This is a critical step along the way to functional quantum computers that can achieve problems far beyond the capacity of traditional systems.
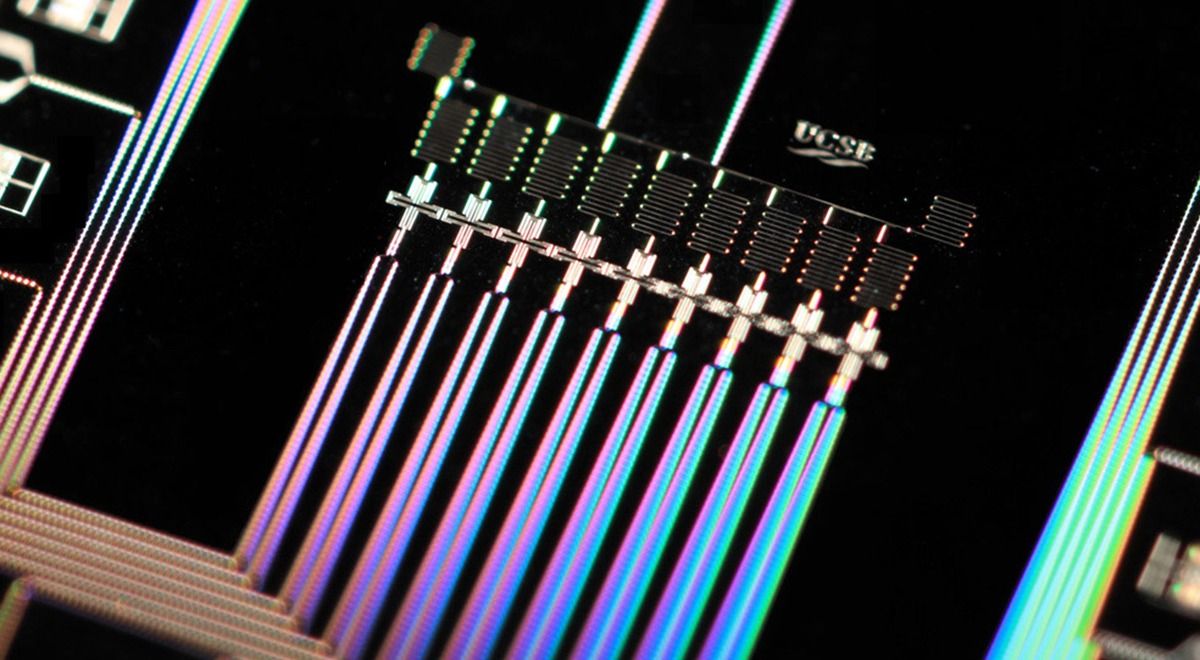

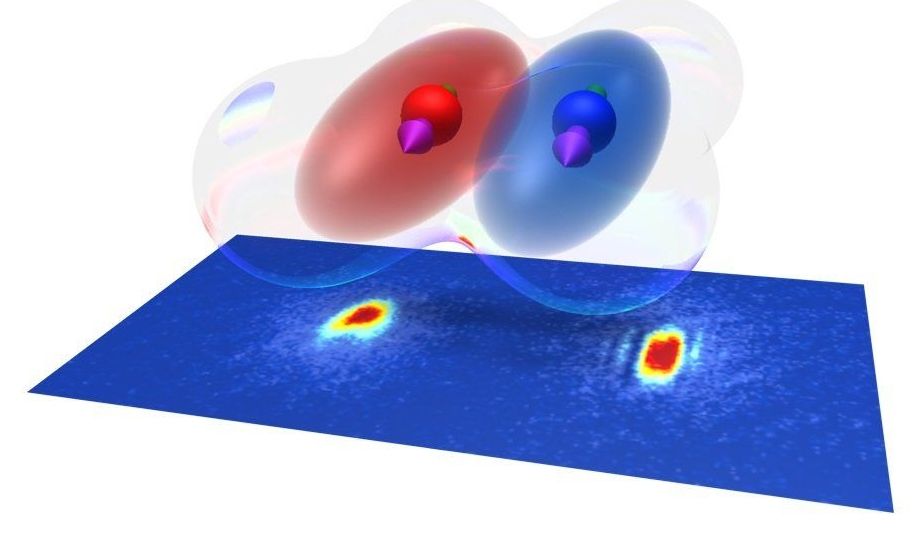
The experimental investigation of ultracold quantum matter makes it possible to study quantum mechanical phenomena that are otherwise inaccessible. A team led by the Innsbruck physicist Francesca Ferlaino has now mixed quantum gases of two strongly magnetic elements, erbium and dysprosium, and created a dipolar quantum mixture.
A few years ago, it seemed unfeasible to extend the techniques of atom manipulation and deep cooling in the ultracold regime to many-valence-electron atomic species. The reason is the increasing complexity in the atomic spectrum and the unknown scattering properties. However, a team of researchers, led by Ben Lev at Stanford University and an Austrian team directed by Francesca Ferlaino at the University of Innsbruck demonstrated quantum degeneracy of rare-earth species. Ferlaino’s group focused the research on erbium and developed a powerful, yet surprisingly simple approach to produce a Bose-Einstein condensate.
“We have shown how the complexity of atomic physics can open up new possibilities,” says Ferlaino. Magnetic species are an ideal platform to create dipolar quantum matter, in which particles interact with each other via a long-range and orientation dependent interaction as little quantum magnets.

NSW university has set up a Quantum Computer Company
Silicon Quantum Computing Pty. Ltd. (SQC) is working to create and commercialize a quantum computer based on world-leading intellectual property acquired from the Australian Centre of Excellence for Quantum Computation and Communication Technology (CQC2T). We have set ourselves a bold ambition: to develop a 10-qubit quantum integrated circuit prototype in silicon by 2022.

All of today’s computing takes its root from the world of “bits”, where a transistor bit, which lies at the heart of any computing chip, can only be in one of two electrical states: on or off. When on, the bit takes on a value of “1” and when off, it takes on a value of “0”, constraining the bit to only one of two (binary) values. All tasks performed by a computer-like device, whether a simple calculator or a sophisticated computer, are constrained by this binary rule.
Eight bits make up what is called a “byte”. Today, our computing is based on increasing the number of bytes into kilobytes, megabytes, gigabytes and so on. All computing advances we have had thus far, including artificially intelligent programmes, and driverless cars are ultimately reduced to the binary world of the bit.
This is a natural extension of western thought; for centuries, western philosophy has followed the principles of Aristotelian logic, which is based on the law of identity (A is A), the law of contradiction (A is not non-A), and the law of the excluded middle (A cannot be both A and non-A at the same time, just as non-A cannot be both non-A and A at the same time).

Despite growing excitement around the transformative potential of quantum computing, leaders in many industries are still unfamiliar with the technology that’s likely to prove more disruptive than Artificial Intelligence and blockchain. This ignorance seems particularly acute in industries that deal with physical systems and commodities. In an informal survey of two dozen executives in transportation, logistics, construction and energy, only eight had heard of quantum computing and only two could explain how it works.
In many ways this lack of awareness is understandable. Quantum computing’s value to our digital infrastructure is obvious, but its value to our physical infrastructure is perhaps less evident. Yet, the explosion of power and speed that quantum computers will unleash could indeed have a profound impact on physical systems like our transportation and utility networks. For companies, municipalities and nation states to stay competitive and capture the full benefit of the quantum revolution, leaders must start thinking about how quantum computing can improve our infrastructure.
Unlike classical computers, in which a bit of information can be either a zero or a one, quantum computers are able to take advantage of a third state through a phenomenon known as superposition. Superposition, which is a property of physics at the quantum scale, allows a quantum bit or qubit to be a zero, a one or a zero and a one simultaneously. The result is an astronomical increase in computational capacity over existing transistor-based hardware. Google, for example, has found that its quantum machines can run some algorithms 100 million times faster than conventional processors.



Scientists from around the world are meeting in Sydney to discuss the latest advancements in silicon quantum computing.
Scientists from around the world are landing in Sydney this week to join discussions on the latest research in silicon quantum computing with renowned physicist and Australian of the Year, Professor Michelle Simmons, and UNSW Sydney researchers from the Centre of Excellence for Quantum Computation and Communication Technology (CQCT), including Professor Andrew Dzurak, Professor Sven Rogge and Professor Andrea Morello.
Bringing together more than 200 leading researchers in the field, the Silicon Quantum Electronics Workshop is a global initiative to share research insights and technology advancements in the race to build the world’s first quantum computer – in silicon.