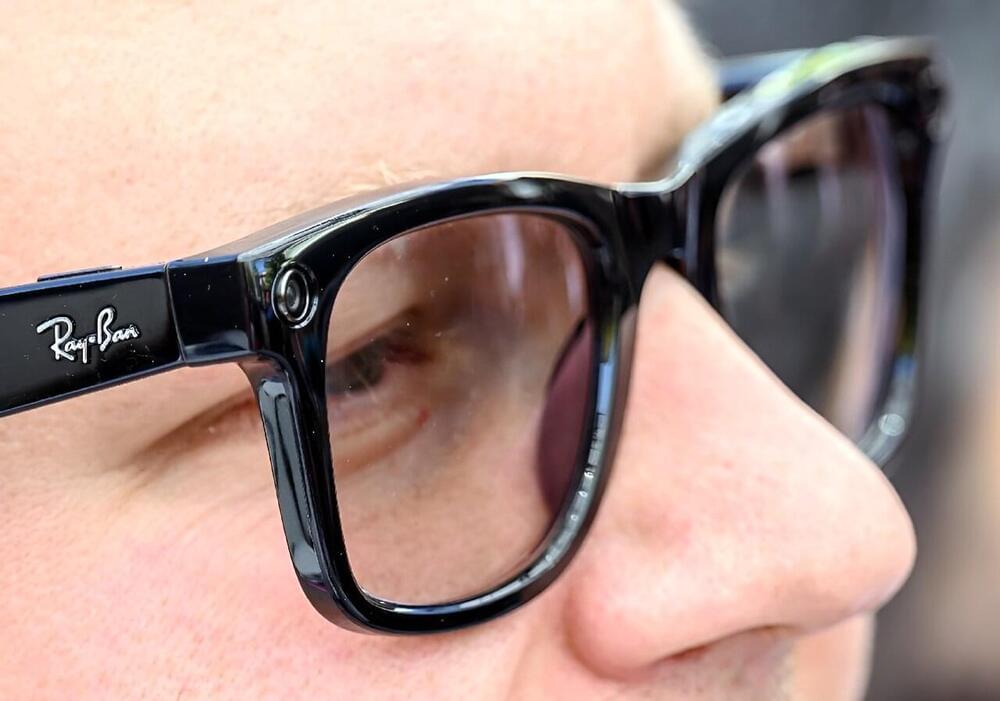
People will laugh and dismiss it and make comparisons to googles clown glasses. But around 2030 Augmented Reality glasses will come out. Basically, it will be a pair of normal looking sunglasses w/ smart phone type features, Ai, AND… VR stuff.
Meta chief Mark Zuckerberg on Wednesday said the tech giant is putting artificial intelligence into digital assistants and smart glasses as it seeks to gain lost ground in the AI race.
Zuckerberg made his announcements at the Connect developers conference at Meta’s headquarters in Silicon Valley, the company’s main annual product event.
“Advances in AI allow us to create different (applications) and personas that help us accomplish different things,” Zuckerberg said as he kicked off the gathering.