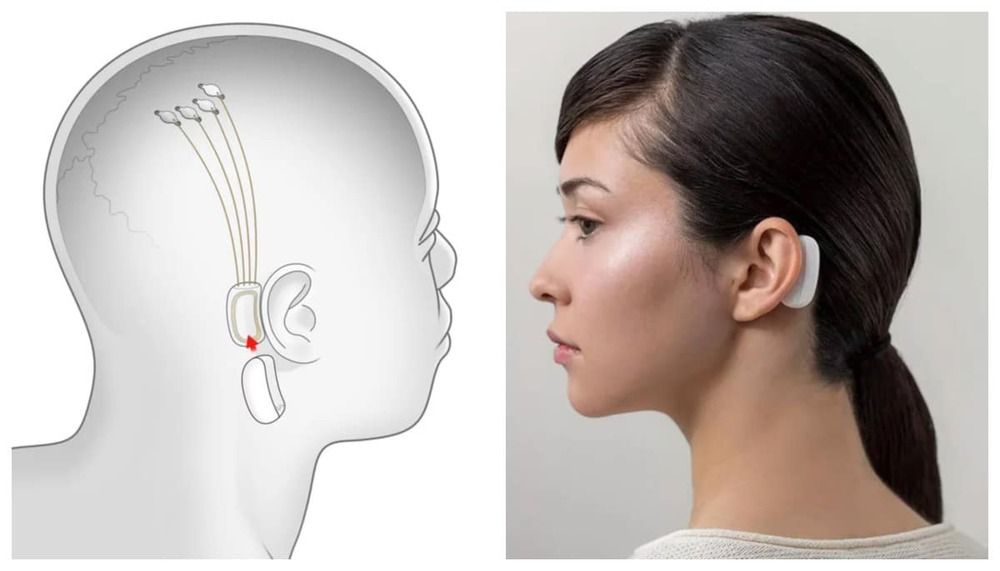
An American scientist is no longer able to see the digits two through nine. New research links this to a rare and degenerative brain condition.



Summary: Findings reveal individual differences in the severity of depressive symptoms following a relationship breakdown are associated with changes in resting-state whole-brain dynamics.
Source: UPF Barcelona
During a person’s life, the experience of a stressful life event can lead to the development of depressive symptoms, even in a non-clinical population. For example, a relationship breakup is a fairly common event and is a powerful risk factor for quality of life, in addition to increasing the risk of a major depressive disorder.
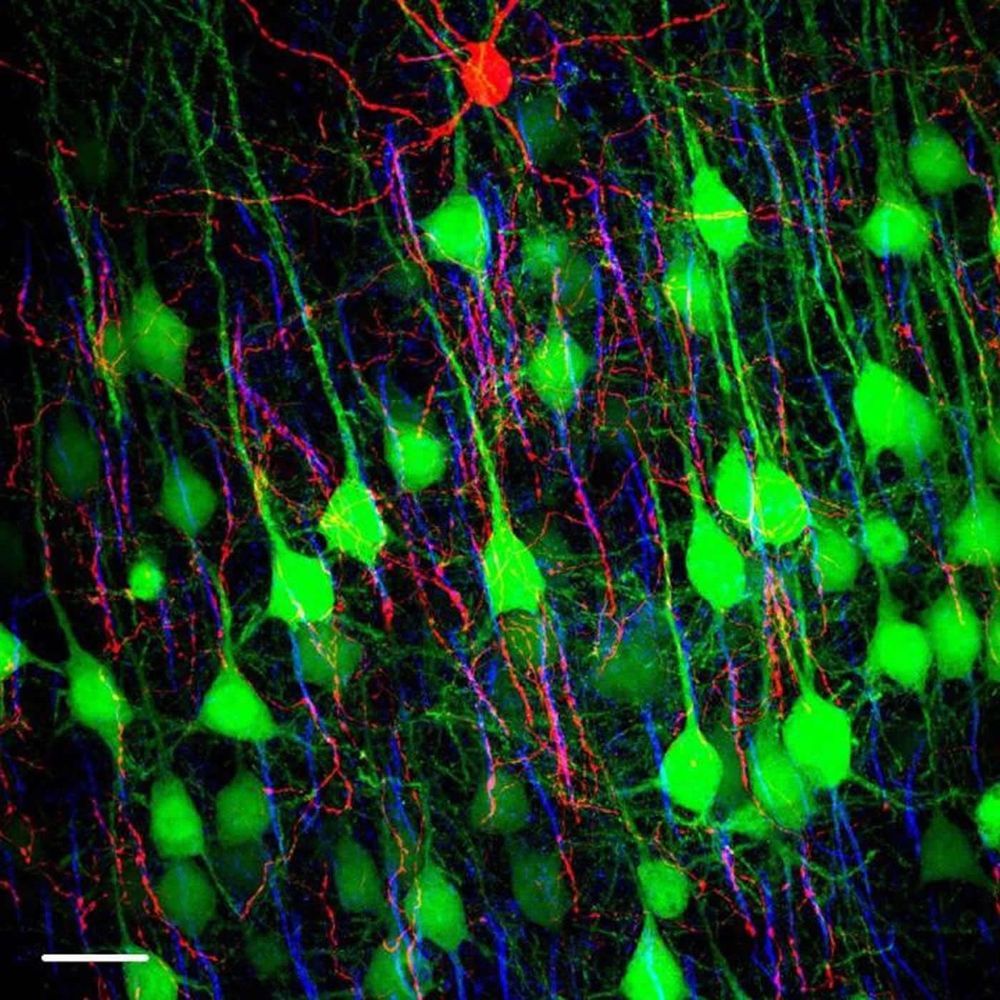
Summary: Chandelier cells have an unusual direct method of communication. Unlike other neurons, chandelier cells connect directly to the part of a target neuron that initiates a spike.
Source: CSHL
Within the intricate network of cells that make up the brain, chandelier cells stand out for their elaborate, branching structure. With an elegant shape similar to that of its namesake, a single chandelier cell reaches out to connect and communicate with more than 100 other neurons. Abnormalities in chandelier cells have been linked to epilepsy, autism, and schizophrenia, underscoring their critical role in keeping brain signaling in balance. However, these cells have been notoriously difficult to study as their numbers are few, so until recently, chandelier cells remained largely enigmatic.
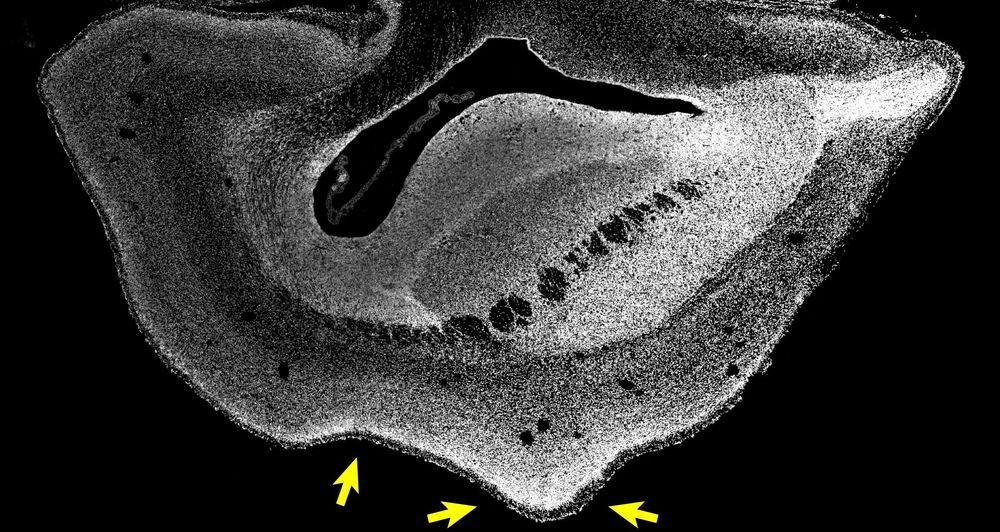
The expansion of the human brain during evolution, specifically of the neocortex, is linked to cognitive abilities such as reasoning and language. A certain gene called ARHGAP11B that is only found in humans triggers brain stem cells to form more stem cells, a prerequisite for a bigger brain. Past studies have shown that ARHGAP11B, when expressed in mice and ferrets to unphysiologically high levels, causes an expanded neocortex, but its relevance for primate evolution has been unclear.
Researchers at the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics (MPI-CBG) in Dresden, together with colleagues at the Central Institute for Experimental Animals (CIEA) in Kawasaki and the Keio University in Tokyo, both located in Japan, now show that this human-specific gene, when expressed to physiological levels, causes an enlarged neocortex in the common marmoset, a New World monkey. This suggests that the ARHGAP11B gene may have caused neocortex expansion during human evolution. The researchers published their findings in the journal Science.
The human neocortex, the evolutionarily youngest part of the cerebral cortex, is about three times bigger than that of the closest human relatives, chimpanzees, and its folding into wrinkles increased during evolution to fit inside the restricted space of the skull. A key question for scientists is how the human neocortex became so big. In a 2015 study, the research group of Wieland Huttner, a founding director of the MPI-CBG, found that under the influence of the human-specific gene ARHGAP11B, mouse embryos produced many more neural progenitor cells and could even undergo folding of their normally unfolded neocortex. The results suggested that the gene ARHGAP11B plays a key role in the evolutionary expansion of the human neocortex.
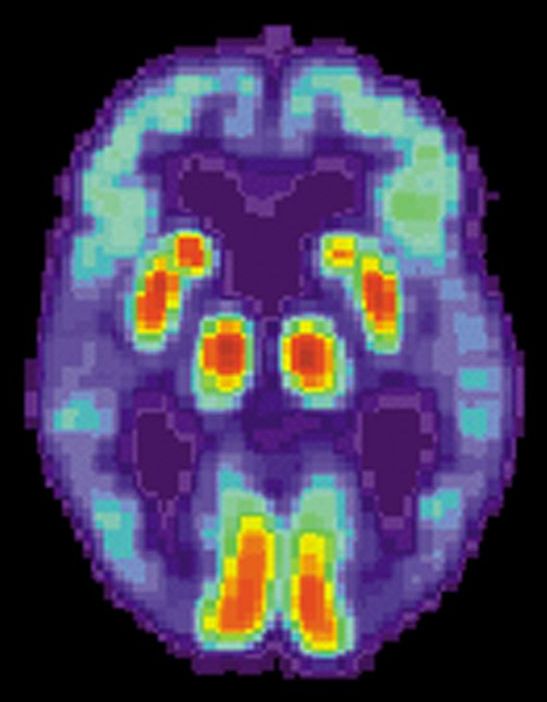
A new study by Florida State University researchers may help answer some of the most perplexing questions surrounding Alzheimer’s disease, an incurable and progressive illness affecting millions of families around the globe.
FSU Assistant Professor of Psychology Aaron Wilber and graduate student Sarah Danielle Benthem showed that the way two parts of the brain interact during sleep may explain symptoms experienced by Alzheimer’s patients, a finding that opens up new doors in dementia research. It is believed that these interactions during sleep allow memories to form and thus failure of this normal system in a brain of a person with Alzheimer’s disease may explain why memory is impaired.
The study, a collaboration among the FSU Program in Neuroscience, the University of California, Irvine, and the University of Lethbridge in Alberta, Canada, was published online in the journal Current Biology and will appear in the publication’s July 6 issue.

:ooooooo.
Superhero-like stretching capabilities aren’t just for Elastigirl. Researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology have come up with a new technology that can make any tissue sample exceptionally flexible.
ELAST technology (Entangled Link-Augmented Stretchable Tissue-hydrogel) is a chemical process that makes tissue samples very thin, very stretchy, compressible, and borderline indestructible. With it, lab technicians can more quickly and easily conduct fluorescent labeling in cells, proteins, or other genetic materials within organs like the brain or lungs. That, in turn, could enable faster research discoveries.
The MIT researchers published their work last month in the journal Nature Methods.

How does our memory work, and how can we optimize its mechanisms on a daily basis? These questions are at the heart of many neuroscience research projects. Among the brain structures examined to better understand memory mechanisms, the reward system is now at the center of investigations. Through the examination of brain activity in healthy human subjects, scientists from the University of Geneva (UNIGE) have highlighted the lasting positive effect of a reward—monetary, in this case—on the ability of individuals to retain a variety of information. Moreover, and much more surprisingly, the research team demonstrated that the average accumulation of reward should be neither too small nor too large. By ensuring an effective neural dialog between the reward circuit and the memory circuit, this delicate balance allows the proper encoding of memories in our brain. These results can be read in Nature Communications.
Empirically, it seems quite logical that obtaining a reward can improve the memories associated with it. But what are the brain mechanisms at work, and how can we exploit them to optimize our memory capacity?
“The positive influence of a reward on memory is a well-known phenomenon,” says Sophie Schwartz, full professor in the Department of Basic Neurosciences at the UNIGE Faculty of Medicine, who led this work. “However, our experiment aimed to take a further step in understanding this mechanism by looking at two important aspects: does the effect last over time and what role does the accumulation of reward play?”
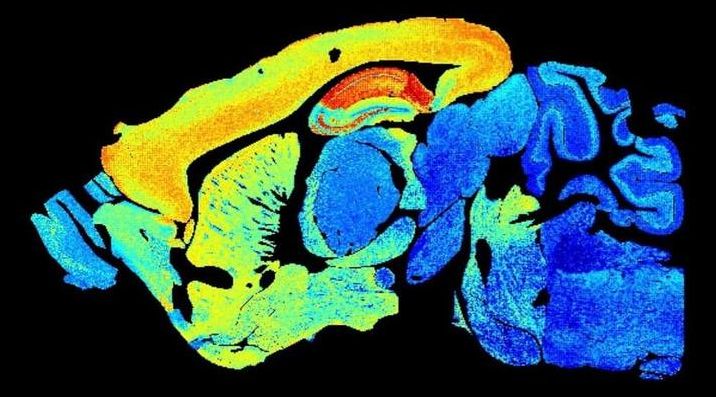
Just as our human relationships and connections can nudge, push, or dramatically shift societal values and consequences, the connections between neurons form intricate networks that dictate the outcome of your mind. Your thoughts, memories, behaviors; your values, world view, mental health—everything that makes you you is calculated and stored in these connections, called synapses, that dot our brains like billions of stars in the night sky.
If a connectome—a large-scale snapshot of all your neural connections—is a loose “copy” of you at one moment in time, synapses are a fluid representation of how you change and grow through time. Similar to human connections, synapses come in different varieties and evolve as we age. Yet until now, capturing how these synapses change as we move through time has been nearly impossible.
Last week, in a technological tour-de-force, a European team from the United Kingdom, France, and Sweden, led by Dr. Seth G.N. Grant at the University of Edinburgh, redefined impossibility with a paper in Science. Peering into the brains of mice at different ages—one day, one week, and all the way up to an elderly 18 months—the team constructed maps of roughly 5 billion synapses, outlining a timeline of their diversity and numbers in over 100 different brain regions with age.