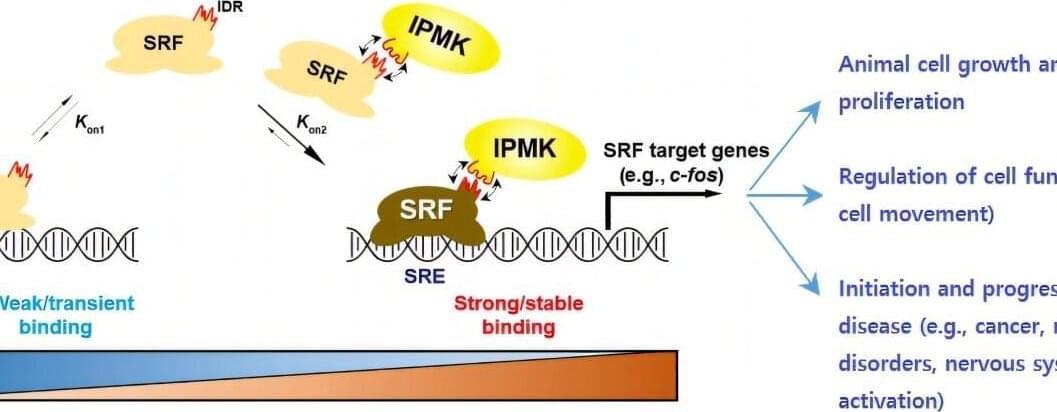
Though the notion of the supernatural has captivated humanity across continents and centuries, the most compelling path to explaining such mysteries may reside in the fundamental operations of nature itself. The premise that there is no realm beyond the natural order underpins the hypothesis that any genuine paranormal or spiritual phenomenon, if it exists, must be quantum in character. On the surface, this sounds audacious: quantum theory is already widely deemed one of the most counterintuitive scientific frameworks, replete with superpositions, entanglement, and the undeniable role of altering reality via measurement. Yet these very features seem to provide the most plausible scaffolding upon which experiences such as extrasensory perception (ESP), clairvoyance, telepathy, contact with disembodied spirits, psychokinesis, reincarnation, or even a continuation of existence in an afterlife, could be built.
Those who have conducted painstaking investigations into alleged parapsychological happenings often begin with the simplest question: Can these events be rigorously documented? The Princeton Engineering Anomalies Research (PEAR) program endeavored to place mind–machine interactions under stringent laboratory conditions for more than two decades, testing whether human intention could alter random-event generators. Their experimental data reported “small but consistent deviations from expected outputs” (Jahn & Dunne, 1987, p. 45). Mainstream critics rightly pointed to the difficulty of reconciling such deviations with known physics. However, these critics also noted that if the data were taken at face value, the underlying mechanism could only be teased out by exploring deeper layers of reality that engage both mind and matter — precisely the realm where quantum theory holds sway.
As we delve further into the annals of psychical research, Dean Radin’s contributions provide an illuminating guide. In The Conscious Universe: The Scientific Truth of Psychic Phenomena, Radin (1997) summarizes meta-analyses across thousands of trials testing telepathy, clairvoyance, and precognition. He concludes that “if psi is real, then we will see small but systematic deviations from chance expectations across many studies” (p. 136). Over and over, this is what he reports. Conventional interpretations falter, but an appeal to quantum processes — whose probabilistic nature might be subtly influenced by consciousness — begins to feel less like arcane speculation and more like a coherent, if daring, hypothesis.