We’ve been trying for a long time to make a tiny Sun on Earth, one that would sustainably produce energy by nuclear fusion of hydrogen or similar atoms. Come to think of it, I’d like one for my basement.
Fusion requires quite a bit of heat to get going, but once it does, it starts producing its own heat. If you can keep that system contained so it doesn’t expand too much or allow too much heat to escape, further fusion happens. If it reaches a point where self-heating becomes the primary driver of fusion, you have yourself a “burning plasma”.
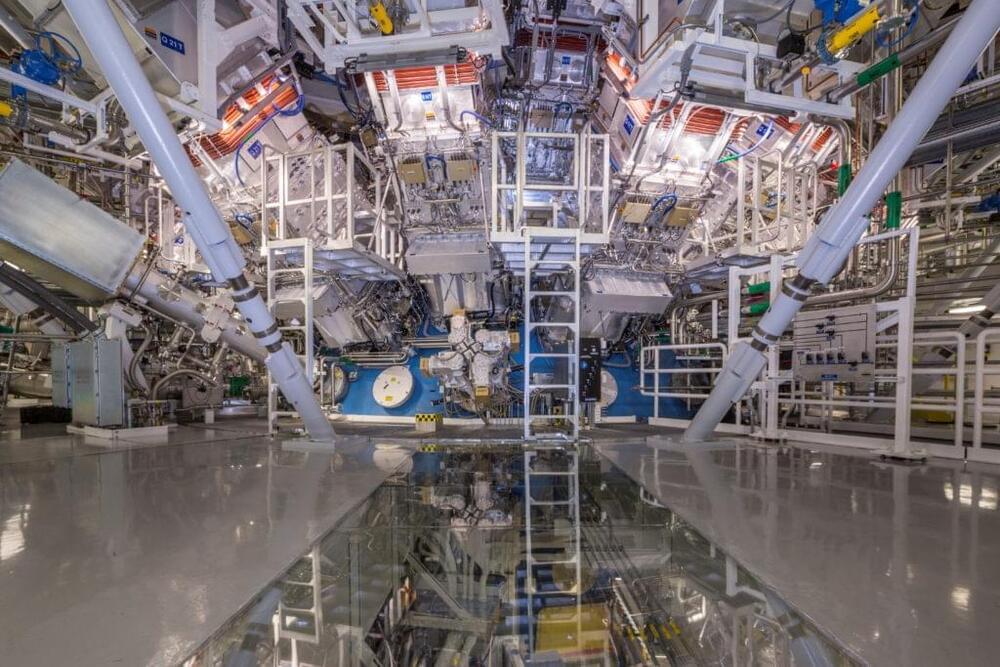
The actual Sun has a pretty easy time sustaining fusion because of the crushing gravity at its center, but we Earthlings need to be a bit more creative to achieve that here at home (because we don’t have any 4-nonillion pound weights handy). The burning plasma, indeed a tiny star, is one of the key milestones on the path to usable nuclear fusion. Until now, no one had ever made such a thing.