Author Heinrich Päs shares 5 key insights from his new book, The One: How an Ancient Idea Holds the Future of Physics.


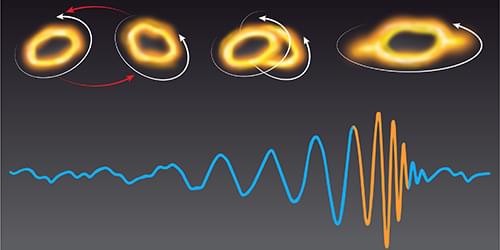
Simulations show that nonlinear spacetime dynamics manifest in the postmerger gravitational-wave signal of binary black hole coalescence.
“Spacetime tells matter how to move; matter tells spacetime how to curve.” This statement by physicist John Wheeler captures a defining feature of general relativity: its prediction of nonlinear spacetime dynamics. Such nonlinear evolution should be most evident in energetic spacetime events such as merging black holes, prompting the question of whether we can test for it using observations of gravitational waves emitted during such mergers. Two independent teams, led by Keefe Mitman at the California Institute of Technology [1] and Mark Ho-Yeuk Cheung at Johns Hopkins University in Maryland [2], show that this is the case. Using numerical simulations, they show the presence of nonlinearity in postmerger gravitational-wave signals.
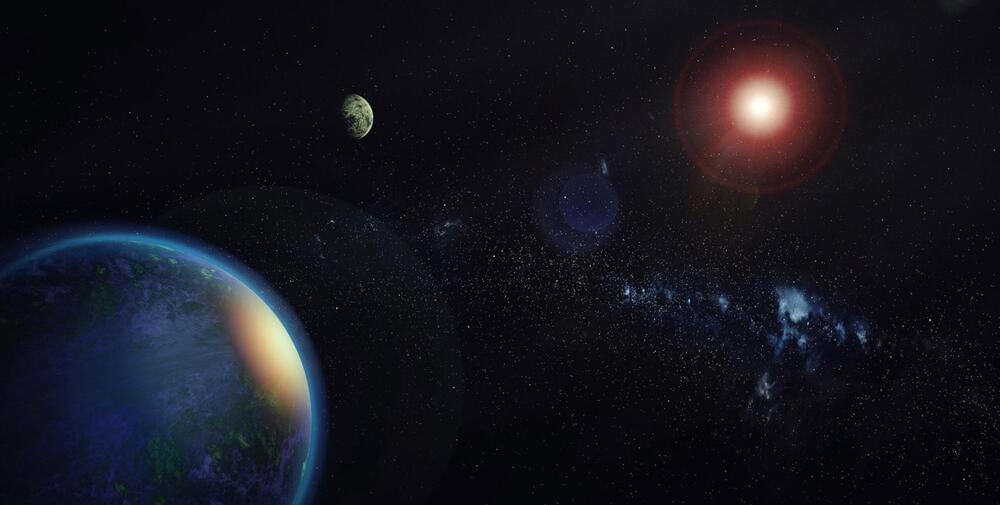

A pair of worlds that are just around the corner in cosmic terms look to be in the right spot to potentially host life as we know it.
A report in the February issue of the journal Astronomy and Astrophysics details the discovery of two exoplanets the orbit the red M-dwarf star GJ (or Gliese) 1002 in its habitable zone and are not far off from the mass of Earth.
These two characteristics top the list of things that make another planet worth getting excited about in terms of the odds it might have some sort of critters or even just primitive microorganisms hanging out.

A group of physicists may have discovered that black holes are actually made of and not only that but they may be responsible for the expansion of the universe itself.
Links to the research findings:
https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/2041-8213/acb704
https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/1538-4357/acac2e
Dr. Tamar Gutnick, first author and former postdoctoral researcher in the Physics and Biology Unit at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST), said, “If we want to understand how the brain works, octopuses are the perfect animal to study as a comparison to mammals. They have a large brain, an amazingly unique body, and advanced cognitive abilities that have developed completely differently from those of vertebrates.”
“Octopuses have eight powerful and ultra-flexible arms, which can reach anywhere on their body. If we tried to attach wires to them, they would immediately rip it off, so we needed to get the equipment out of their reach by placing it under their skin.”
Scientists settled on small and lightweight data loggers as the solution, initially designed to track the brain activity of birds during flight. The team modified the devices to be waterproof and compact enough to slip inside the octopuses easily. Up to 12 hours of continuous recording were possible with the batteries, which had to operate in a low-air condition.
West Virginia University physicists have made a breakthrough on an age-old limitation of the first law of thermodynamics.
Paul Cassak, professor and associate director of the Center for KINETIC Plasma Physics, and graduate research assistant Hasan Barbhuiya, both in the Department of Physics and Astronomy, are studying how energy gets converted in superheated plasmas in space.
Their findings, published in Physical Review Letters, will revamp scientists’ understanding of how plasmas in space and laboratories get heated up, and may have a wide variety of further applications across physics and other sciences.
John Vervaeke and Donald Hoffman talk about infinity, ego, death, non-dualism, and what is reality. Sponsors:
- Brilliant: https://brilliant.org/TOE for 20% off.
- Masterworks: https://www.masterworks.com promo code TOE
- Shopify: https://www.shopify.com/theories to start your free trial.
*New* TOE Website (early access to episodes): https://theoriesofeverything.org/
Patreon: https://patreon.com/curtjaimungal.
Crypto: https://tinyurl.com/cryptoTOE
PayPal: https://tinyurl.com/paypalTOE
Twitter: https://twitter.com/TOEwithCurt.
Discord Invite: https://discord.com/invite/kBcnfNVwqs.
iTunes: https://podcasts.apple.com/ca/podcast/better-left-unsaid-wit…1521758802
Pandora: https://pdora.co/33b9lfP
Spotify: https://open.spotify.com/show/4gL14b92xAErofYQA7bU4e.
Subreddit r/TheoriesOfEverything: https://reddit.com/r/theoriesofeverything.
LINKS MENTIONED:
- Important TOE ep: Lilian Dindo: https://youtu.be/L_hI7JNsbt0
- Important TOE ep: Karl Friston (Part 2): https://youtu.be/SWtFU1Lit3M
- The Meaning Crisis: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLND1JCRq8Vuh3f0P5qjrSdb5eC1ZfZwWJ
- Donald Hoffman theolocution w/ Joscha Bach: https://youtu.be/bhSlYfVtgww.
- John Vervaeke theolocution w/ Joscha Bach: https://youtu.be/rK7ux_JhHM4
- John Vervaeke theolocution w/ Bernardo Kastrup: https://youtu.be/zw6BFDJ765w.
- John Vervaeke solo TOE podcast: https://youtu.be/3p8o3-7mvQc.
- Donald Hoffman solo TOE podcast: https://youtu.be/CmieNQH7Q4w.
TIMESTAMPS:
00:00:00 Introduction.
00:03:10 Zen, intelligibility, and Neoplatonism.
00:05:26 Physics and consciousness.
00:07:16 Spacetime and Nima Arkani Hamed.
00:09:34 What do they find impactful about one another’s work?
00:14:27 What does “fundamental” mean?
00:22:08 Reality vs. Fundamentality.
00:25:07 Gödel’s incompleteness is NOT about TOEs.
00:35:49 Science predicts its own demise.
00:46:00 Psychosis, derealization, and the terror of delving into TOEs.
01:02:17 Morality and “the ego“
01:08:04 Infinity and “the one“
01:28:47 Coleman Mandula theorem.
01:31:59 Debate: Spacetime is real vs. unreal.
01:52:03 Reality, evolution and infinity.
02:08:35 Truth, misframing, and love.
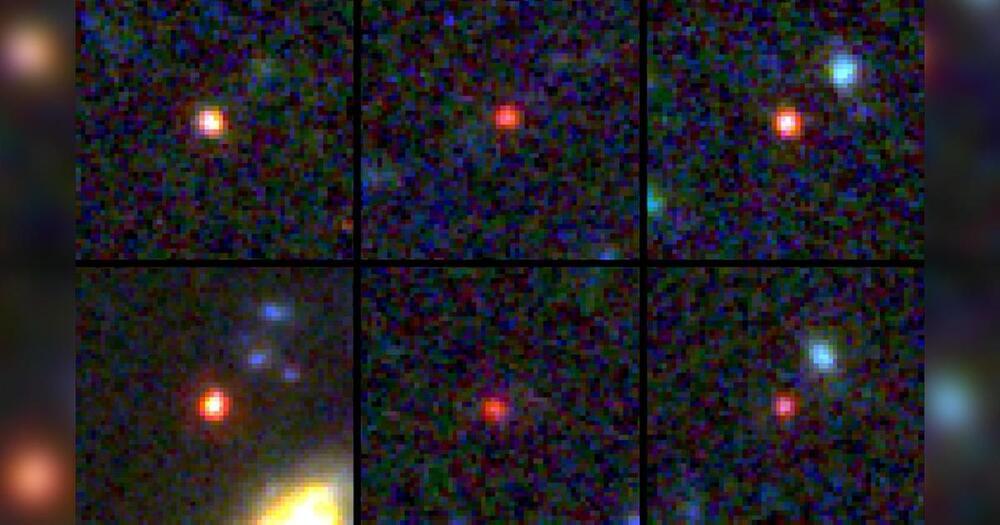

“These objects are way more massive than anyone expected,” said study coauthor Joel Leja, assistant professor of astronomy and astrophysics at Penn State University, in a statement. “We expected only to find tiny, young, baby galaxies at this point in time, but we’ve discovered galaxies as mature as our own in what was previously understood to be the dawn of the universe.”
The telescope observes the universe in infrared light, which is invisible to the human eye, and is capable of detecting the faint light from ancient stars and galaxies. By peering into the distant universe, the observatory can essentially see back in time up to about 13.5 billion years ago. (Scientists have determined the universe is about 13.7 billion years old.)
The operations center for the telescope is in Baltimore City, at the Space Telescope Science Institute on the Johns Hopkins campus.