An experiment, performed by Istituto Nazionale di Ricerca Metrologica (INRIM) on 200 km of the Italian Quantum Backbone, in collaboration with Toshiba Europe, shows that coherent laser interferometry considerably improves the performances of quantum key distribution protocols in long-distance, real-world networks. The study has been published in Nature Communications.
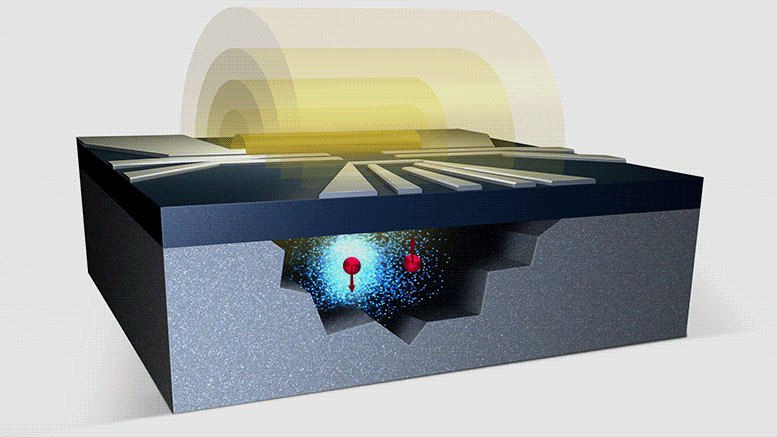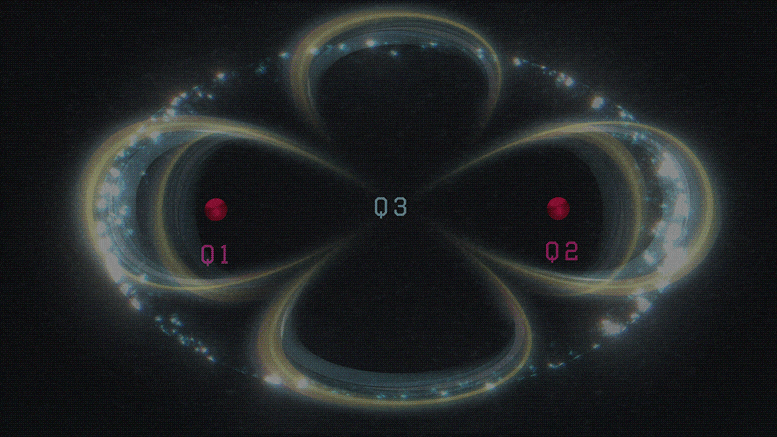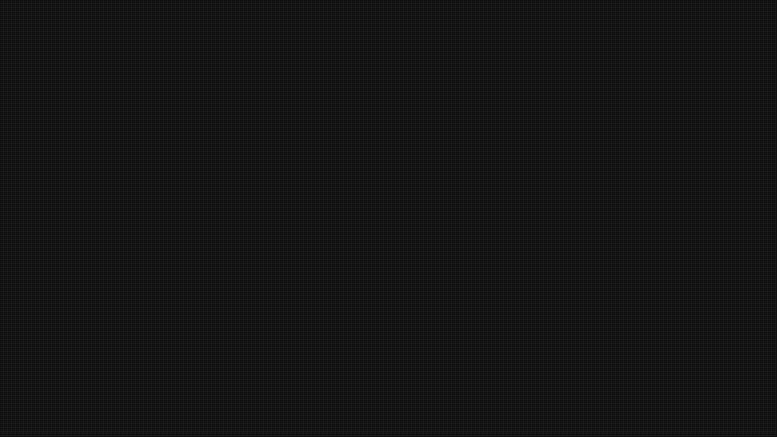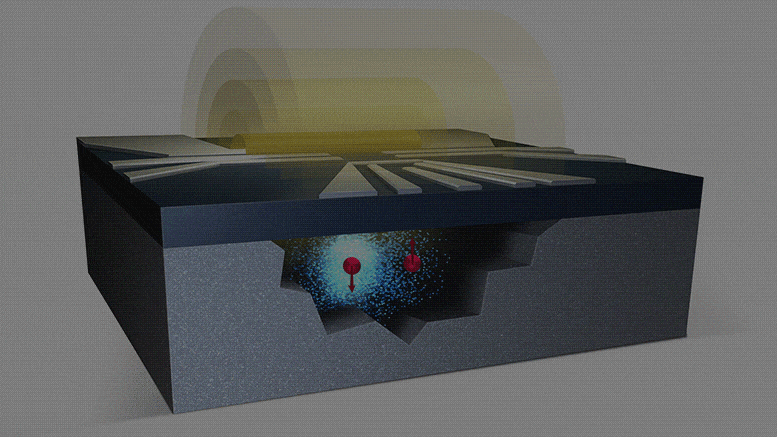
Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) protocols enable cryptographic keys to be shared between distant parties with an intrinsic security guaranteed by the laws of quantum mechanics. This is made possible by the transmission of single photons, the elementary particles of which light is made of.
The interest for this subject extends well beyond the scientific community, and has now a strong strategic and commercial relevance. The European Commission, within the “European Quantum Communication Infrastructure” intitative, aims at integrating quantum key distribution technologies into specific services throughout the European Union within the next 10 years, and INRIM will take part in the design of this infrastructure with the OQTAVO project.