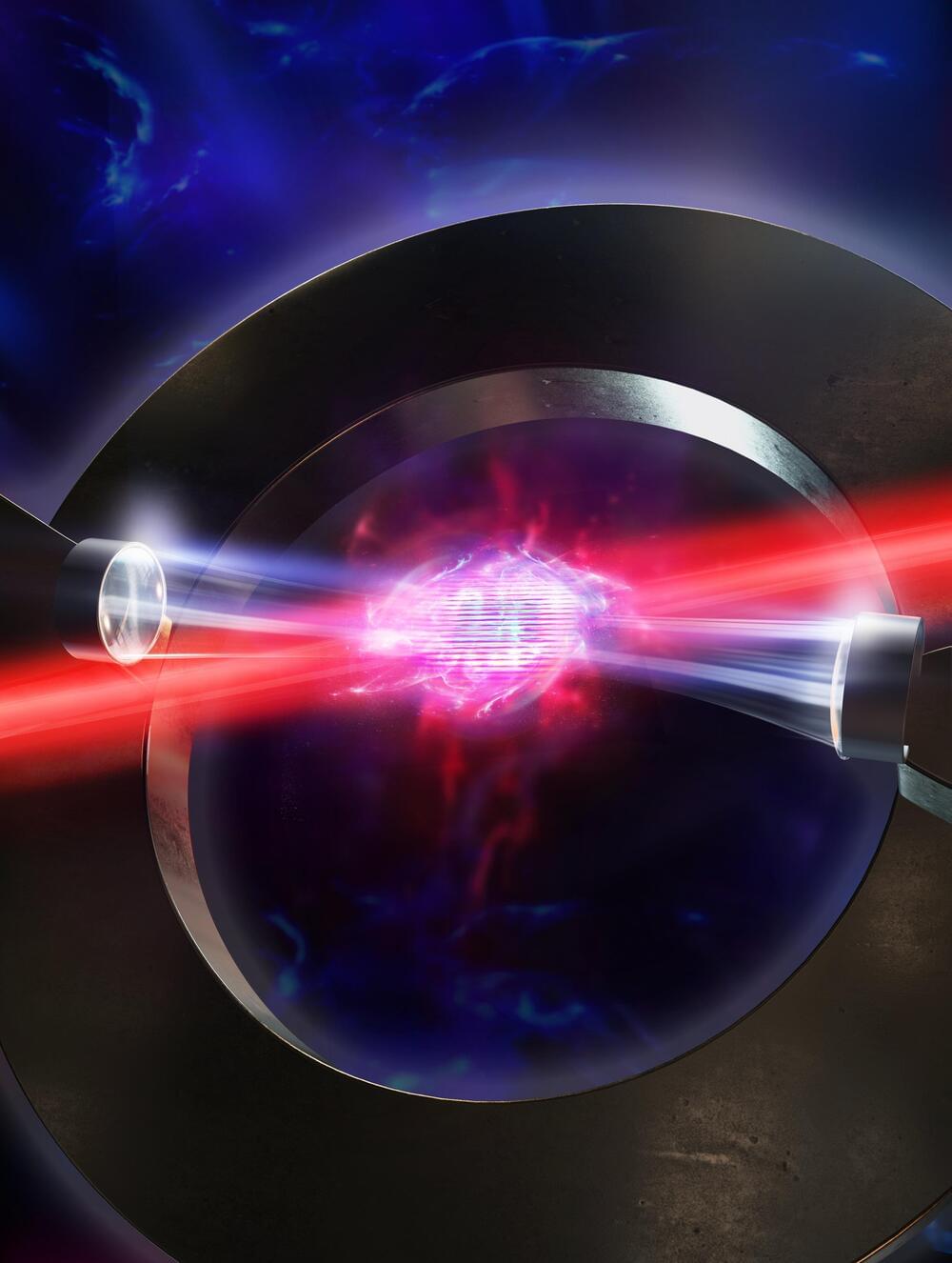
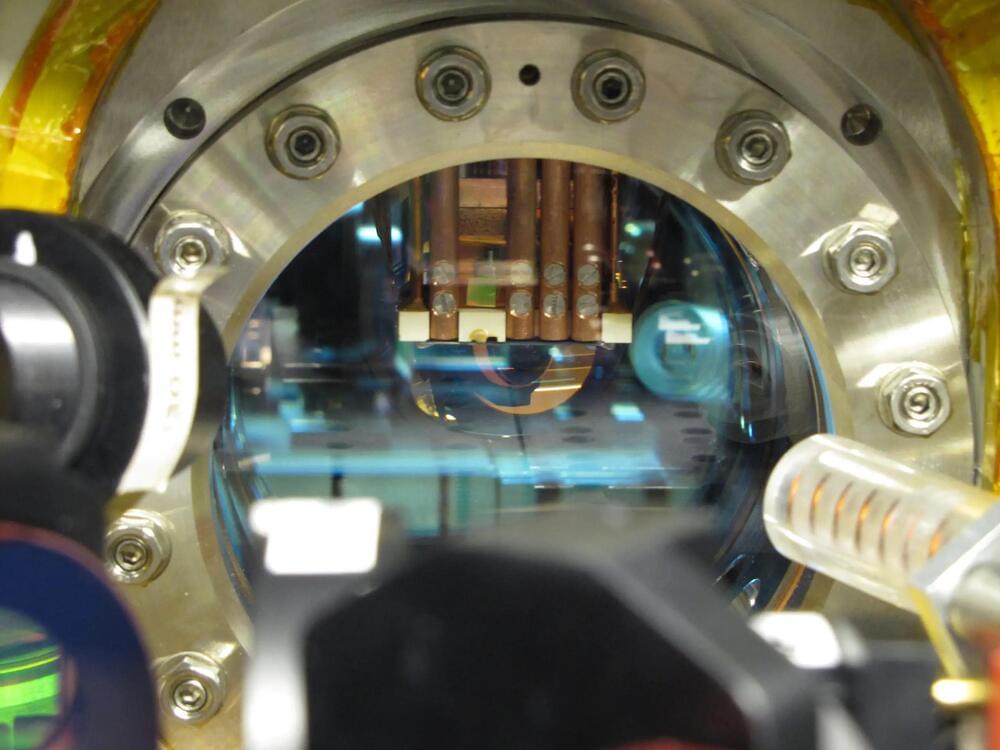
Scientists at EPFL have found a new way to create a crystalline structure called a “density wave” in an atomic gas. The findings can help us better understand the behavior of quantum matter, one of the most complex problems in physics. The research was published May 24 in Nature.
“Cold atomic gases were well known in the past for the ability to ‘program’ the interactions between atoms,” says Professor Jean-Philippe Brantut at EPFL. “Our experiment doubles this ability.” Working with the group of Professor Helmut Ritsch at the University of Innsbruck, they have made a breakthrough that can impact not only quantum research but quantum-based technologies in the future.
Scientists have long been interested in understanding how materials self-organize into complex structures, such as crystals. In the often-arcane world of quantum physics, this sort of self-organization of particles is seen in “density waves,” where particles arrange themselves into a regular, repeating pattern or order; like a group of people with different colored shirts on standing in a line but in a pattern where no two people with the same color shirt stand next to each other.