A recent experiment showed this virtually limitless form of clean power is possible on Earth. Now, one of the most complex energy projects in history aims to make nuclear fusion a reality for the whole planet.




Today is the opening of The CAPT.(DR.) IDAHOSA WELLS OKUNBO STEM AND INNOVATION CENTER in the rural area of Iyara, warri, delta state, Nigeria.aa.
View insights.
21 post reach.
Physicists optimized a nuclear fusion reactor to overcome a problem that causes heat loss and prevents the device from sustaining fusion.
Traditional Argentine barbecues date back to the 16th century. One inventor created a new twist on the custom, turning discarded fruit from cider production into logs that can replace firewood and charcoal.
MORE WORLD WIDE WASTE VIDEOS:
Briquettes Made From Coconut Waste Could Reduce Deforestation | World Wide Waste.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=meBd1GHC2yg.
The Danger of Ukraine’s Nuclear Waste | World Wide Waste.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=r88prlEbtmg.
How To Make Paint From Pollution | World Wide Waste.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=21InDm4iUXc.
#FruitPulp #WorldWideWaste #BusinessInsider.
Business Insider tells you all you need to know about business, finance, tech, retail, and more.
Visit us at: https://www.businessinsider.com.
Subscribe: https://www.youtube.com/user/businessinsider.
BI on Facebook: https://read.bi/2xOcEcj.
BI on Instagram: https://read.bi/2Q2D29T
BI on Twitter: https://read.bi/2xCnzGF
BI on Snapchat: https://www.snapchat.com/discover/Business_Insider/5319643143
Boot Camp on Snapchat: https://www.snapchat.com/discover/Boot_Camp/3383377771
How logs of fruit pulp replace firewood and charcoal | world wide waste.
Physicists at EPFL, within a large European collaboration, have revised one of the fundamental laws that has been foundational to plasma and fusion research for over three decades, even governing the design of megaprojects like ITER. The update shows that we can actually safely use more hydrogen fuel in fusion reactors, and therefore obtain more energy than previously thought.
Fusion is one of the most promising sources of future energy. It involves two atomic nuclei combining into one, thereby releasing enormous amounts of energy. In fact, we experience fusion every day: the sun’s warmth comes from hydrogen nuclei fusing into heavier helium atoms.
There is currently an international fusion research megaproject called ITER, which aims to replicate the fusion processes of the sun to create energy on the Earth. Its aim is the creation of high temperature plasma that provides the right environment for fusion to occur, producing energy.
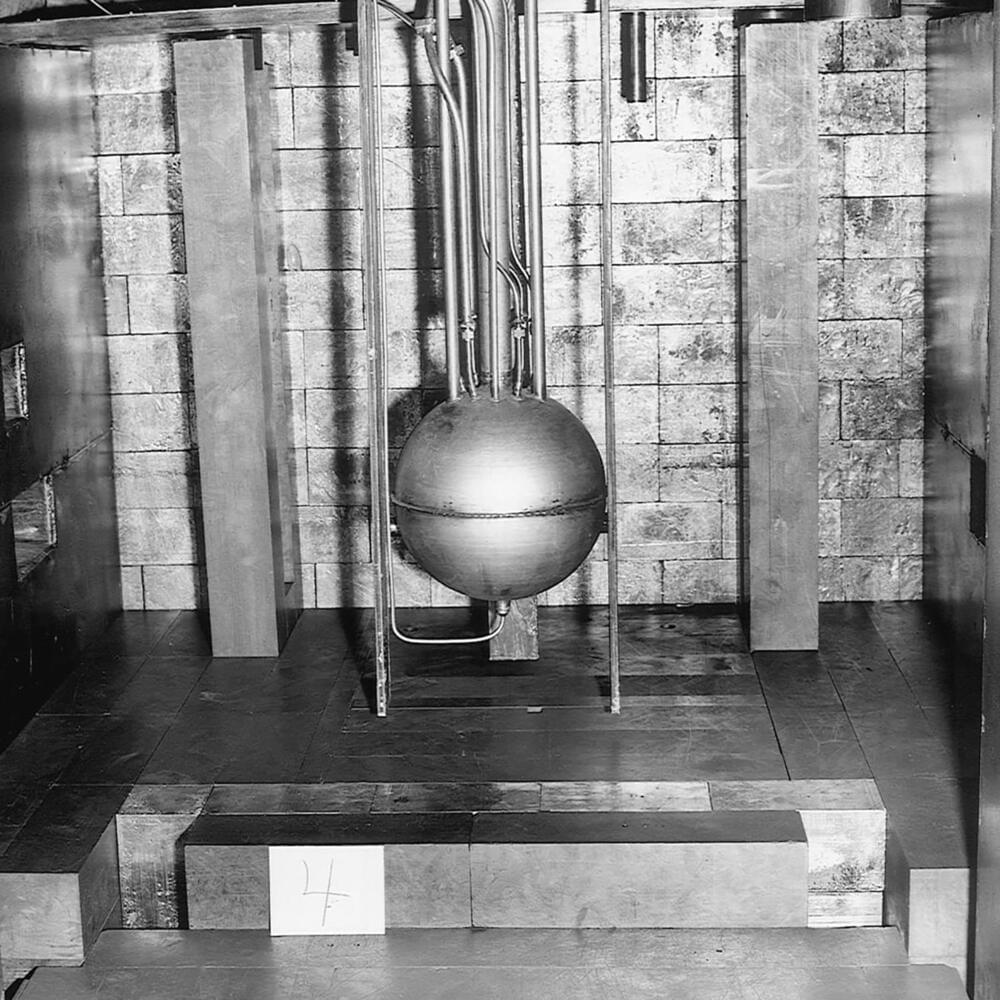

50-milliwatt Water Boiler reactor went critical at Los Alamos National Laboratory. It held about 20 ounces of uranium dissolved in a water-filled, 12-inch sphere. It was the first nuclear reactor to use enriched uranium, and the first critical assembly built at the lab.


Performed by Moxie — the Mars Oxygen In-Situ Resource Utilization Experiment — the strategy definitely incited hope for extraterrestrial survival. Future human missions could take versions of Moxie to Mars instead of carrying oxygen from Earth to sustain them.
But, Moxie is powered by a nuclear battery onboard.
“In the near future, we will see the crewed spaceflight industry developing rapidly,” said Yingfang Yao, a material scientist at Nanjing University.

The Facility for Rare Isotope Beams (FRIB) at Michigan State University (MSU) in East Lansing had a budget of $730 million, most of it funded by the US Department of Energy, with a $94.5 million contribution from the state of Michigan. MSU contributed an additional $212 million in various ways, including the land. It replaces an earlier National Science Foundation accelerator, called the National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory (NSCL), at the same site. Construction of FRIB started in 2014 and was completed late last year, “five months early and on budget”, says nuclear physicist Bradley Sherrill, who is FRIB’s science director.
For decades, nuclear physicists had been pushing for a facility of its power — one that could produce rare isotopes orders of magnitude faster than is possible with the NSCL and similar accelerators worldwide. The first proposals for such a machine came in the late 1980s, and consensus was reached in the 1990s. “The community was adamant that we need to get a tool like this,” says Witold Nazarewicz, a theoretical nuclear physicist and FRIB’s chief scientist.