Nice work; understanding the quantum effects in nanomechanical systems is closer to reality in being achieved. Imagine a nanobot or microbot with quantum mechanic properties.
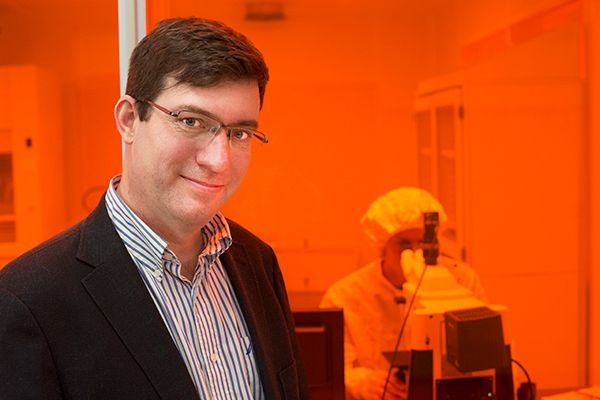
Rob Knobel is probing the ultimate limits of nanomechanical systems to develop and build tiny vapour sensors, which could be used as airport security tools to prevent terrorism or drug smuggling.
He and his students are using highly specialized equipment in the $5-million Kingston Nano Fabrication Laboratory (KNFL), which opened a year ago in Innovation Park, to fabricate nanosensors made from graphene, a form of carbon a single atom thick.
“Graphene is the strongest, lightest material yet discovered, and it has remarkable electrical and mechanical properties. We’re developing graphene chemical sensors that can detect vapours in parts per billion or trillion concentration. These could potentially be used for detecting explosives or biological agents,” says Dr. Knobel, an associate professor, the Chair of Engineering Physics and a Queen’s Engineering graduate himself.