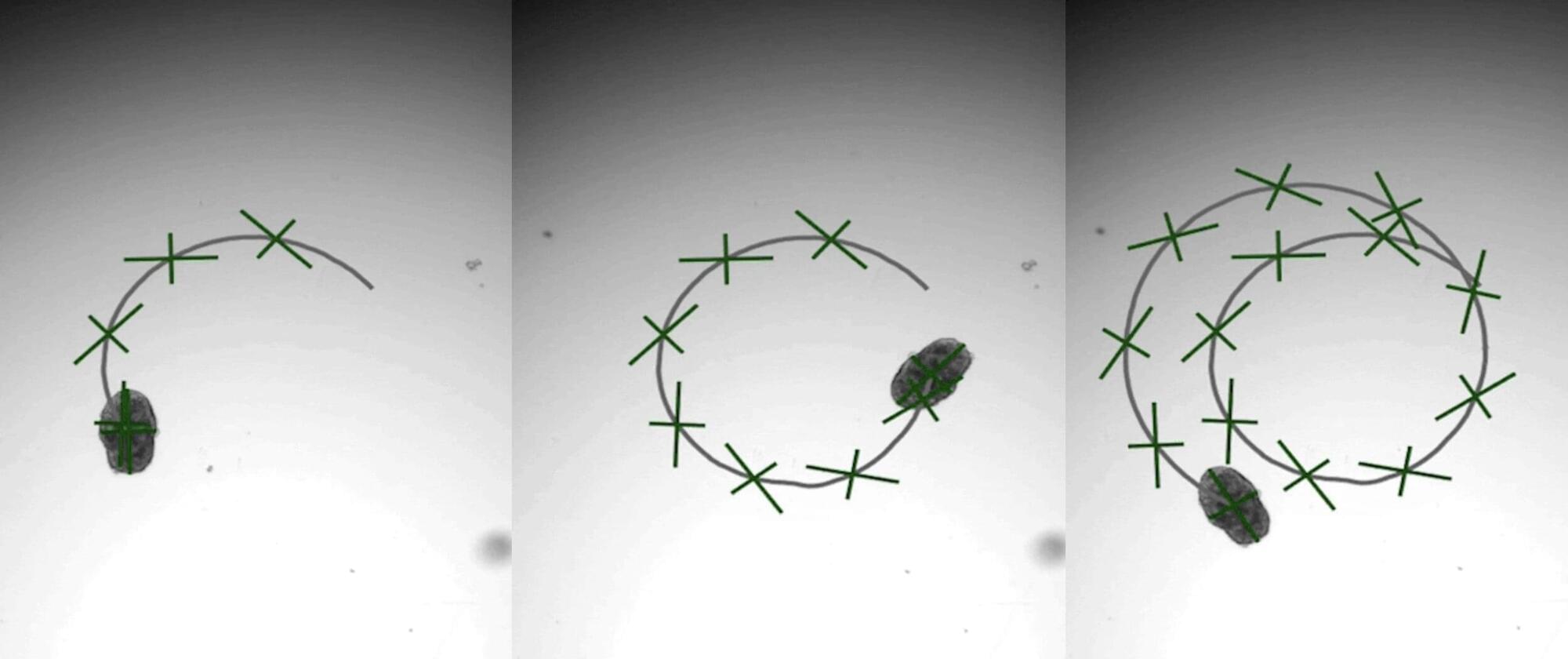
A brand-new engineering approach to generate “designer” biological robots using human lung cells is underway in Carnegie Mellon University’s Ren lab. Referred to as AggreBots, these microscale living robots may one day be able to traverse through the body’s complex environments to deliver desired therapeutic or mechanical interventions, once greater control is achieved over their motility patterns. In new research published in Science Advances, the group provides a novel tissue engineering platform capable of achieving customizable motility in AggreBots by actively controlling their structural parameters.
Biobots are microscopic, man-made biological machines capable of autonomous movement and programmability to perform specific tasks or behaviors. Previously, enabling biobots’ motility has been centered around using muscle fibers, which allow them to move by contracting and relaxing like real muscles.
A novel, alternative mechanism of actuation can be found by using cilia, the nanoscopic, hair-like, organic propellers that continuously move fluids in the body (like in the lungs) and help some aquatic creatures, like Paramecium or comb jellies, swim. However, a reliable way to control the exact shape and structure of a cilia-powered biobot (CiliaBot, for short), and thereby its motility outcome, has proven difficult to come by.