Physicists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory and Stony Brook University (SBU) have shown that particles produced in collimated sprays called jets retain information about their origins in subatomic particle smashups. The study was recently published as an Editor’s Suggestion in the journal Physical Review Letters.
“Despite extensive research, the connection between a jet’s initial conditions and its final particle distribution has remained elusive,” said Charles Joseph Naim, a research associate at the Center for Frontiers in Nuclear Science (CFNS) in SBU’s Department of Physics and Astronomy. “This study, for the first time, establishes a direct connection between the ‘entanglement entropy’ at the earliest stage of jet formation and the particles that emerge as a jet evolves.”
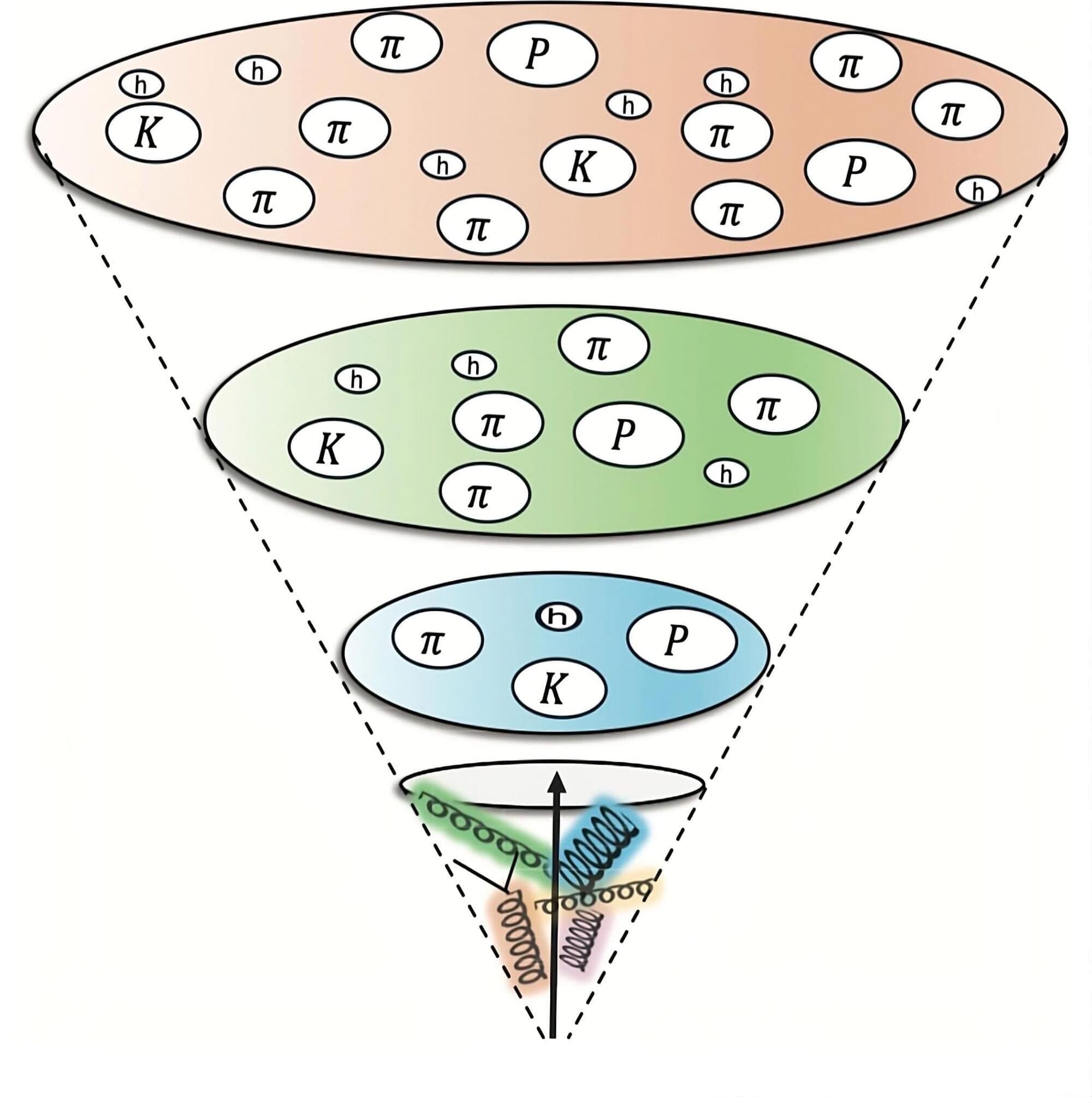
The evidence comes from an analysis of jet particles emerging from proton-proton collisions captured by the ATLAS experiment at the Large Hadron Collider, a 17-mile-circumference circular collider located at CERN, the European Organization for Nuclear Research. In these powerful collisions, the individual building blocks of the colliding protons, known as quarks and gluons, scatter off one another and sometimes get knocked free with enormous amounts of energy. But quarks can’t stay free for long. They and the gluons that normally hold them together immediately begin to split and reconnect through a branching process called fragmentation. The result is the formation of many new composite particles made of pairs or triplicates of quarks—collectively known as hadrons—that spray out of the collision in a coordinated way, that is, as a jet.