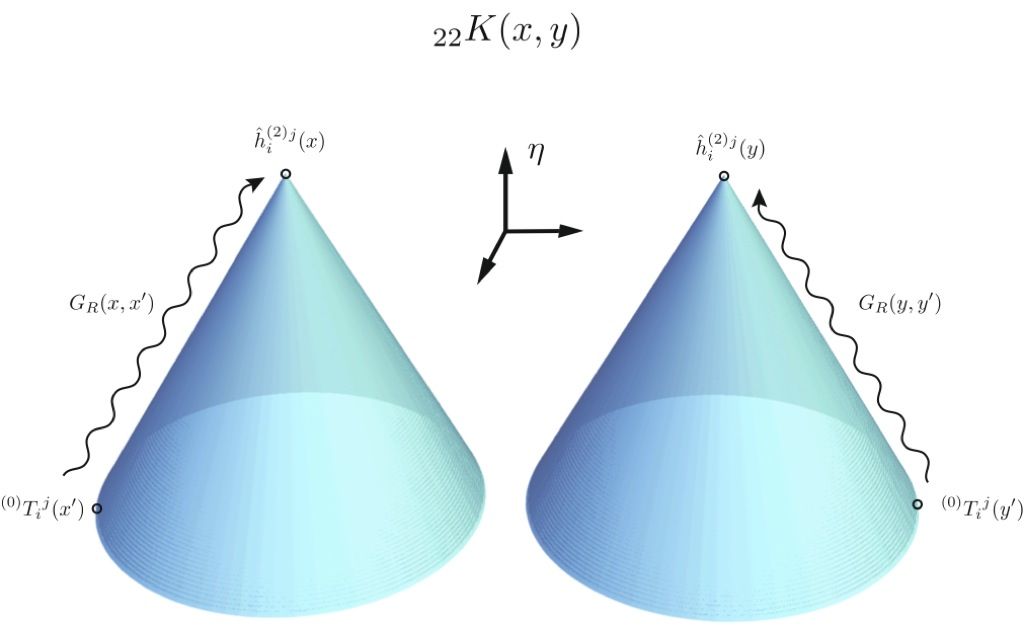
We examine the effect of the stress tensor of a quantum matter field, such as the electromagnetic field, on the spectrum of primordial gravity waves expected in inflationary cosmology. We find that the net effect is a small reduction in the power spectrum, especially at higher frequencies, but which has a different form from that described by the usual spectral index. Thus this effect has a characteristic signature, and is in principle observable. The net effect is a sum of two contributions, one of which is due to quantum fluctuations of the matter field stress tensor. The other is a quantum correction to the graviton field due to coupling to the expectation value of this stress tensor. Both contributions are sensitive to initial conditions in the very early universe, so this effect has the potential to act as a probe of these initial conditions.
J. Hsiang, L. Ford, K. Ng, et. al. Thu, 5 Jan 17 31/58.