Not everyone wants AI to do everything for them. Will the risk of losing transparency and visibility into code change how GitHub made collaborative coding so powerful?



Risk is certainly an area of concern for CFOs when it comes to implementing generative AI.
However, Andrew McAfee, a principal research scientist at MIT, has a message for CFOs regarding the technology: “Risk tolerance needs to shift,” McAfee said.
“The risks are real, but they are manageable,” Andrew McAfee told a group of CFOs.

Immigration to and living on Mars have long been depicted in science fiction. But before that dream turns into reality, there is a hurdle humans have to overcome—the lack of chemicals such as oxygen essential for long-term survival on the planet. However, the recent discovery of water activity on Mars is promising.
Scientists are now exploring the possibility of decomposing water to produce oxygen through electrochemical water oxidation driven by solar power with the help of oxygen evolution reaction (OER) catalysts. The challenge is to find a way to synthesize these catalysts in situ using materials on Mars, instead of transporting them from the Earth, which is costly.
To tackle this problem, a team led by Prof. Luo Yi, Prof. Jiang Jun, and Prof. Shang Weiwei from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), recently made it possible to synthesize and optimize OER catalysts automatically from Martian meteorites with their robotic artificial intelligence (AI)-chemist.
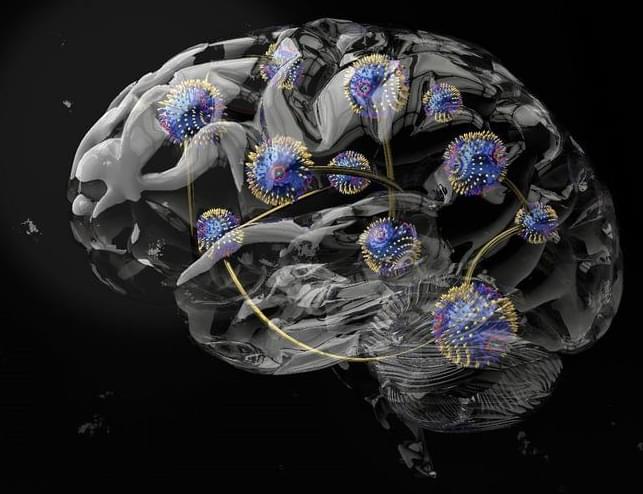
“This work brings us a step closer to realizing the full potential of physical reservoirs to create computers that not only require significantly less energy, but also adapt their computational properties to perform optimally across various tasks, just like our brains,” said Dr. Oscar Lee.
A recent study published in Nature Materials examines a breakthrough approach in physical reservoir computing, also known as a neuromorphic or brain-inspired method and involves using a material’s physical properties to adhere to a myriad of machine learning duties. This study was conducted by an international team of researchers and holds the potential to help physical reservoir computing serve as a framework towards making machine learning more energy efficient.
Artist rendition of connected chiral (twisted) magnets used as a computing avenue for brain-inspired, physical reservoir computing. (Credit: Dr. Oscar Lee)
For the study, the researchers used a magnetic field and temperature variances on chiral (twisted) magnets—which served as the computing channel—they found the materials could be used for a myriad of machine learning needs. What makes this discovery extraordinary is that physical reservoir computing has been found to have limits, specifically pertaining to its ability to be rearranged. Additionally, the team discovered that the chiral magnets performed better at certain computing tasks based on changes in the magnetic field phases used throughout the experiments.

The devices are controlled via voice commands or a smartphone app.
Active noise control technology is used by noise-canceling headphones to minimize or completely block out outside noise. These headphones are popular because they offer a quieter, more immersive listening experience—especially in noisy areas. However, despite the many advancements in the technology, people still don’t have much control over which sounds their headphones block out and which they let pass.
Semantic hearing
Now, deep learning algorithms have been developed by a group of academics at the University of Washington that enable users to select which noises to filter through their headphones in real-time. The system has been named “semantic hearing” by its creators.
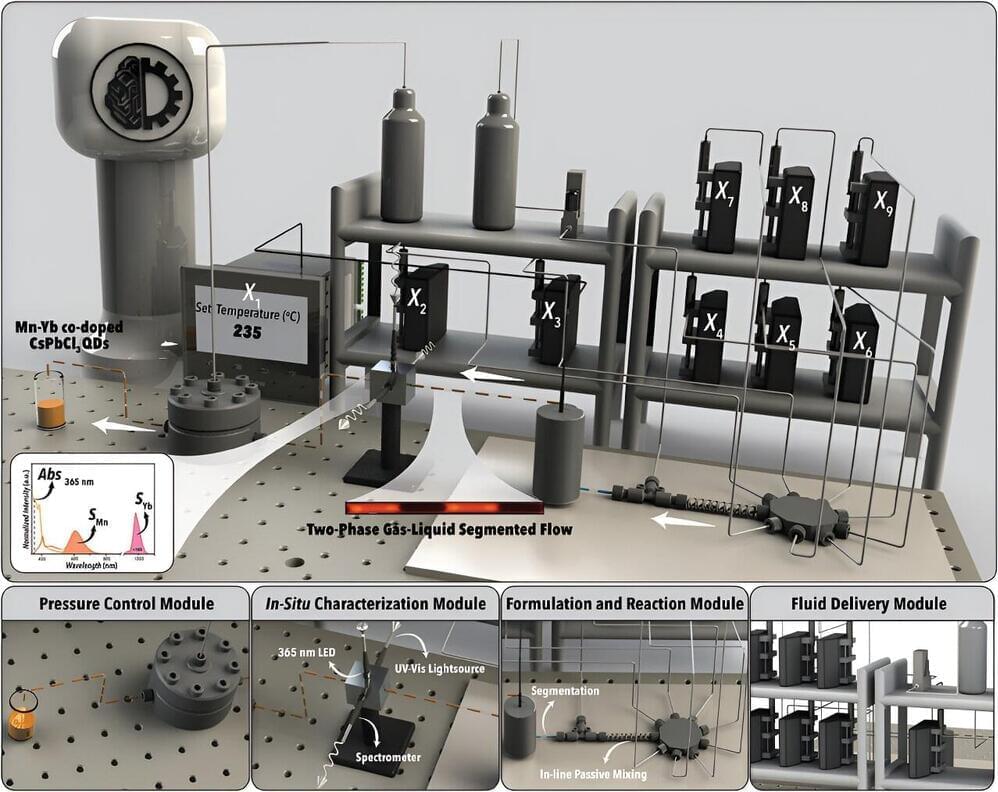
It can take years of focused laboratory work to determine how to make the highest quality materials for use in electronic and photonic devices. Researchers have now developed an autonomous system that can identify how to synthesize “best-in-class” materials for specific applications in hours or days.
The new system, called SmartDope, was developed to address a longstanding challenge regarding enhancing properties of materials called perovskite quantum dots via “doping.”
“These doped quantum dots are semiconductor nanocrystals that you have introduced specific impurities to in a targeted way, which alters their optical and physicochemical properties,” explains Milad Abolhasani, an associate professor of chemical engineering at North Carolina State University and corresponding author of the paper “Smart Dope: A Self-Driving Fluidic Lab for Accelerated Development of Doped Perovskite Quantum Dots,” published open access in the journal Advanced Energy Materials.
