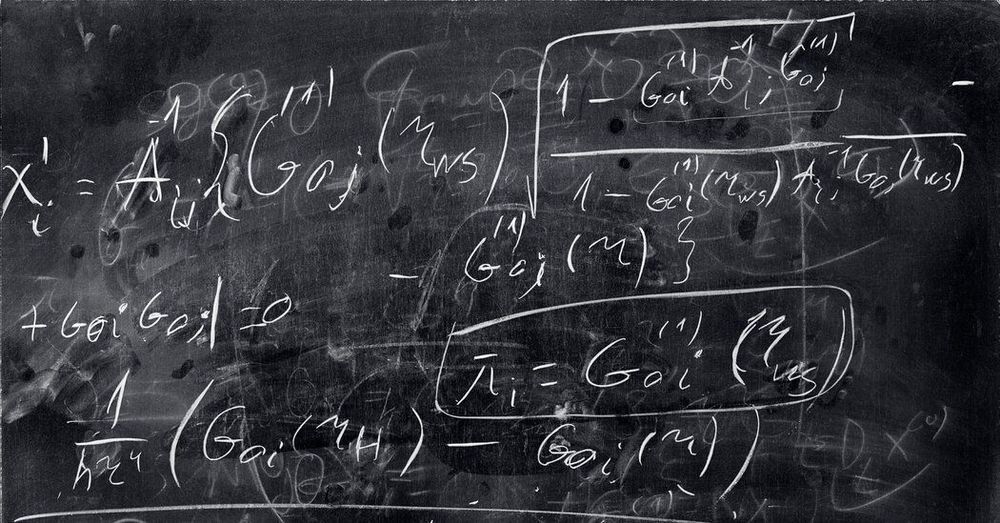Two physicists from the University of Luxembourg have now unambiguously shown that quantum-mechanical wavelike interactions are indeed crucial even at the scale of natural biological processes.
Quantum wavelike behaviour plays a key role in modern science and technology, with applications of quantum mechanics ranging from lasers and high-speed fiber communications, to quantum computers and photosynthesis in plants. A natural question is whether quantum wave phenomena could also be relevant for structure formation and dynamical processes in biological systems in living cells. This question has not been addressed convincingly up to now due to the lack of efficient quantum methods that are applicable to systems as large as whole proteins under physiological conditions (i.e. solvated in water and at room temperature).
Now writing in Science Advances, Prof. Alexandre Tkatchenko and doctoral researcher Martin Stöhr from the Department of Physics and Materials Science at the University of Luxembourg have investigated the folding process of proteins in water using a fully quantum-mechanical treatment for the first time. Protein folding is the physical process by which a chain of amino acids acquires its native biologically functional structure due to interactions between amino acids and the influence of surrounding water. A key novel finding of the present study is that the interaction between the protein and the surrounding water has to be described by quantum-mechanical wavelike behavior, which also turns out to be critical in the dynamics of the protein folding process.