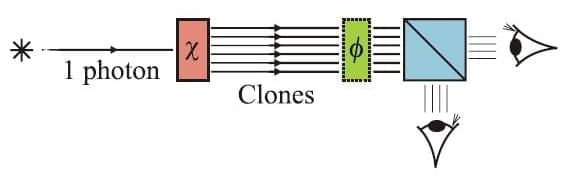
(PhysOrg.com) — By greatly amplifying one photon from an entangled photon pair, physicists have theoretically shown that human eyes can be used as detectors to observe quantum effects. Usually, detecting quantum phenomena requires sensitive photon detectors or similar technology, keeping the quantum world far removed from our everyday experience. By showing that it’s possible to perform quantum optics experiments with human eyes as detectors, the physicists can bring quantum phenomena closer to the macroscopic level and to everyday life.
The group of physicists is from the University of Geneva, and includes Pavel Sekatski, Nicolas Brunner (also from the University of Bristol), Cyril Branciard, Nicolas Gisin, and Christoph Simon. In their study published in a recent issue of Physical Review Letters, the scientists theoretically show how human eyes can be used to detect a large Bell inequality violation, which proves the existence of quantum entanglement.
As the physicists explain, the key to achieving human-eye detection of quantum effects is to use the process of quantum cloning by stimulated emission. Recently, using quantum cloning, researchers in Rome have experimentally created tens of thousands of clones starting from a single-photon. Then, by amplifying one photon of an entangled pair, the researchers managed to demonstrate entanglement. In order to do this, specific detectors are required, which can distinguish two orthogonal amplified states with a high success rate.