
Category: physics – Page 228

Scientists discovers new properties of magnetism that could change our computers
Benjy WangProbably could be limited by a simulation restart.
Jim RohrichNo limits.
Omuterema Akhahenda shared a link.
PHYSICS:
Our electronics can no longer shrink and are on the verge of overheating. But in a new discovery from the University of Copenhagen, researchers have uncovered a fundamental property of magnetism, which may become relevant for the development of a new generation of more powerful and less hot computers.
JUST IN! Elon Musk & NASA’s New Light Speed Engine DEFIES Laws Of PHYSICS!
Subscribe — https://bit.ly/3myAZOn.
You’d be instantly where you want to be if you moved at the speed of light. Indeed, light-speed travel has been a fantasy of many scientists and aerospace engineers who look for ways to achieve it.
And now, it seems Elon Musk and NASA have broken that fantasy code to build a light-speed engine that defies the laws of physics.
About Elon Musk Live.
🎥 Videos about Elon Musk, SpaceX, Tesla, Neuralink, The Boring Company and more.
🔔 Subscribe for more Elon Musk, SpaceX, Tesla, Neuralink, The Boring Company and more.
📝 Written, voiced and produced by Elon Musk Live.
Watch More Elon Musk Live Videos Here:
👑 Elon Musk: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list…
🚀 SpaceX: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list…
🚗 Tesla: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list…
⚠️ Copyright Disclaimers.
• Section 107 of the U.S. Copyright Act states: “Notwithstanding the provisions of sections 106 and 106A, the fair use of a copyrighted work, including such use by reproduction in copies or phonorecords or by any other means specified by that section, for purposes such as criticism, comment, news reporting, teaching (including multiple copies for classroom use), scholarship, or research, is not an infringement of copyright.”
• We use images and content in accordance with the YouTube Fair Use copyright guidelines.
#ElonMusk #SpaceX #NASA

Professor Sean Carroll explains the theories of Presentism and Eternalism
It’s said that the clock is always ticking, but there’s a chance that it isn’t. The theory of “presentism” states that the current moment is the only thing that’s real, while “eternalism” is the belief that all existence in time is equally real. Find out if the future is really out there and predictable—just don’t tell us who wins the big game next year.
This video is episode two from the series “Mysteries of Modern Physics: Time”, Presented by Sean Carroll.
Learn more about the physics of time at https://www.wondrium.com/YouTube.
00:00 Science and Philosophy Combine When Studying Time.
2:30 Experiments Prove Continuity of Time.
6:47 Time Is Somewhat Predictable.
8:10 Why We Think of Time Differently.
8:49 Our Perception of Time Leads to Spacetime.
11:54 We Dissect Presentism vs Eternalism.
15:43 Memories and Items From the Past Make it More Real.
17:47 Galileo Discovers Pendulum Speeds Are Identical.
25:00 Thought Experiment: “What if Time Stopped?”
29:07 Time Connects Us With the Outside World.
Welcome to Wondrium on YouTube.
Here, you can enjoy a carefully curated selection of the history, science, and math videos you’ve come to know and love from brands like The Great Courses, and more.
If you’ve ever wanted to travel back in time, wondered about the science of life, wished for a better understanding of math, or dreamt of exploring the stars … then Wondrium will be your new favorite channel on YouTube!
Self-driving microscopes discover shortcuts to new materials
Researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory are teaching microscopes to drive discoveries with an intuitive algorithm, developed at the lab’s Center for Nanophase Materials Sciences, that could guide breakthroughs in new materials for energy technologies, sensing and computing.
“There are so many potential materials, some of which we cannot study at all with conventional tools, that need more efficient and systematic approaches to design and synthesize,” said Maxim Ziatdinov of ORNL’s Computational Sciences and Engineering Division and the CNMS. “We can use smart automation to access unexplored materials as well as create a shareable, reproducible path to discoveries that have not previously been possible.”
The approach, published in Nature Machine Intelligence, combines physics and machine learning to automate microscopy experiments designed to study materials’ functional properties at the nanoscale.
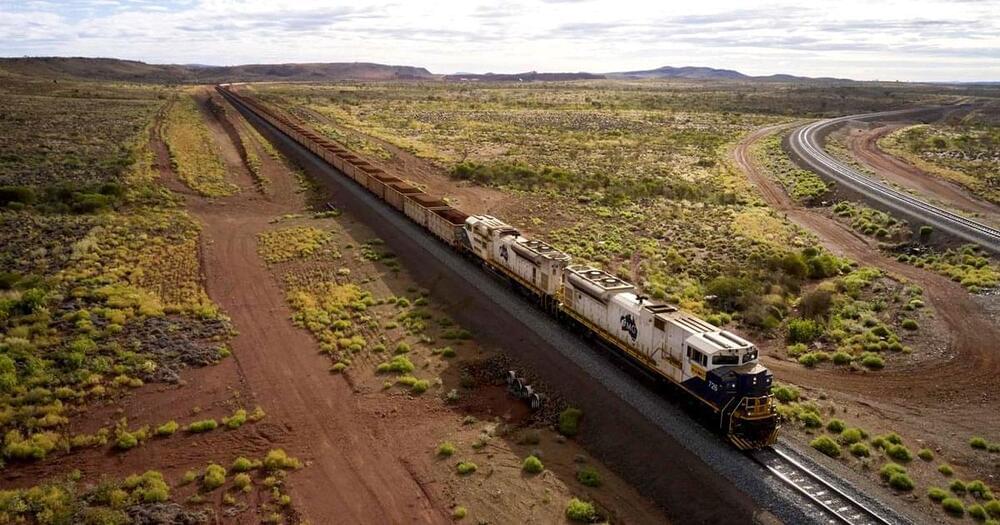

Ingenious Electric Train Fully Charges Itself
Australian mining company Fortescue is looking to reduce the carbon footprint of its operations by allowing a specially designed electric “Infinity Train” to roll down a hill to recharge its massive batteries — without ever relying on an external charging system.
“The Infinity Train has the capacity to be the world’s most efficient battery electric locomotive,” Fortescue CEO Elizabeth Gaines said in a statement. “The regeneration of electricity on the downhill loaded sections will remove the need for the installation of renewable energy generation and recharging infrastructure, making it a capital efficient solution for eliminating diesel and emissions from our rail operations.”
It’s a cleverly designed system: since the train is far lighter on the way up, it will generate enough energy fully loaded with iron ore on the way down to make it back up to the mine. In other words, it might sound like a perpetual motion machine — which is impossible, of course — but in reality it’s just an ingenious exploit of conventional physics.
Physicists figured out how launching a Falcon 9 changes the atmosphere
When researchers simulated the exhaust from a Falcon 9 rocket launch, they found that it releases high concentrations of CO2 in the upper atmosphere.

How could we find a wormhole hiding in the Milky Way?
If there was a wormhole in the center of our galaxy, how could we tell? Two physicists propose that carefully watching the motions of a star orbiting the Milky Way’s supermassive black hole might help scientists start to check. The researchers published the idea in a recent paper in the journal Physical Review D.
A wormhole is a hypothetical concept that connects two separate areas of space-time. Wormholes often appear in science fiction narratives like the 2014 film Interstellar as a convenient way to get from point A to point B in the vast universe. Physicists have many theories that describe how wormholes might behave, if they exist, but haven’t yet found any.


Physicists Found a Way to Trigger The Strange Glow of Warp Speed Acceleration
Every time you take a step, space itself glows with a soft warmth.
Called the Fulling–Davies–Unruh effect (or sometimes just Unruh effect if you’re pushed for time), this eerie glow of radiation emerging from the vacuum is akin to the mysterious Hawking radiation that’s thought to surround black holes.
Only in this case, it’s the product of acceleration rather than gravity.