Submarine neutrino detectors will hunt for dark matter, distant star explosions, and more.


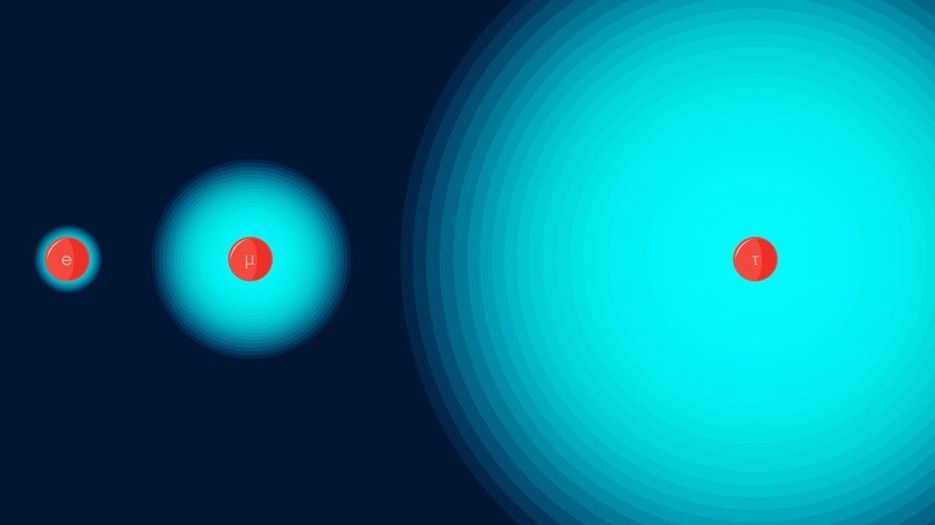
Bosons and fermions, the two classes into which all particles—from the sub-atomic to atoms themselves—can be sorted, behave very differently under most circumstances. While identical bosons like to congregate, identical fermions tend to be antisocial. However, in one dimension—imagine particles that can only move on a line—bosons can become as stand-offish as fermions, so that no two occupy the same position. Now, new research shows that the same thing—bosons acting like fermions—can happen with their velocities. The finding adds to our fundamental understanding of quantum systems and could inform the eventual development of quantum devices.
“All particles in nature come in one of two types, depending on their ‘spin,’ a quantum property with no real analogue in classical physics,” said David Weiss, Distinguished Professor of Physics at Penn State and one of the leaders of the research team. “Bosons, whose spins are whole integers, can share the same quantum state, while fermions, whose spins are half integers, cannot. When the particles are cold or dense enough, bosons behave completely differently from fermions. Bosons form ‘Bose-Einstein condensates,’ congregating in the same quantum state. Fermions, on the other hand, fill available states one by one to form what is called a ‘Fermi sea.’”
Researchers at Penn State have now experimentally demonstrated that, when bosons expand in one dimension—the line of atoms is allowed spread out to become longer—they can form a Fermi sea. A paper describing the research appears March 27, 2020 in the journal Science.

In 2005, the obituary of physicist Asher Peres in the magazine Physics Today told us that when a journalist asked him if quantum teleportation could transport a person’s soul as well as their body, the scientist replied: “No, not the body, just the soul.” More than just a simple joke, Peres’ response offers a perfect explanation, encoded in a metaphor, of the reality of a process that we have seen countless times in science fiction. In fact, teleportation does exist, although in the real world it is quite different from the famous “Beam me up, Scotty!” associated with the Star Trek series.
Teleportation in real science began to take shape in 1993 thanks to a theoretical study published by Peres and five other researchers in Physical Review Letters, which laid the foundation for quantum teleportation. Apparently, it was co-author Charles Bennett’s idea to associate the proposed phenomenon with the popular idea of teleportation, but there is an essential difference between fiction and reality: in the latter it’s not matter that travels, but rather information, which transfers properties from the original matter to that of the destination matter.
Quantum teleportation is based on a hypothesis described in 1935 by physicist Albert Einstein and his colleagues Boris Podolsky and Nathan Rosen, known as the EPR paradox. As a consequence of the laws of quantum physics, it was possible to obtain two particles and separate them in space so that they would continue to share their properties, as two halves of a whole. Thus, an action on one of them (on A, or Alice, according to the nomenclature used) would instantaneously have an effect on the other (on B, or Bob). This “spooky action at a distance”, in Einstein’s words, would seem capable of violating the limit of the speed of light.
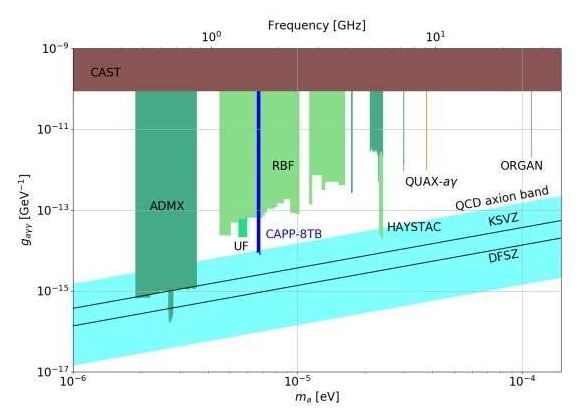
Researchers at the Center for Axion and Precision Physics Research (CAPP), within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS, South Korea), have reported the first results of their search of axions, elusive, ultra-lightweight particles that are considered dark matter candidates. IBS-CAPP is located at Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST). Published in Physical Review Letters, the analysis combines data taken over three months with a new axion-hunting apparatus developed over the last two years.
Proving the existence of axions could solve two of the biggest mysteries in modern physics at once: why galaxies orbiting within galaxy clusters are moving far faster than expected, and why two fundamental forces of nature follow different symmetry rules. The first conundrum was raised back in the 1930s, and was confirmed in the 1970s when astronomers noticed that the observed mass of the Milky Way galaxy could not explain the strong gravitational pull experienced by the stars in the galaxies. The second enigma, known as the strong CP problem, was dubbed by Forbes magazine as “the most underrated puzzle in all of physics” in 2019.
Symmetry is an important element of particle physics and CP refers to the Charge+Parity symmetry, where the laws of physics are the same if particles are interchanged with their corresponding antiparticles © in their mirror images ℗. In the case of the strong force, which is responsible for keeping nuclei together, CP violation is allowed theoretically, but has never been detected, even in the most sensitive experiments. On the other hand, CP symmetry is violated both theoretically and experimentally in the weak force, which underlies some types of radioactive decays. In 1977, theoretical physicists Roberto Peccei and Helen Quinn proposed the Peccei-Quinn symmetry as a theoretical solution to this problem, and two Nobel laureates in Physics, Frank Wilczek and Steven Weinberg, showed that the Peccei-Quinn symmetry results in a new particle: the axion. The particle was named after an American detergent, because it should clean the strong interactions mess.

What is interaction, and when does it occur? Intuition suggests that the necessary condition for the interaction of independently created particles is their direct touch or contact through physical force carriers. In quantum mechanics, the result of the interaction is entanglement—the appearance of non-classical correlations in the system. It seems that quantum theory allows entanglement of independent particles without any contact. The fundamental identity of particles of the same kind is responsible for this phenomenon.
Quantum mechanics is currently the best and most accurate theory used by physicists to describe the world around us. Its characteristic feature, however, is the abstract mathematical language of quantum mechanics, notoriously leading to serious interpretational problems. The view of reality proposed by this theory is still a subject of scientific dispute that, over time, is only becoming hotter and more interesting. New research motivation and intriguing questions are brought forth by a fresh perspective resulting from the standpoint of quantum information and the enormous progress of experimental techniques. These allow verification of the conclusions drawn from subtle thought experiments directly related to the problem of interpretation. Moreover, researchers are now making enormous progress in the field of quantum communication and quantum computer technology, which significantly draws on non-classical resources offered by quantum mechanics.
Pawel Blasiak from the Institute of Nuclear Physics of the Polish Academy of Sciences in Krakow and Marcin Markiewicz from the University of Gdansk focus on analyzing widely accepted paradigms and theoretical concepts regarding the basics and interpretation of quantum mechanics. The researchers are trying to determine to what extent the intuitions used to describe quantum mechanical processes are justified in a realistic view of the world. For this purpose, they try to clarify specific theoretical ideas, often functioning in the form of vague intuitions, using the language of mathematics. This approach often results in the appearance of inspiring paradoxes. Of course, the more basic the concept to which a given paradox relates, the better, because it opens up new doors to deeper understanding a given problem.
Higgs boson laser.
Electroweak processes in high-energy lepton collisions are considered in a situation where the incident center-of-mass energy lies below the reaction threshold, but is boosted to the required level by subsequent laser acceleration. Within the framework of laser-dressed quantum field theory, we study the laser-boosted process $\ell^+ \ell^- \to HZ^0$ in detail and specify the technical demands needed for its experimental realization. Further, we outline possible qualitative differences to field-free processes regarding the detection of the produced Higgs bosons.

Scientists have accidentally discovered a completely new form of matter that works in the same way as the lightsabers used in Star Wars.
A team of physicists were messing around with photons when they managed to get the particles to stick together and form a molecule.
The molecule behaves, they claim, just like a lightsaber by moving the light particles around in a solid mass and is unlike any matter seen before.
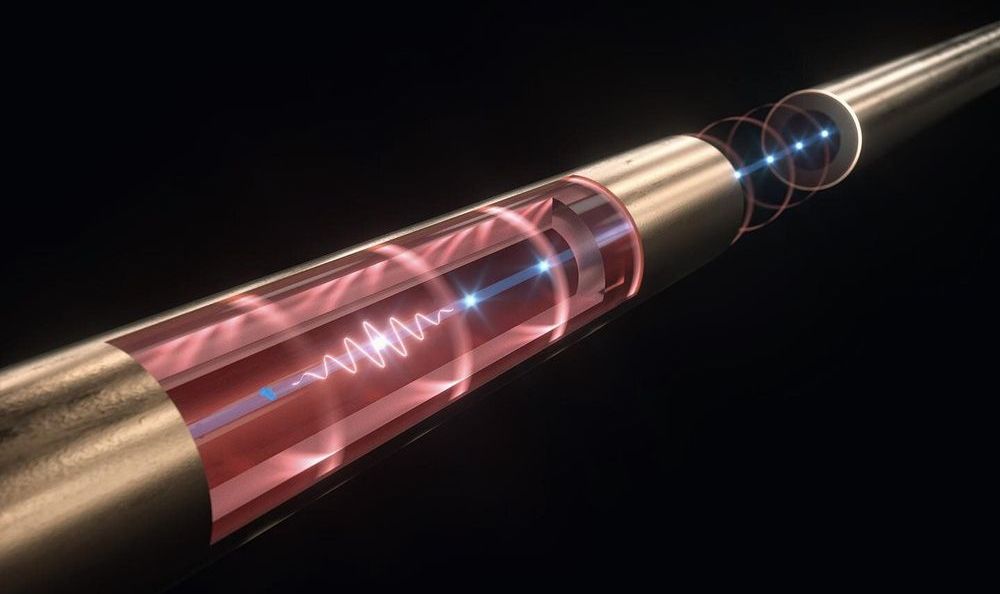
A team of DESY scientists has built a miniature double particle accelerator that can recycle some of the laser energy fed into the system to boost the energy of the accelerated electrons a second time. The device uses narrowband terahertz radiation which lies between infrared and radio frequencies in the electromagnetic spectrum, and a single accelerating tube is just 1.5 centimetres long and 0.79 millimetres in diameter. Dongfang Zhang and his colleagues from the Center for Free-Electron laser Science (CFEL) at DESY present their experimental accelerator in the journal Physical Review X.
The miniature size of the device is possible due to the short wavelength of terahertz radiation. “Terahertz-based accelerators have emerged as promising candidates for next-generation compact electron sources,” explains Franz Kärtner, Lead Scientist at DESY and head of the CFEL group that built the device. Scientists have successfully experimented with terahertz accelerators before, which could enable applications where large particle accelerators are just not feasible or necessary. “However, the technique is still in an early stage, and the performance of experimental terahertz accelerators has been limited by the relatively short section of interaction between the terahertz pulse and the electrons,” says Kärtner.
For the new device, the team used a longer pulse comprising many cycles of terahertz waves. This multicycle pulse significantly extends the interaction section with the particles. “We feed the multicycle terahertz pulse into a waveguide that is lined with a dielectric material”, says Zhang. Within the waveguide, the pulse’s speed is reduced. A bunch of electrons is shot into the central part of the waveguide just in time to travel along with the pulse. “This scheme increases the interaction region between the terahertz pulse and the electron bunch to the centimetre range—compared to a few millimetres in earlier experiments,” reports Zhang.
In the heart of a galaxy cluster 200 million light-years away, astronomers have failed to detect hypothetical particles called axions.
This places new constraints on how we believe these particles work — but it also has pretty major implications for string theory, and the development of a Theory of Everything that describes how the physical Universe works.
“Until recently I had no idea just how much X-ray astronomers bring to the table when it comes to string theory, but we could play a major role,” said astrophysicist Christopher Reynolds of the University of Cambridge in the UK.