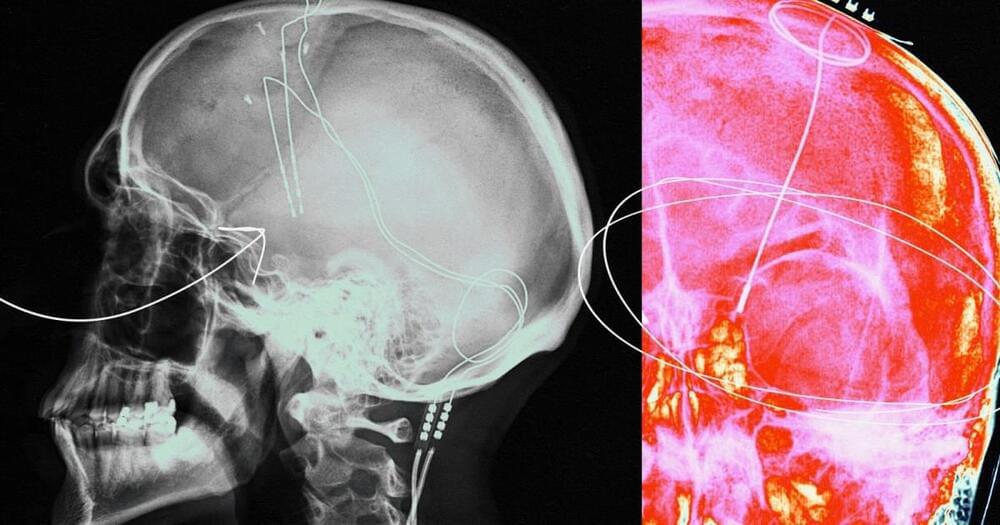
Thanks in part to Elon Musk, the field of brain-computer interfaces has captured both public and investor interest, with a cadre of companies now developing implantable devices.


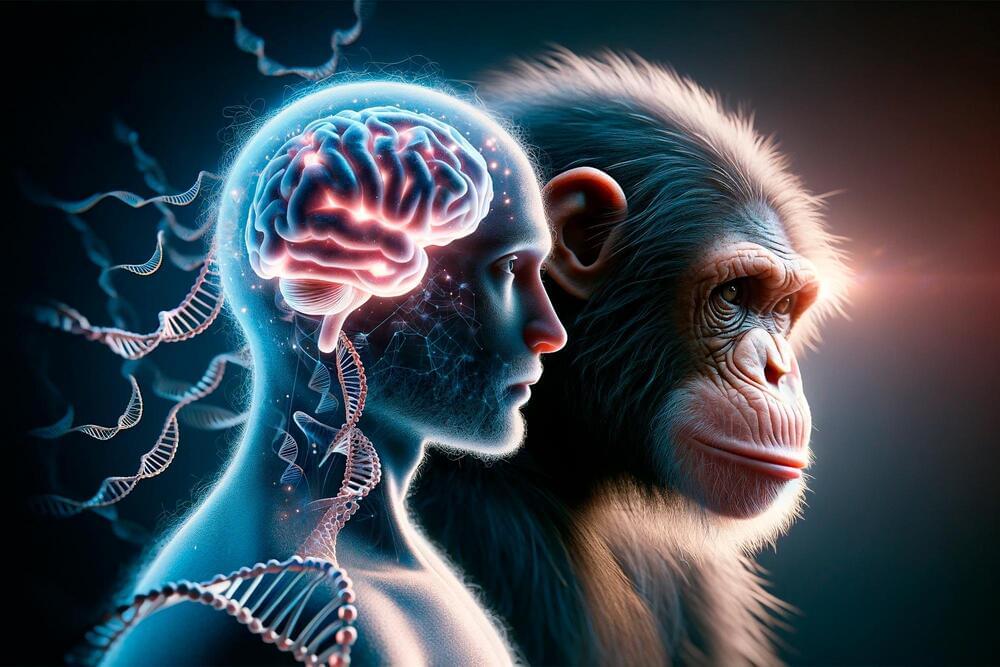
The researchers found 139 genes that are common across the primate groups but highly divergent in their expression in human brains.
An international team led by researchers at the University of Toronto has uncovered over 100 genes that are common to primate brains but have undergone evolutionary divergence only in humans – and which could be a source of our unique cognitive ability.
The researchers, led by Associate Professor Jesse Gillis from the Donnelly Centre for Cellular and Biomolecular Research and the Department of Physiology at U of T’s Temerty Faculty of Medicine, found the genes are expressed differently in the brains of humans compared to four of our relatives – chimpanzees, gorillas, macaques, and marmosets.
Facing an alcohol crisis, the US sees 12% of adult deaths linked to abuse. Excessive drinking risks permanent brain damage, Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome. Symptoms mimic drunkenness and can lead to irreversible psychosis. Prevention? Cut back or quit. Concerned? Seek medical advice for potential Vitamin B1 treatment.

Spontaneous behavior in different individuals can be decomposed and understood using a relatively small number of neurobehavioral modules—the compositional modes—and elucidate a compositional neural basis of behavior.\
This video is part of the SNAC seminar series organized by Mac Shine, Joe Lizier, Ben Fulcher, and Eli Muller (The University of Sydney).

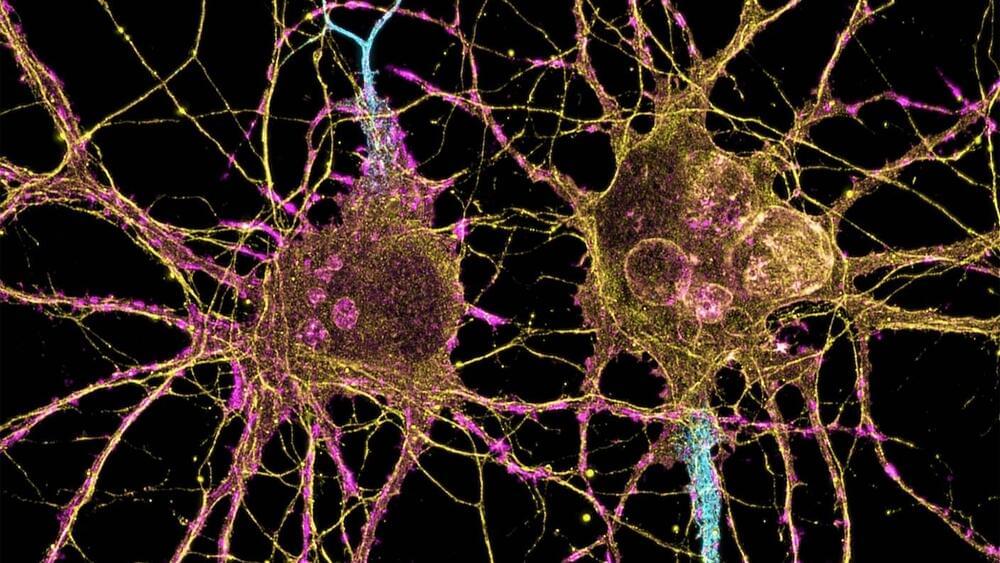
A team of researchers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst has developed the first dual-color optoelectronic neural probe.
Unlike previous, single probes, which often control brain activity in only one direction—excitation or inhibition, but not both—this new design can enhance and silence the electrical activities of the same neurons within specific cortical layers of the brain. It promises aid the investigation of tightly packed neural microcircuits within the cortex and deep brain regions and, in the longer term, add to the functional mapping of the brain.
Guangyu Xu, assistant associate professor of electrical and computer engineering, an appointee of the Dev and Linda Gupta Professorship at UMass Amherst, and principal investigator of the study hopes the device can ultimately help researchers identify the origin of brain diseases.

For many people struggling with obesity, the drug is a potential lifesaver. Excess weight is associated with higher incidences of stroke, heart and liver disease, sleep apnea, joint problems, and some cancers. A major clinical trial this year in tens of thousands of overweight people without diabetes found the main ingredient in Ozempic, semaglutide, reduced the risk of stroke and heart attack, while lowering the chances of death due to cardiovascular problems.
Perhaps even more importantly, the drug is gradually changing societal views on obesity—it’s not due to lack of will power, but a chronic medical condition that can be treated.
But Ozempic and similar drugs—like Wegovy, another semaglutide-based medication that has been FDA-approved for weight loss—are already set for the next chapter: tackling a wide range of brain disorders, including Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Clinical trials are underway for addiction, and the drugs are showing early promise battling bipolar disorder and depression.