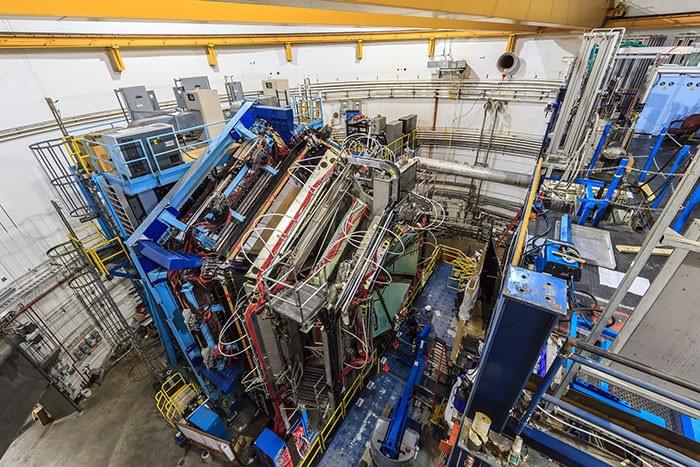
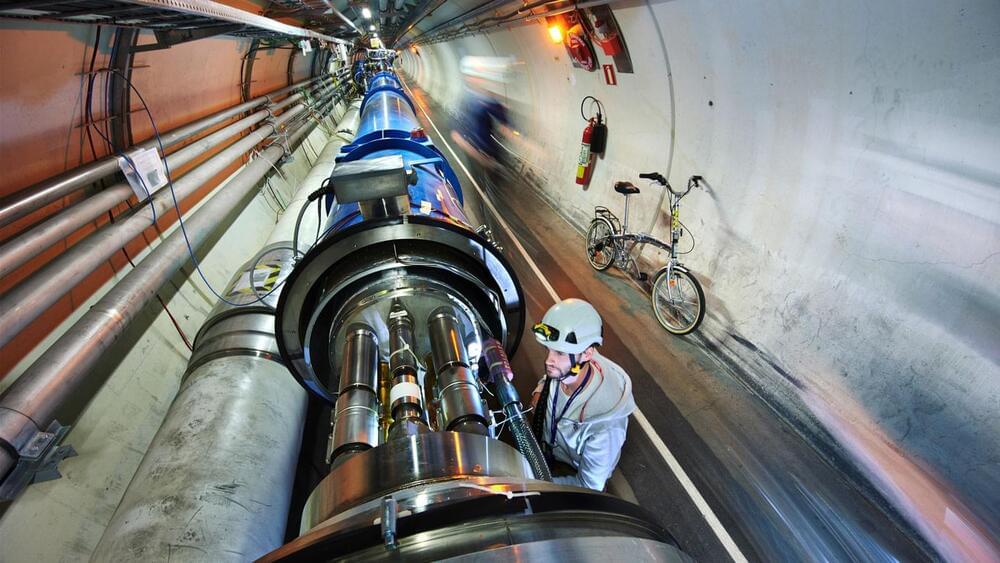
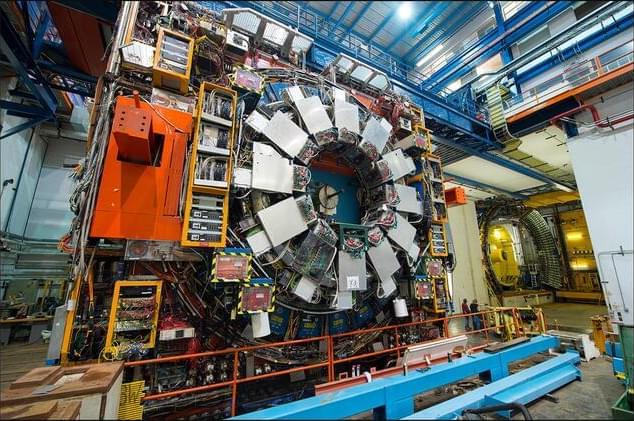
Where is all the new physics? In the decade since the Higgs boson’s discovery, there have been no statistically significant hints of new particles in data from the Large Hadron Collider (LHC). Could they be sneaking past the standard searches? At the recent Rencontres de Moriond conference, the ATLAS collaboration at the LHC presented several results of novel types of searches for particles predicted by supersymmetry.
Supersymmetry, or SUSY for short, is a promising theory that gives each elementary particle a “superpartner”, thus solving several problems in the current Standard Model of particle physics and even providing a possible candidate for dark matter. ATLAS’s new searches targeted charginos and neutralinos – the heavy superpartners of force-carrying particles in the Standard Model – and sleptons – the superpartners of Standard Model matter particles called leptons. If produced at the LHC, these particles would each transform, or “decay”, into Standard Model particles and the lightest neutralino, which does not further decay and is taken to be the dark-matter candidate.
ATLAS’s newest search for charginos and sleptons studied a particle-mass region previously unexplored due to a challenging background of Standard Model processes that mimics the signals from the sought-after particles. The ATLAS researchers designed dedicated searches for each of these SUSY particle types, using all the data recorded from Run 2 of the LHC and looking at the particles’ decays into two charged leptons (electrons or muons) and “missing energy” attributed to neutralinos. They used new methods to extract the putative signals from the background, including machine-learning techniques and “data-driven” approaches.