The dean of Stanford University’s medical school thinks artificial intelligence will transform the medicines you take, the care you get, and the training of doctors.


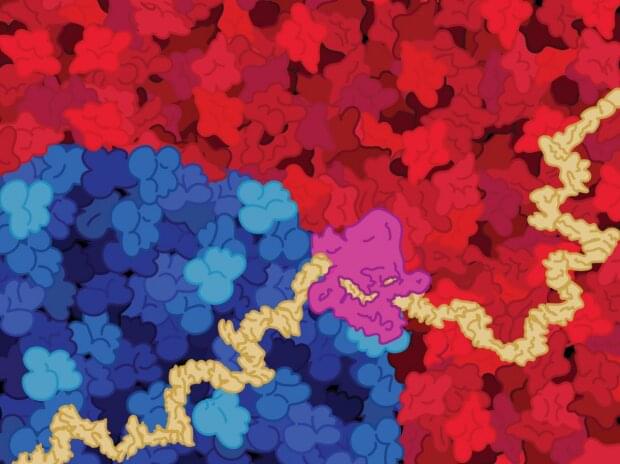
A team of New York University computer scientists has created a neural network that can explain how it reaches its predictions. The work reveals what accounts for the functionality of neural networks—the engines that drive artificial intelligence and machine learning—thereby illuminating a process that has largely been concealed from users.
The breakthrough centers on a specific usage of neural networks that has become popular in recent years—tackling challenging biological questions. Among these are examinations of the intricacies of RNA splicing—the focal point of the study—which plays a role in transferring information from DNA to functional RNA and protein products.
“Many neural networks are black boxes —these algorithms cannot explain how they work, raising concerns about their trustworthiness and stifling progress into understanding the underlying biological processes of genome encoding,” says Oded Regev, a computer science professor at NYU’s Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences and the senior author of the paper, which was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.


Annika Hauptvogel, head of technology and innovation management at Siemens, describes the industrial metaverse as “immersive, making users feel as if they’re in a real environment; collaborative in real time; open enough for different applications to seamlessly interact; and trusted by the individuals and businesses that participate”—far more than simply a digital world.
The industrial metaverse will revolutionize the way work is done, but it will also unlock significant new value for business and societies. By allowing businesses to model, prototype, and test dozens, hundreds, or millions of design iterations in real time and in an immersive, physics-based environment before committing physical and human resources to a project, industrial metaverse tools will usher in a new era of solving real-world problems digitally.
“The real world is very messy, noisy, and sometimes hard to really understand,” says Danny Lange, senior vice president of artificial intelligence at Unity Technologies, a leading platform for creating and growing real-time 3D content. “The idea of the industrial metaverse is to create a cleaner connection between the real world and the virtual world, because the virtual world is so much easier and cheaper to work with.”
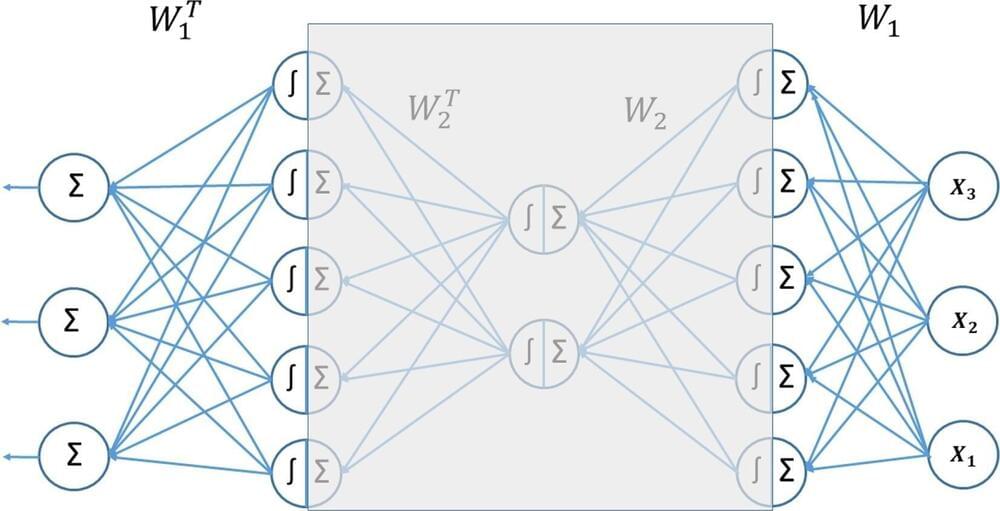
Researchers from the University of Jyväskylä were able to simplify the most popular technique of artificial intelligence, deep learning, using 18th-century mathematics. They also found that classical training algorithms that date back 50 years work better than the more recently popular techniques. Their simpler approach advances green IT and is easier to use and understand.
The recent success of artificial intelligence is significantly based on the use of one core technique: deep learning. Deep learning refers to artificial intelligence techniques where networks with a large number of data processing layers are trained using massive datasets and a substantial amount of computational resources.
Deep learning enables computers to perform complex tasks such as analyzing and generating images and music, playing digitized games and, most recently in connection with ChatGPT and other generative AI techniques, acting as a natural language conversational agent that provides high-quality summaries of existing knowledge.



That looks promising. 90% accuracy isn’t bad. Now the trick is getting there though we have options on our own solar system possibly. You never know until you try. I doubt we’ll find high level life remnants but perhaps something much less like at most insect level but more likely microbial. I’m just guessing of course.
A team of scientists supported in part by NASA have outlined a simple and reliable method to search for signs of past or present life on other worlds that employs machine learning techniques. The results show that the method can distinguish both modern and ancient biosignatures with an accuracy of 90 percent.
The method is able to detect whether or not a sample contains materials that were tied to biological activity. What the research team refers to as a “routine analytical method” could be performed with instruments on missions including spacecraft, landers, and rovers, even before samples are returned to Earth. In addition, the method could be used to shed light on the history of ancient rocks on our own planet.
The team used molecular analyses of 134 samples containing carbon from abiotic and biotic sources to train their software to predict a new sample’s origin. Using pyrolysis gas chromatography, the method can detect subtle differences in a sample’s molecular patterns and determine whether or not a sample is biotic in origin. When testing the method, samples originating from a wide variety of biotic sources were identified, including things like shells, human hair, and cells preserved in fine-grained rock. The method was even able to identify remnants of life that have been altered by geological processes, such as coal and amber.