A study of thousands of people finds that neural connections in the brain start to break down quickly around age 44, but the research hints that ketone supplements could potentially help slow that brain aging.

Researchers from the German Primate Center—Leibniz Institute for Primate Research and the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics have discovered two specific genes that evolve exclusively in humans jointly influence the development of the cerebrum. They have thus provided evidence that these genes contribute together to the evolutionary enlargement of the brain.
The work has been published in Science Advances.
The results show that the two genes act in a finely tuned interplay: one ensures that the progenitor cells of the brain multiply more, while the other causes these cells to transform into a different type of progenitor cell—the cells that later form the nerve cells of the brain. In the course of evolution, this interplay has led to the human brain being unique in its size and complexity.
Everything the brain does—from storing memories to interpreting sights to regulating emotions—requires energy, all produced by cellular organelles called mitochondria.
However, surprisingly little is known about the distribution and diversity of the brain’s tiny energy processors and how they influence brain health. For instance, how many mitochondria does the brain have? Are they uniformly distributed across the whole brain? Are all brain mitochondria the same? Do changes in the brain’s mitochondria affect mood, cognition, and the development of neurological and psychiatric conditions?
To begin answering these and other questions, Columbia University researchers have created MitoBrainMap, the first-ever atlas of the brain’s mitochondria.
Changes in the heart might mean more than just cardiovascular risk – they could also signal early shifts in brain health.
A large meta-analysis found that even subtle heart problems, like issues with how the heart pumps or relaxes, are linked to smaller brain volumes, particularly in areas related to memory.
Heart Issues May Signal Early Dementia Risk.

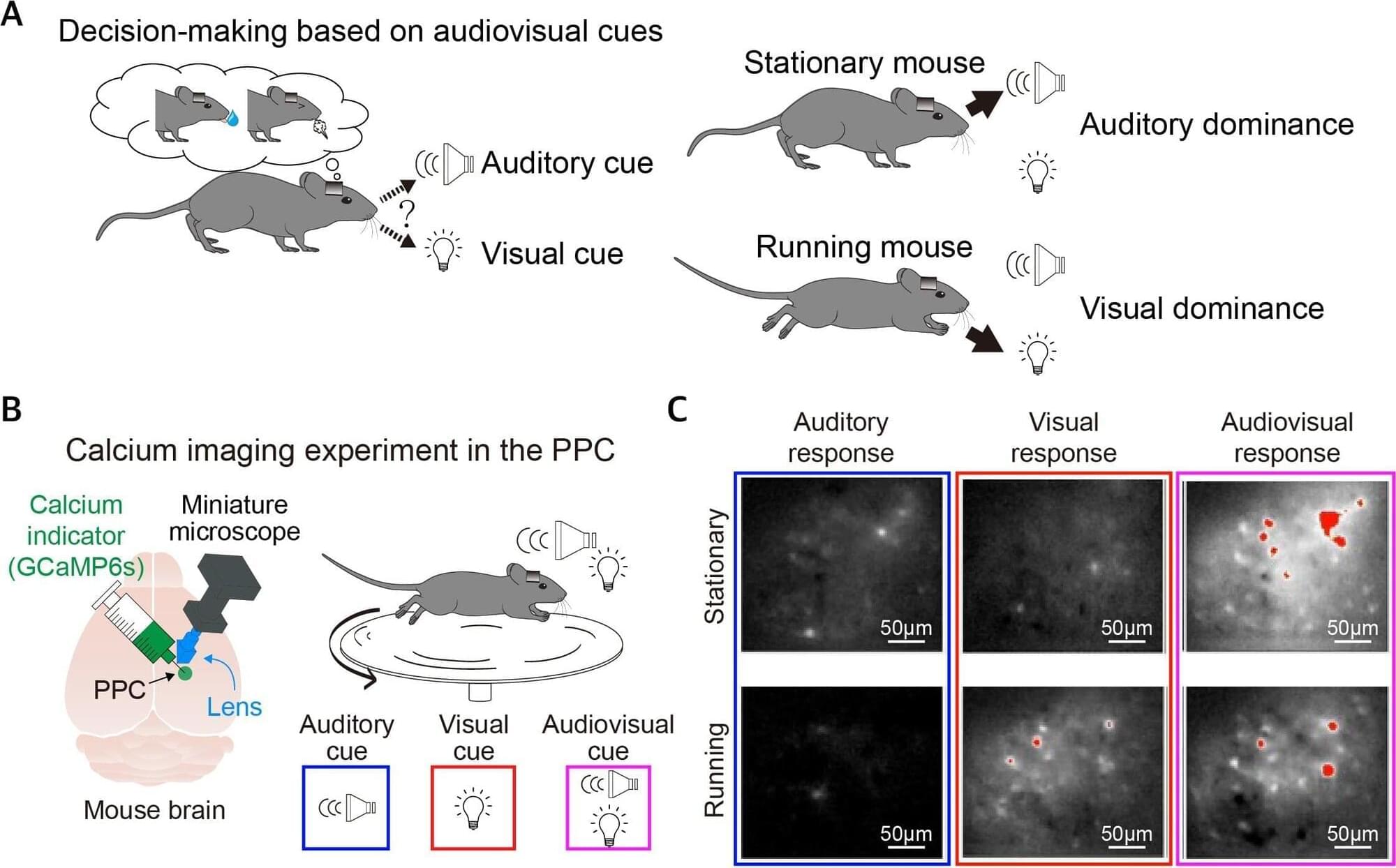
A research team at the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) has uncovered a fundamental principle of how the brain prioritizes vision and hearing differently depending on whether we are still or in motion. The study, led by Dr. Lee Seung-Hee, Associate Director of the IBS Center for Synaptic Brain Dysfunctions and Associate Professor at KAIST, provides new insights into how movement alters the brain’s sensory decision-making process.
In daily life, we constantly process visual (sight) and auditory (sound) information to navigate the world. For instance, when watching a movie, our brain seamlessly integrates images and sounds to create a complete experience. However, when moving—such as when walking on a busy street—our brain may prioritize visual information over sound.
Until now, it was unclear how the brain decides which sense to prioritize in different situations. This is particularly relevant for individuals with sensory processing disorders such as autism or schizophrenia, where the brain may struggle to integrate sensory information correctly. Understanding how the brain naturally shifts between sensory inputs could lead to better treatments for these conditions.
By way of an answer, I’ll offer one of the physicist Richard Feynman’s most famous dictums: What I cannot create, I do not understand. For much of its history, biology has been a reductionist science, driven by the principle that the best way to understand the mind-boggling complexity of living things is to dissect them into their constituent parts—organs, cells, proteins, molecules. But life isn’t a clockwork; it’s a dynamic system, and unexpected things emerge from the interactions between all those little parts. To truly understand life, you can’t just break it down. You have to be able to put it back together, too.
The C. elegans nematode is a tiny worm, barely as long as a hair is wide, with less than a thousand cells in its body. Of those, only 302 are neurons—about as small as a brain can get. “I remember, when my first child was born, how proud I was when they reached the age they could count to 302,” said Netta Cohen, a computational neuroscientist who runs a worm lab at the University of Leeds. But there’s no shame in smallness, Cohen emphasized: C. elegans does a lot with a little. Unlike its more unpleasant cousins, it’s not a parasite, outsourcing its survival needs to bigger organisms. Instead, it’s what biologists call a “free-living” animal. “It can reproduce, it can eat, it can forage, it can escape,” Cohen said. “It’s born and it develops, and it ages and it dies—all in a millimeter.”
Worm people like Cohen are quick to tell you that no fewer than four Nobel Prizes have been awarded for work on C. elegans, which was the first animal to have both its genome sequenced and its neurons mapped. But there’s a difference between schematics and an operating manual. “We know the wiring; we don’t know the dynamics,” Cohen said. “You would think that’s an ideal problem for a physicist or a computer scientist or a mathematician to solve.”


The term “memorability” refers to the likelihood that a particular stimulus, such as an object, face or sound, will be remembered by those exposed to it. Over the past few years, some psychology studies have been exploring the extent to which some stimuli are intrinsically more memorable than others, or in other words, whether people are generally more likely to remember them compared to other stimuli of the same type.
Researchers at the University of Chicago recently set out to specifically investigate the memorability of voices. Their findings, published in Nature Human Behaviour, suggest that some voices are more memorable than others and their memorability can be consistently predicted across different listeners.
“Research on intrinsic memorability—the consistencies in what people remember and forget—is a fairly new but active area of cognitive psychology,” Cambria Revsine, first author of the paper, told Medical Xpress. “Many studies from our lab and others have extensively explored this phenomenon over the past decade, finding that participants tend to remember the same images of faces, scenes, objects, and much more. However, no prior study to our knowledge has investigated the memorability of auditory stimuli.”