Increased serotonin in the gut epithelium is anxiolytic and anti-depressive which is mediated through vagal signaling.


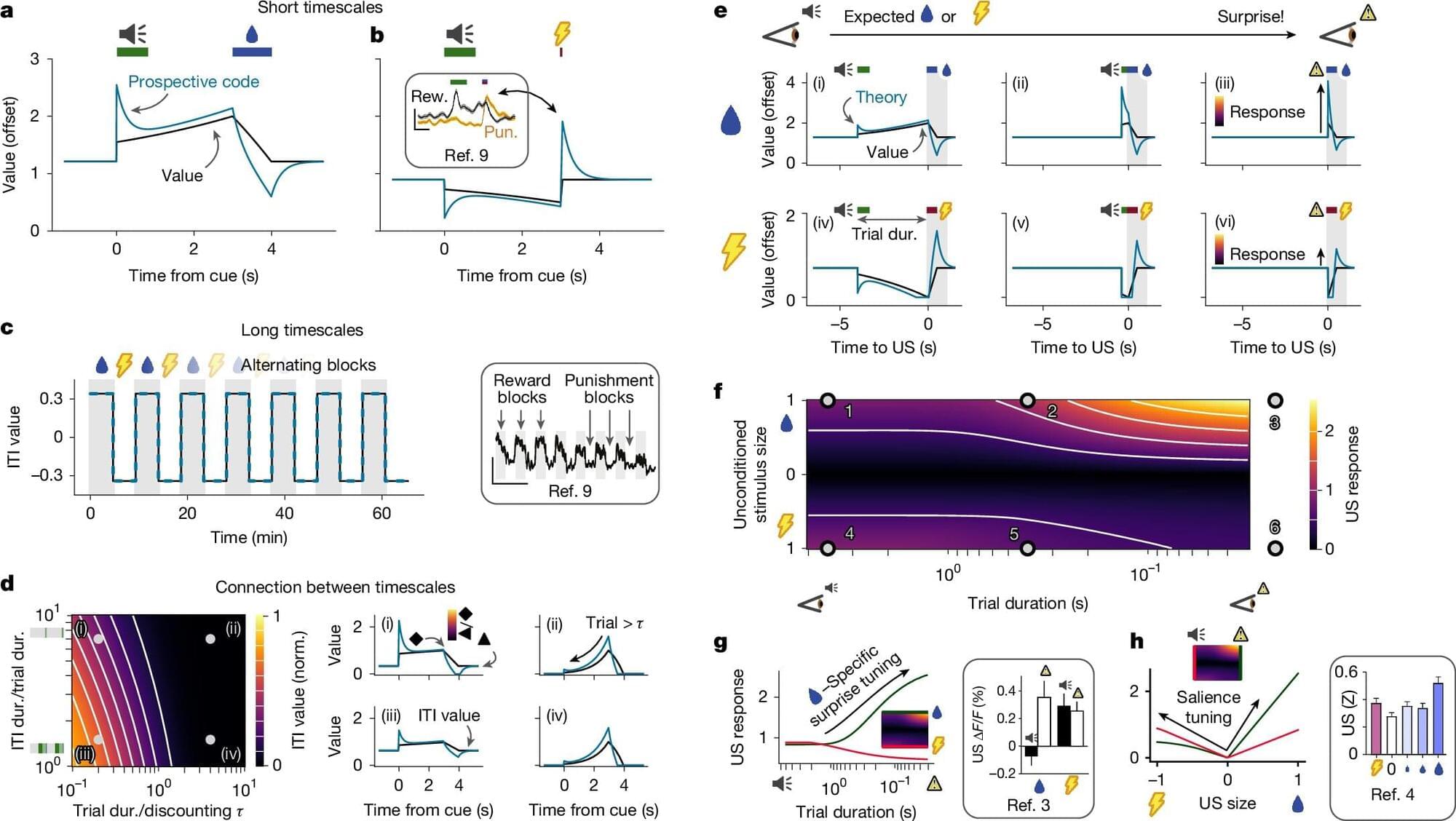
In our day-to-day lives, we’re constantly making a slew of decisions, from immediate matters to prospects on the far horizon. But the evolutionary nuts-and-bolts of how our brains weigh these numerous daily decisions and what role is played by the neurotransmitter serotonin has been shrouded in mystery.
Now, a new study led by an interdisciplinary University of Faculty of Medicine team delivers fascinating findings that potentially unravel a hidden aspect of what our nervous system’s extraordinarily complex serotonin system is really doing inside our skulls.
Published in the journal Nature, this study from a highly impactful international collaboration offers “broad implications across neuroscience, psychology, and psychiatry, enhancing our understanding of serotonin’s role in mood regulation, learning, and motivated behavior.”
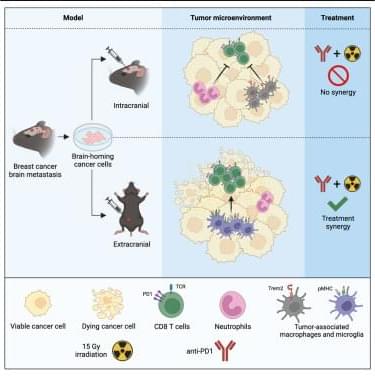
Wischnewski et al. demonstrate suppressed CD8+ T cell cytotoxicity in breast cancer brain metastases, contrasting with genetically identical extracranial tumors. Neutrophils and Trem2+ macrophages drive this suppression, limiting the efficacy of combined irradiation and anti-PD1 therapy, highlighting potential therapeutic targets for brain metastases.

New research from The University of Manchester may reshape our understanding of what happens to the immune system when we fast. The study on mice shows that the brain’s hypothalamus controls how the immune system adapts during fasting, through a handful of highly specialized neurons responsible for making animals hungry.
Published in Science Immunology, the study shows the brain’s perception of hunger or fullness, rather than actual eating or caloric restriction, is enough to drive changes in the body’s immune cells.
The findings cast doubt on the current view that a lack of nutrients alone controls how the immune system responds to fasting, indicating the brain has a critical role, beyond the simple absence of food.
Scientists Just Merged Human Brain Cells With AI – Here’s What Happened!
What happens when human brain cells merge with artificial intelligence? Scientists have just achieved something straight out of science fiction—combining living neurons with AI to create a hybrid intelligence system. The results are mind-blowing, and they could redefine the future of computing. But how does it work, and what does this mean for humanity?
In a groundbreaking experiment, researchers successfully integrated human brain cells with AI, creating a system that learns faster and more efficiently than traditional silicon-based computers. These “biocomputers” use lab-grown brain organoids to process information, mimicking human thought patterns while leveraging AI’s speed and scalability. The implications? Smarter, more adaptive machines that think like us.
Why is this such a big deal? Unlike conventional AI, which relies on brute-force data crunching, this hybrid system operates more like a biological brain—learning with less energy, recognizing patterns intuitively, and even showing early signs of creativity. Potential applications include ultra-fast medical diagnostics, self-improving robots, and brain-controlled prosthetics that feel truly natural.
But with great power comes big questions. Could this lead to conscious machines? Will AI eventually surpass human intelligence? And what are the ethical risks of blending biology with technology? This video breaks down the science, the possibilities, and the controversies—watch to the end for the full story.
How did scientists merge brain cells with AI? What are biocomputers? Can AI become human-like? What is hybrid intelligence? Will AI replace human brains?This video will answer all these question. Make sure you watch all the way though to not miss anything.
#ai.

As you age you naturally lose neurons and muscle mass and experience a decline in fertility and wound healing ability. Previous research in animals has offered several potential techniques for turning back the biological clock in specific tissues, including exercise and calorie restriction. However, age reversal of blood cells or at whole organism level has so far been elusive.

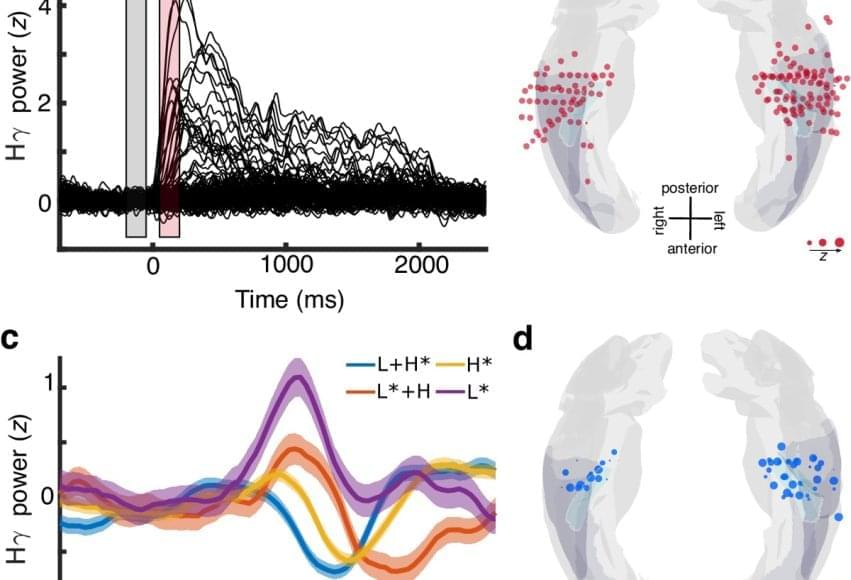
To explore how the brain deciphers the melody of speech, researchers worked with the rare group of patients who had electrodes implanted in their brains as part of epilepsy treatment. While these patients actively listened to an audiobook recording of “Alice in Wonderland,” scientists tracked activity in multiple brain regions in real time.
Using the intracerebral recordings from the electrodes deep in the patient’s brain, researchers noted the Heschl’s gyrus section processed subtle changes in voice pitch — not just as sound, but as meaningful linguistic units. The brain encoded pitch accents separately from the sounds that make up words.
The author says the research also revealed that the hidden layer of meaning carried by prosodic contours — the rise and fall of speech — is encoded much earlier in auditory processing than previously thought.
Similar research was conducted in non-human primates, but researchers found those brains lacked this abstraction, despite processing the same acoustic cues.
By unlocking the hidden layer of speech, the team discovered how the brain processes pitch accents, revealing profound implications for various fields.
“Our findings could transform speech rehabilitation, AI-powered voice assistants, and our understanding of what makes human communication unique,” the author said.
