To capture the information that a brain contains, you need to cut it into billions and billions of slices.
Category: neuroscience – Page 830
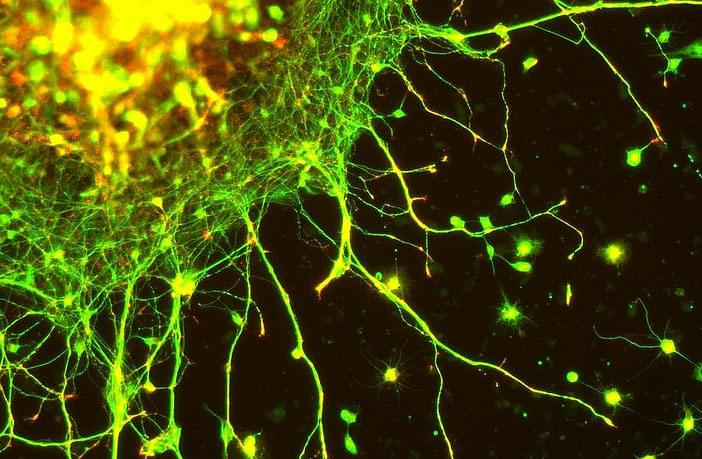
Lab-grown mini-brains could help find treatments for Alzheimer’s and other diseases
To assess whether a compound holds promise for treating a disease, researchers usually begin by studying its use in animals. This allows us to see if the compound has a chance of curing the disease.
Animal models, however, rarely reproduce all aspects of a disease. The alternative is to represent the disease in cell cultures. While at first glance, Petri dishes look quite different from a person with a disease, the reality could be quite different when you look at them more closely.
Alzheimer’s has been cured more than 400 times in laboratories. How then can we still consider Alzheimer’s to be incurable? The reason is that it has only been cured in animals.
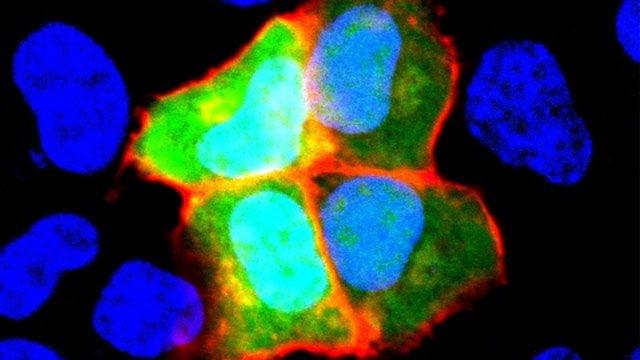
Team Identifies Autoantibody That May Cause Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a disorder that affects how people act, think, and perceive reality. It is often very difficult to treat because it has many different causes and symptoms. In a study published last month in Cell Reports Medicine, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) have identified an autoantibody—a protein that is produced by the immune system to attach to a specific substance from the individual’s own body, rather than to a foreign substance like a virus or bacteria—in some patients with schizophrenia. Notably, they also found that this autoantibody caused schizophrenia-like behaviors and changes in the brain when they injected it into mice.
When considering possible autoantibodies that might cause schizophrenia, the research team had a specific protein in mind. Previous research has suggested that neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM1), which helps cells in the brain talk to one another via specialized connections known as synapses, may have a role in the development of schizophrenia.
“We decided to look for autoantibodies against NCAM1 in around 200 healthy controls and 200 patients with schizophrenia,” explains lead author of the study Hiroki Shiwaku. “We only found these autoantibodies in 12 patients, suggesting that they may be associated with the disorder in just a small subset of schizophrenia cases.”
Scientists Discover That the Human Brain Works in 11 Dimensions
A group of photonics researchers at Tampere University have introduced a novel method to control a light beam with another beam through a unique plasmonic metasurface in a linear medium at ultra-low power. This simple linear switching method makes nanophotonic devices such as optical computing and communication systems more sustainable, requiring low intensity of light.
Quantum information was teleported over a network for the first time
When Heroes (now streaming on Peacock!) hit the airwaves in September of 2006, few characters were as immediately beloved as the appropriately named Hiro Nakamura. Granted the ability to manipulate space-time, Hiro could not only slow down, speed up, and stop time, he could also teleport from one place to another. That’s a useful skill if you need to get to a specific point in time and space to fight an evil brain surgeon or prevent the end of the world. It’s also useful if you want to build the quantum internet.
Researchers at QuTech — a collaboration between Delft University of Technology and the Netherlands Organization for Applied Scientific Research — recently took a big step toward making that a reality. For the first time, they succeeded in sending quantum information between non-adjacent qubits on a rudimentary network. Their findings were published in the journal Nature.
While modern computers use bits, zeroes, and ones, to encode information, quantum computers us quantum bits or qubits. A qubit works in much the same way as a bit, except it’s able to hold both a 0 and a 1 at the same time, allowing for faster and more powerful computation. The trouble begins when you want to transmit that information to another location. Quantum computing has a communications problem.
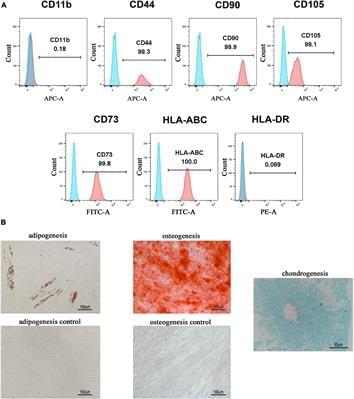
Transplantation of Human Gingiva-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ameliorates Neurotic Erectile Dysfunction in a Rat Model
Circa 2021 Immortality of the male genitalia in humans.
Cavernous nerve injury (CNI) is the main cause of erectile dysfunction (ED) following pelvic surgery. Our previous studies have demonstrated that transplantation of different sources of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) was able to alleviate ED induced by CNI in rat models. However, little is known about the therapeutic effects of human gingiva-derived MSCs (hGMSCs) in CNI ED rats. Herein, we injected the hGMSCs around the bilateral major pelvic ganglia (MPG) in a rat model of CNI and evaluated their efficacy. The results showed that treatment of hGMSCs could significantly promote the recovery of erectile function, enhance smooth muscle and endothelial content, restore neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) expression, and attenuate cell apoptosis in penile tissue. Moreover, penile fibrosis was significantly alleviated after hGMSC administration. In addition, potential mechanism exploration indicated that hGMSCs might exert its functions via skewed macrophage polarity from M1 toward M2 anti-inflammatory phenotype. In conclusion, this study found that transplantation of hGMSCs significantly improved CNI-related ED, which might provide new clues to evaluate their pre-clinical application.
There are many causes of erectile dysfunction (ED), which include psychological factors, neurological disorders (such as multiple sclerosis, temporal lobe epilepsy, and cavernous nerve injury), and vasculogenic disorders (such as atherosclerosis, hypertension, and diabetes mellitus). Neurogenic sexual dysfunction makes up about 10–19% in all causes of erectile dysfunction. Neurotic erectile dysfunction is one of most important complications after radical prostatectomy and rectectomy, owing to intraoperative damage of the pelvic cavernous nerve (CN). It affects not only the physical but also mental health in postoperative patients. Despite the improvement of nerve-sparing techniques, the incidence of neurotic ED still has no substantial improvement. The incidences of ED range from 75 to 80% after pelvic surgery (Schauer et al., 2015).
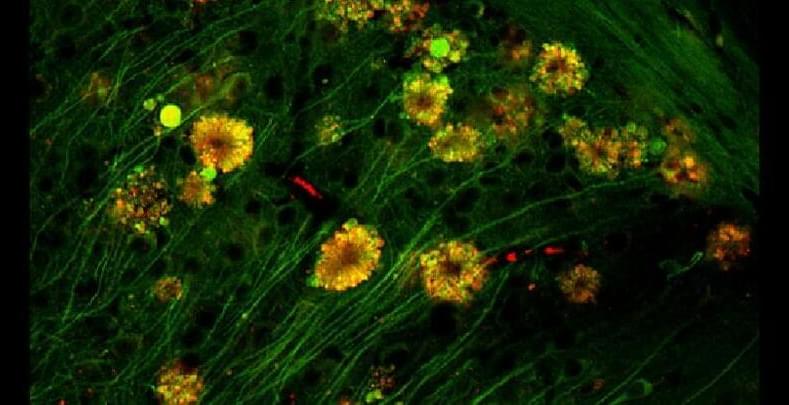
Neural ‘Poisonous Flowers’ Could Be The Source of Alzheimer’s Plaque, Says Study
Alzheimer’s disease has long thwarted our best efforts to pinpoint its underlying causes. Now, a new study in mice suggests that ‘poisonous flowers’ bulging with cellular debris could be the root source of one hallmark of the wretched disease and a beautifully sinister sign of a failing waste disposal system inside damaged brain cells.
The study, led by neuroscientist Ju-Hyun Lee of New York University (NYU) Langone, challenges the long-standing idea that the build-up of a protein called amyloid-beta between neurons is a crucial first step in Alzheimer’s disease, the most common form of dementia.
Instead, it suggests that damage to neurons may take root inside cells well before amyloid plaques fully form and clump together in the brain, a finding which could provide new therapeutic possibilities.

