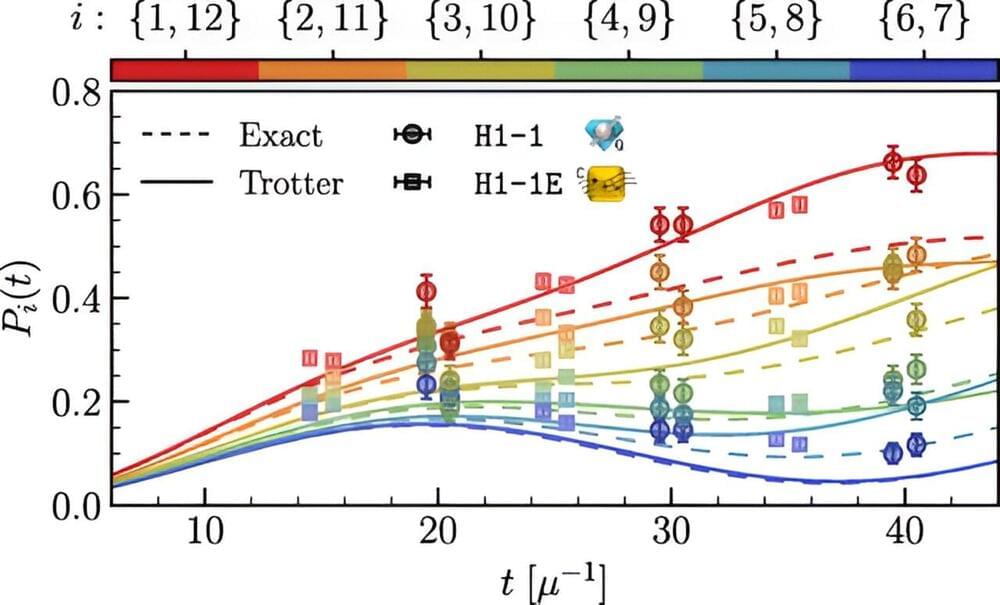
The result is a significant advancement in the field, showcasing the practical applicability of quantum computing in solving complex material science problems. Furthermore, the researchers discovered factors that can improve the durability and energy efficiency of quantum memory devices. The findings have been published in Nature Communications.
In the early 1980s, Richard Feynman asked whether it was possible to model nature accurately using a classical computer. His answer was: no. The world consists of fundamental particles, described by the principles of quantum physics. The exponential growth of the variables that must be included in the calculations pushes even the most powerful supercomputers to their limits. Instead, Feynman suggested using a computer that was itself made up of quantum particles. With his vision, Feynman is considered by many to be the Father of Quantum Computing.
Scientists at Forschungszentrum Jülich, together with colleagues from Slovenian institutions, have now shown that this vision can actually be put into practice. The application they are looking at is a so-called many-body system. Such systems describe the behavior of a large number of particles that interact with each other.