To better understand how neural networks learn to simulate writing, researchers trained simpler versions on synthetic children’s stories.



As creative industries grapple with AI’s explosion into every artistic medium at once, separate calls from artists warning the world to take action before it’s too late are starting to converge. From fake Drake songs to stylized Instagram profile pictures, art conjured with newly sophisticated AI tools is suddenly ubiquitous — and so are conversations about how to rein in the technology before it does irrevocable harm to creative communities.
This week, digital rights organization Fight for the Future partnered with music industry labor group United Musicians and Allied Workers to launch #AIdayofaction, a campaign that calls on Congress to block corporations from obtaining copyrights on music and other art made with AI.
The idea is that by preventing industry behemoths like major record labels, for example, from copyrighting music made with the assistance of AI, those companies will be forced to keep looping humans into the creative process. But those same concerns — and the same potential strategies for pushing back against the onslaught of AI — exist across creative industries.

Generative AI, dominated by proprietary models locked inside big tech companies, is being disrupted by a new wave of open-source models.
Advocates argue open sourcing has vital benefits like enabling wider access, fostering innovation, and promoting transparency. Many people argue that open source will win in the marketplace.
But that conclusion is not obvious.
Open-sourcing generative AI is fundamentally different from the open-source movement that has given us tools like TensorFlow, MySQL or Kubernetes. Open-source dominated those arenas because the investment required — time and brain power — could be crowdsourced. But generative AI requires data and energy, both of which are increasingly… More.
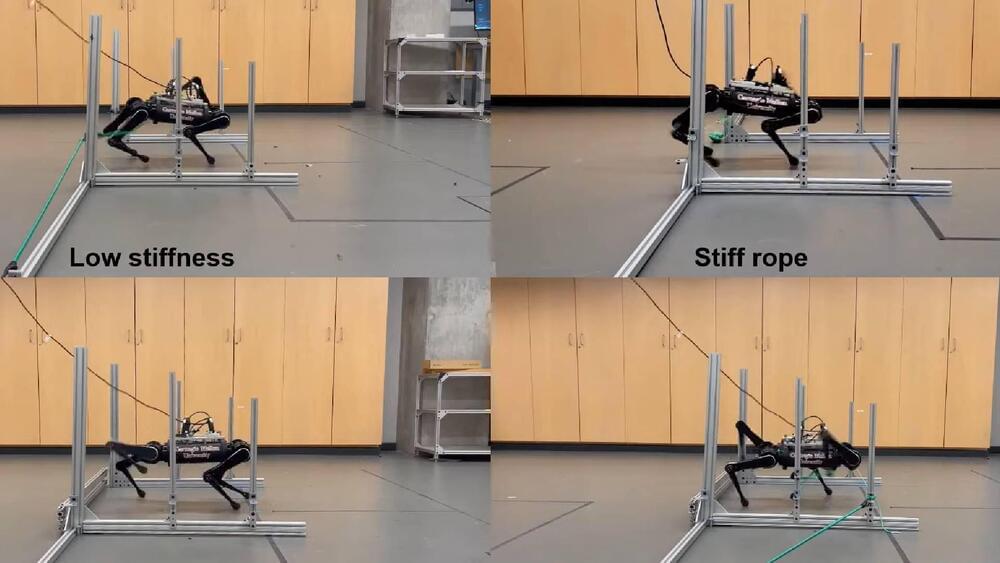
In order for robots to effectively partake in search and rescue operations, they need to effectively navigate obstacles in their way. One area that is particularly common and difficult to venture into is vegetation.
Robots typically use a combination of sensors to perceive their surroundings such as ultrasonic sensors, Lidar (Light Detection and Ranging), infrared sensors and camera systems. However, these are not often enough to allow robots to actually bypass the vegetation so commonly found in real outdoor environments.
That’s why engineers at Carnegie Mellon University are working on solving this particular dilemma.
Instead of looking at individual neurons, they look at combinations of neurons that form patterns or features.
Artificial neural networks are like digital versions of our brains. They learn from data, not rules, and they can perform extraordinary tasks, from translating languages to playing chess. But how do they do it? What is the logic behind their calculations? And how can we trust them to be safe and reliable?
XH4D/iStock.
AI brains: How do they work?

Have you recently been thinking about the Roman Empire? According to a viral social media trend, the answer is decidedly yes, assuming that you are a man. The backstory is that an online video postulated that men daily tend to think about the Roman Empire and a follow-up by women asking their male friends, partners, or relatives began to flood the Internet. Seemingly, most men insisted that they did indeed have frequent thoughts about the Roman Empire. A hashtag associated with the Roman Empire has ballooned to incurring over a billion hits.
Before I get into some further details on the contentious hubbub, a question that immediately struck me and has now been rattling around in the AI… More.
A viral trend online is that men are supposedly thinking daily about the Roman Empire. If so, this begs the question of whether generative AI might be doing likewise.

Understanding causality can’t come from passive observation, because the relevant counterfactuals often do not arise. If X is followed by Y, no matter how regularly, the only way to really know that is a causal relation is to intervene in the system: to prevent X and see if Y still happens. The hypothesis has to be tested. Causal knowledge thus comes from causal intervention in the world. What we see as intelligent behavior is the payoff for that hard work.
The implication is that artificial general intelligence will not arise in systems that only passively receive data. They need to be able to act back on the world and see how those data change in response. Such systems may thus have to be embodied in some way: either in physical robotics or in software entities that can act in simulated environments.
Artificial general intelligence may have to be earned through the exercise of agency.
We are a community of machine learning enthusiasts/researchers/journalists/writers who share interesting news and articles about the applications of AI. You will never miss any updates on ML/AI/CV/NLP fields because we post them daily. We hope that you subscribe to us so that you’ll be up-to-date with the latest developments around the world in terms of machine learning and related areas.
The most widely used machine learning algorithms were designed by humans and thus are hindered by our cognitive biases and limitations. Can we also construct meta-learning algorithms that can learn better learning algorithms so that our self-improving AIs have no limits other than those inherited from computability and physics? This question has been a main driver of my research since I wrote a thesis on it in 1987. In the past decade, it has become a driver of many other people’s research as well. Here I summarize our work starting in 1994 on meta-reinforcement learning with self-modifying policies in a single lifelong trial, and — since 2003 — mathematically optimal meta-learning through the self-referential Gödel Machine. This talk was previously presented at meta-learning workshops at ICML 2020 and NeurIPS 2021. Many additional publications on meta-learning can be found at https://people.idsia.ch/~juergen/metalearning.html.
Jürgen Schmidhuber.
Director, AI Initiative, KAUST
Scientific Director of the Swiss AI Lab IDSIA
Co-Founder & Chief Scientist, NNAISENSE
http://www.idsia.ch/~juergen/blog.html.
This video discusses what it would mean to live forever or to have a greatly expanded lifespan. Would we inevitably grow bored with existence? Why do we even want to live longer?
We also discuss the philosophy of the Ship of Theseus as it applies to mind upload or body transfer. If you transfer your mind to a new body, are you still the same person? We conclude that the answer is yes if and only if you experience no discontinuities in consciousness.
Finally, we discuss a few different ways that new bodies might be formed as technology advances. Digital avatars and robotic bodies are just a few of the possibilities.
Can You Upload Your Mind & Live Forever?
Digital immortality: would you upload your mind to a computer?
https://www.dazeddigital.com/life-culture/article/60341/1/mi…-elon-musk.
Uploading your consciousness will never work, a neuroscientist explains.