A total of 5,726 participants had their memory tested. Out of the 24 substances that were assessed for improving memory, these are the 5 most promising nootropics.


The researchers, Prof. Itamar Kahn of the Technion’s Rappaport Faculty of Medicine in Israel and Prof. Nancy Ratner of Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center (CCHMC), claimed that such a breakthrough demonstrates a potential new treatment for cognitive damages in the brain white matter, the areas of the central nervous system.
“The participants treated with AMX0035 demonstrated a significant slowing of ALS disease progression as measured by the ALSFRS-R. This is a milestone in our fight against ALS,” said Sabrina Paganoni, MD, Ph.D., principal investigator of the CENTAUR study.
An experimental medication slows the progression of the neurodegenerative disease called Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), or Lou Gehrig’s disease, according to recently released results from a clinical trial run by investigators at the Sean M. Healey & AMG Center for ALS at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and Amylyx Pharmaceuticals, Inc., the company that manufactures the medication. The findings, reported in the New England Journal of Medicine, offer hope that a treatment may one day be available for patients with ALS, a fatal condition with no cure that attacks the nerve cells in the brain and the spinal cord to progressively hinder individuals’ ability to move, speak, eat, and even breathe.
Called AMX0035, the oral medication is a combination of two drugs, sodium phenylbutyrate and taurursodiol, that each target a different cell component important for protecting against nerve cell death.
In the CENTAUR trial, 137 participants with ALS were randomized in a two-toone ratio to receive AMX0035 or placebo. Over six months, participants who were treated with AMX0035 had better functional outcomes than those treated with placebo as measured by the ALS Functional Rating Scale (ALSFRS-R), a questionnaire that evaluates several activities of daily living such as a patient’s ability to walk, hold a pen or swallow food.

Electrons may have some type of extremely rudimentary mind.
While there are many versions of panpsychism, the version I find appealing is known as constitutive panpsychism. It states, to put it simply, that all matter has some associated mind or consciousness, and vice versa. Where there is mind there is matter and where there is matter there is mind. They go together. As modern panpsychists like Alfred North Whitehead, David Ray Griffin, Galen Strawson, and others have argued, all matter has some capacity for feeling, albeit highly rudimentary feeling in most configurations of matter.
Panpsychists look at the many rungs on the complexity ladder of nature and see no obvious line between mind and no-mind. Philosopher Thomas Nagel famously asked in 1974 what is it like to be a bat, to echolocate and fly? We can’t know with any certainty, but we can reasonably infer, based on observation of their complex behaviors and the close genetic kinship between all mammals and humans—and the fact that evolution proceeds incrementally—that bats have a rich inner life. By the same logic, we can look steadily at less-complex forms of behavior that allow us to reasonably infer some kind of mind associated with all types of matter. Yes, including even the lowly electron.
Worldwide, 800,000 people die annually due to suicide (1 every 40 seconds) — There are more than twice as many suicides as homicides — Suicide is now the 10th leading cause of death in the US, and the 2nd leading cause of death among individuals between ages of 10 and 34 — Dr. Christine Moutier, M.D., Chief Medical Officer, American Foundation for Suicide Prevention, joins me on ideaXme to discuss her organization’s work in suicide prevention science and impacting these disturbing trends — #Ideaxme #Suicide #Depression #MentalHealth #Psychiatry #Anxiety #Stress #Trauma #Coronavirus #Burnout #WellBeing #Resilience #Health #Wellness #Longevity #Aging #IraPastor #Bioquark #Regenerage National Institute of Mental Health National Academy of Medicine.
Ira Pastor, ideaXme life sciences ambassador and founder of Bioquark, interviews Dr. Christine Moutier, MD, Chief Medical Officer, at the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention (AFSP).
Ira Pastor comments:
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), close to 800,000 people die due to suicide every year, which is one person every 40 seconds. Suicide is a global phenomenon and occurs throughout the lifespan, and there are indications that for each adult who died by suicide, there may have been more than 20 others attempting suicide.
According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) “Leading Causes of Death Report”, in 2017 suicide was the tenth leading cause of death overall in the United States, claiming the lives of over 47,000 people; Suicide was the second leading cause of death among individuals between the ages of 10 and 34, and the fourth leading cause of death among individuals between the ages of 35 and 54. There were more than twice as many suicides in the United States as there were homicides.
The brain is an inherently dynamic system, and much work has focused on the ability to modify neural activity through both local perturbations and changes in the function of global network ensembles. Network controllability is a recent concept in network neuroscience that purports to predict the influence of individual cortical sites on global network states and state changes, thereby creating a unifying account of local influences on global brain dynamics. While this notion is accepted in engineering science, it is subject to ongoing debates in neuroscience as empirical evidence linking network controllability to brain activity and human behavior remains scarce. Here, we present an integrated set of multimodal brain–behavior relationships derived from fMRI, diffusion tensor imaging, and online repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) applied during an individually calibrated working memory task performed by individuals of both sexes. The modes describing the structural network system dynamics showed direct relationships to brain activity associated with task difficulty, with difficult-to-reach modes contributing to functional brain states in the hard task condition. Modal controllability (a measure quantifying the contribution of difficult-to-reach modes) at the stimulated site predicted both fMRI activations associated with increasing task difficulty and rTMS benefits on task performance. Furthermore, fMRI explained 64% of the variance between modal controllability and the working memory benefit associated with 5 Hz online rTMS. These results therefore provide evidence toward the functional validity of network control theory, and outline a clear technique for integrating structural network topology and functional activity to predict the influence of stimulation on subsequent behavior.
SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT The network controllability concept proposes that specific cortical nodes are able to steer the brain into certain physiological states. By applying external perturbation to these control nodes, it is theorized that brain stimulation is able to selectively target difficult-to-reach states, potentially aiding processing and improving performance on cognitive tasks. The current study used rTMS and fMRI during a working memory task to test this hypothesis. We demonstrate that network controllability correlates with fMRI modulation because of working memory load and with the behavioral improvements that result from a multivisit intervention using 5 Hz rTMS. This study demonstrates the validity of network controllability and offers a new targeting approach to improve efficacy.
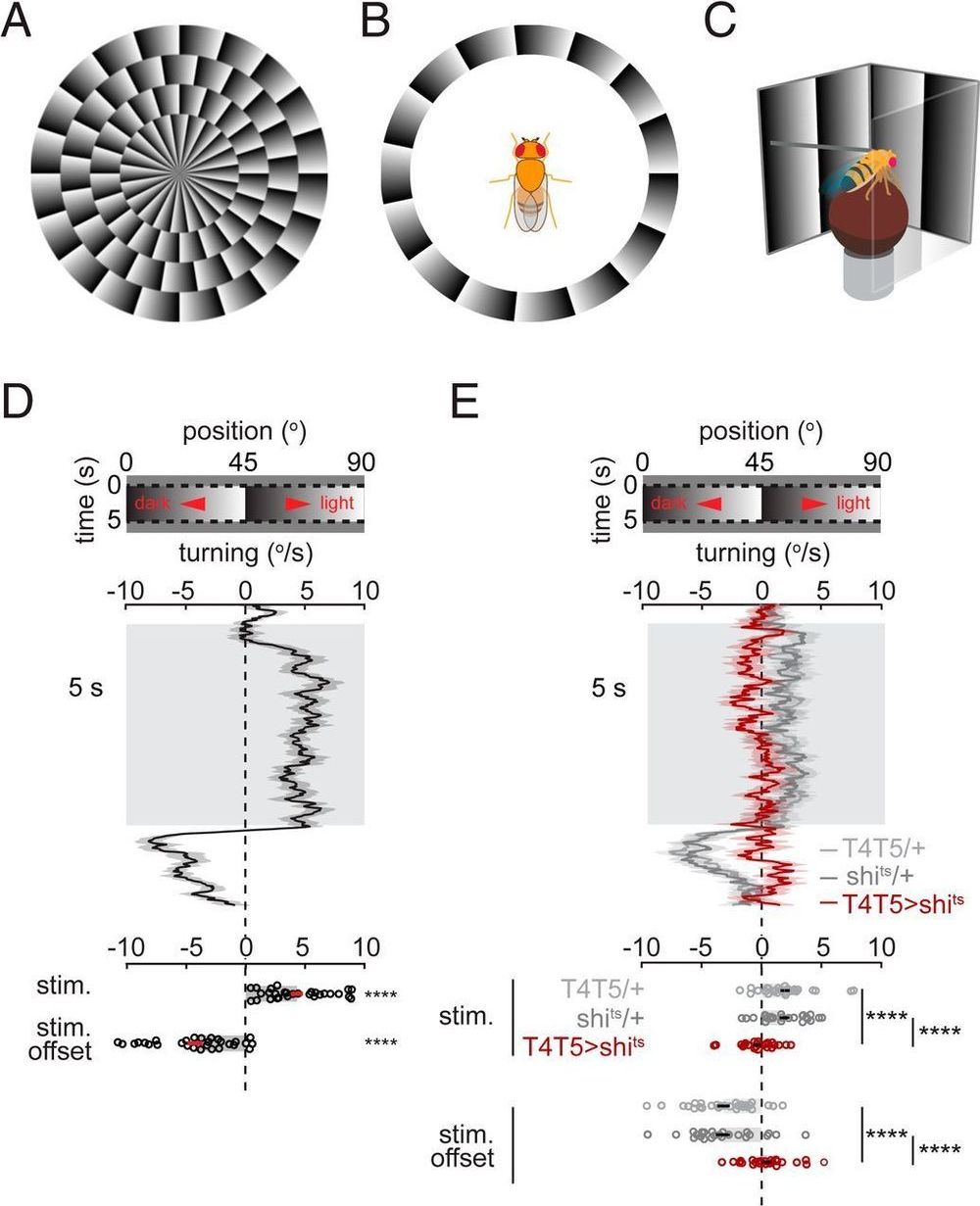
Most of the time, visual circuitry in our brains faithfully reports visual scenes. Sometimes, however, it can report motion in images that are in fact stationary, leading us to perceive illusory motion. In this study, we establish that fruit flies, too, perceive motion in the stationary images that evoke illusory motion in humans. Our results demonstrate how this motion illusion in flies is an artifact of the brain’s strategies for efficiently processing motion in natural scenes. Perceptual tests in humans suggest that our brains may employ similar mechanisms for this illusion. This study shows how illusions can provide insight into visual processing mechanisms and principles across phyla.
Visual motion detection is one of the most important computations performed by visual circuits. Yet, we perceive vivid illusory motion in stationary, periodic luminance gradients that contain no true motion. This illusion is shared by diverse vertebrate species, but theories proposed to explain this illusion have remained difficult to test. Here, we demonstrate that in the fruit fly Drosophila, the illusory motion percept is generated by unbalanced contributions of direction-selective neurons’ responses to stationary edges. First, we found that flies, like humans, perceive sustained motion in the stationary gradients. The percept was abolished when the elementary motion detector neurons T4 and T5 were silenced. In vivo calcium imaging revealed that T4 and T5 neurons encode the location and polarity of stationary edges.
In a recent study conducted in mice, researchers became one step closer to that understanding, discovering that exercise actually strengthens the brain’s resilience to stress. Exercise helps animals cope with stress by enabling an uptick in a crucial neural protein called galanin, the study suggests. This process influences stress levels, food consumption, cognition, and mood.
Leveraging this finding, researchers were able to genetically tweak even sedentary mice’s levels of galanin, shifts that lowered their anxious response to stress.
The study’s authors explain that this study helps pin down the biological mechanisms driving exercise’s positive effects on stress. While further human experiments are needed to confirm these findings, the researchers have practical advice for people looking to get these benefits: perform regular, aerobic exercise.

But U.S. is not the only country engaged in human enhancement and transhumanism, as Russia and China are also in hot pursuit with exoskeletons, vaccines and brain implants. As this competition gains traction, one wonders what the future of their militaries may look like as human beings are steadily integrated with machines to become armies of iron man.
From the blog of Christina Lin at The Times of Israel.