Lithium (Li) secondary batteries, commonly used in electric vehicles, store energy by converting electrical energy to chemical energy and generating electricity to release chemical energy to electrical energy through the movement of Li-ions between a cathode and an anode. These secondary batteries mainly use nickel (Ni) cathode materials due to their high lithium-ion storage capacity. Traditional nickel-based materials have a polycrystalline morphology composed of many tiny crystals which can undergo structural degradation during charging and discharging, significantly reducing their lifespan.
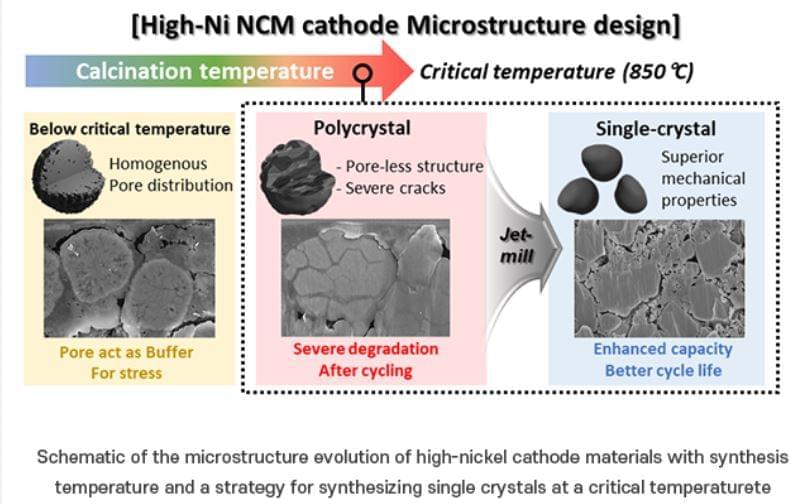
One approach to addressing this issue is to produce the cathode material in a “single-crystal” form. Creating nickel-based cathode materials as single large particles, or “single crystals,” can enhance their structural and chemical stability and durability. It is known that single-crystal materials are synthesized at high temperatures and become rigid. However, the exact process of hardening during synthesis and the specific conditions under which this occurs remain unclear.
To improve the durability of nickel cathode materials for electric vehicles, the researchers focused on identifying a specific temperature, referred to as the “critical temperature,” at which high-quality single-crystal materials are synthesized. They investigated various synthesis temperatures to determine the optimal conditions for forming single crystals in synthesis of a nickel-based cathode material (N884). The team systematically observed the impact of temperature on the material’s capacity and long-term performance.