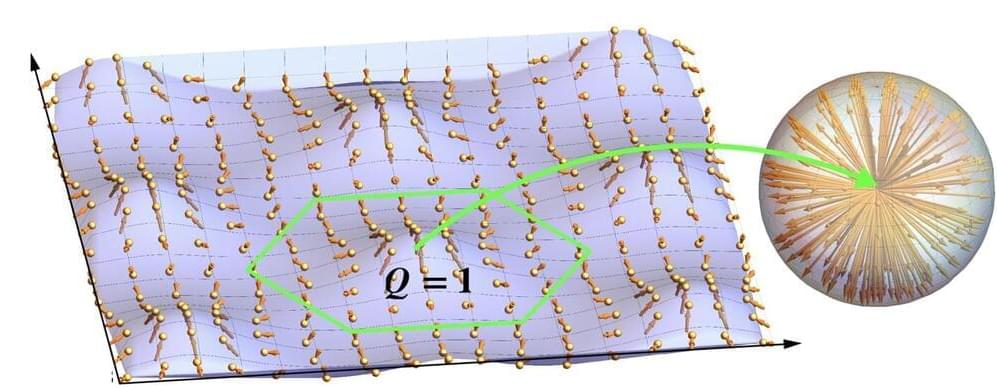
New theoretical work establishes an analogy between systems that are dynamically frustrated, such as glasses, and thermodynamic systems whose members have conflicting goals, such as predator–prey ecosystems.
A system is geometrically frustrated when its members cannot find a configuration that simultaneously minimizes all their interaction energies, as is the case for a two-dimensional antiferromagnet on a triangular lattice. A nonreciprocal system is one whose members have conflicting, asymmetric goals, as exemplified by an ecosystem of predators and prey. New work by Ryo Hanai of Kyoto University, Japan, has identified a powerful mathematical analogy between those two types of dynamical systems [1]. Nonreciprocity alters collective behavior, yet its technological potential is largely untapped. The new link to geometrical frustration will open new prospects for applications.
To appreciate Hanai’s feat, consider how different geometric frustration and nonreciprocity appear at first. Frustration defies the approach that physics students are taught in their introductory classes, based on looking at the world through Hamiltonian dynamics. In this approach, energy is to be minimized and states of matter characterized by their degree of order. Some of the most notable accomplishments in statistical physics have entailed describing changes between states—that is, phase transitions. Glasses challenge that framework. These are systems whose interactions are so spatially frustrated that they cannot find an equilibrium spatial order. But they can find an order that’s “frozen” in time. Even at a nonzero temperature, everything is stuck—and not just in one state. Many different configurations coexist whose energies are nearly the same.