Early evolutionary pressures likely generated our shared, fundamental nature of mind.
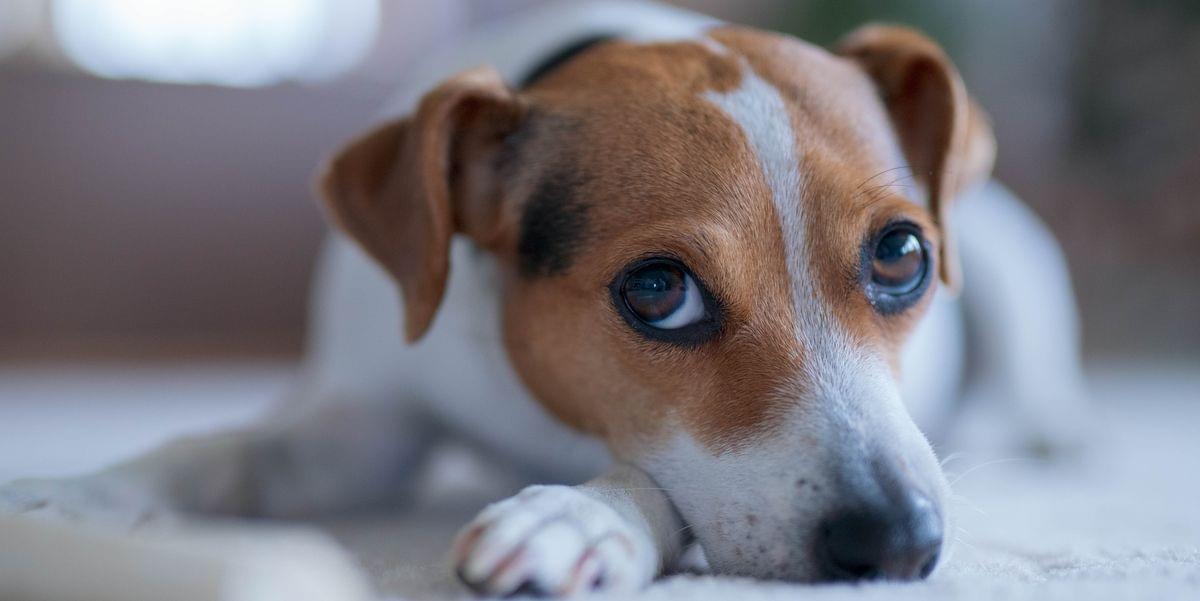


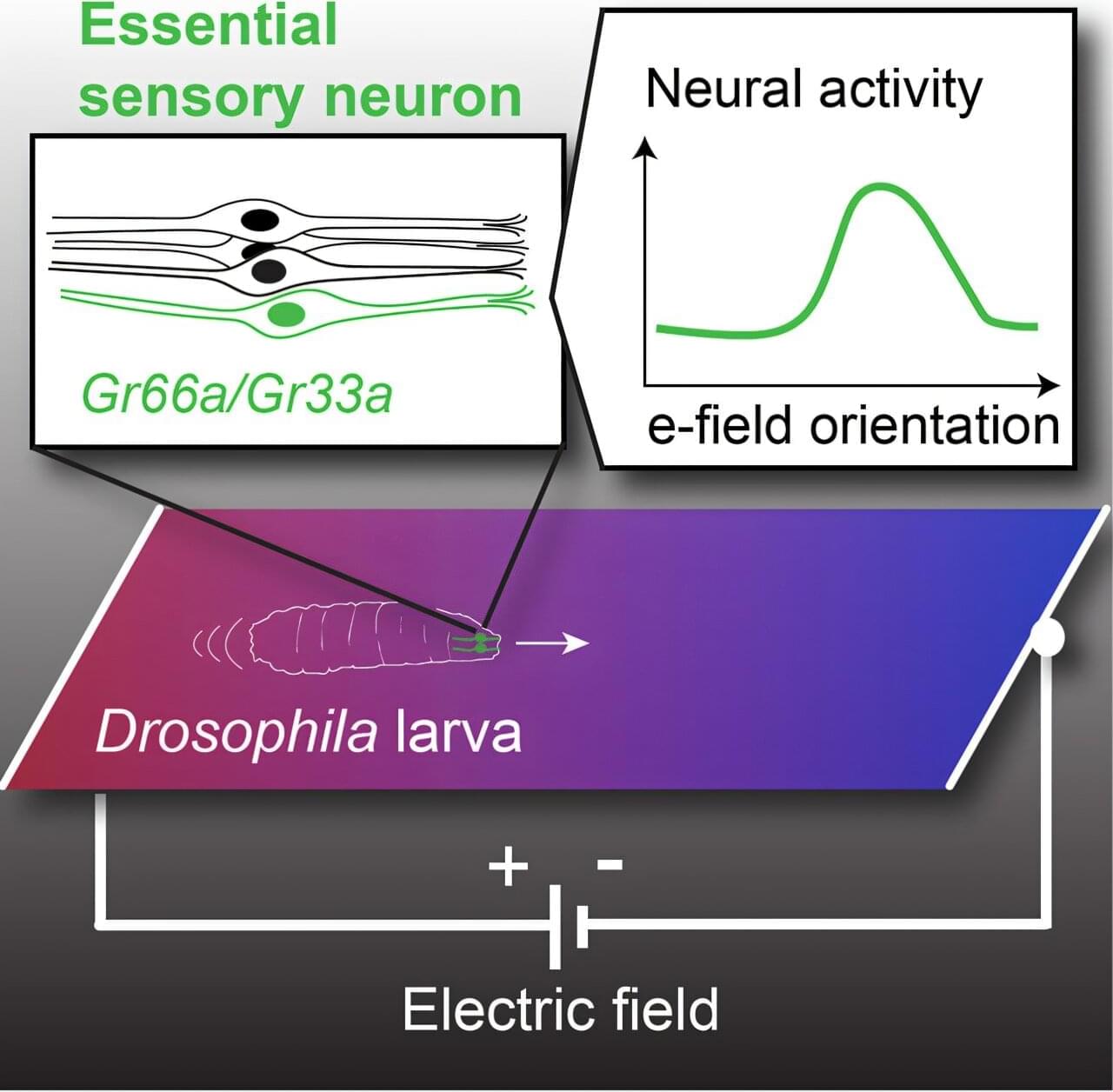
While it may be an unfamiliar sensation to humans, electroreception is relatively commonplace in the animal kingdom. Sharks, bees and even the platypus all share this ability to detect electric fields in their environment.
Scientists at UC Santa Barbara have just added fruit flies to that list. A team of researchers led by Matthieu Louis found that fruit fly larvae can sense electric fields and navigate toward the negative electric potential using a small set of sensory neurons in their head.
The findings, published in Current Biology, present an immense opportunity. Fruit flies are arguably the most commonly used experimental animals, the basis for studies in fields as disparate as genetics, neurobiology and aging. Uncovering electroreception in fruit flies opens new avenues of research into the basis of this sense and could even lead to new techniques in bioengineering.
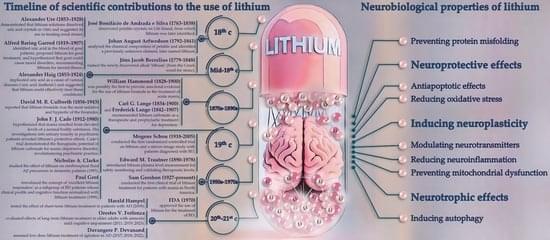
Lithium was introduced into psychiatric practice in the late nineteenth century and has since become a standard treatment for severe psychiatric disorders, particularly those characterized by psychotic agitation. It remains the most effective agent for managing acute mania and preventing relapses in bipolar disorder. Despite potential adverse effects, lithium’s use should be carefully considered relative to other treatment options, as these alternatives may present distinct safety and tolerability profiles. The World Health Organization classifies lithium salts as ‘essential’ medications for inclusion in global healthcare systems. Over the past two decades, the growing recognition of lithium’s efficacy—extending beyond mood stabilization to include reducing suicide risk and inducing neuroprotection—has led to its incorporation into clinical practice guidelines.
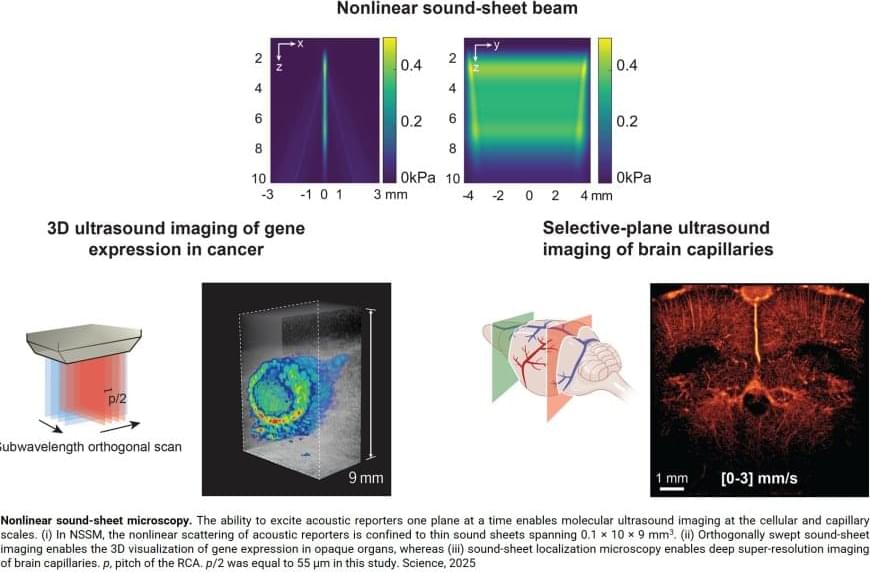
Key to this innovation in ultrasound imaging—a method called Nonlinear sound sheet microscopy —was the discovery of a sound-reflecting probe. The author said: “This probe is a nanoscale gas-filled vesicle that lights up in ultrasound images, making cells visible. These vesicles have a protein shell and we can engineer them to tune their brightness in images. We used these gas vesicles to track cancer cells.”
In addition to revealing cells, the team used ultrasound and microbubbles as probes circulating in the blood stream to detect brain capillaries. The author said: “To our knowledge, nonlinear sound sheet microscopy is the first technique capable of observing capillaries in living brains. This breakthrough has tremendous potential to diagnose small vessel diseases in patients.” Since microbubble probes are already approved for human use, this technique could be deployed in hospitals in a few years.
Ultrasound is one of the most widely used imaging techniques in medicine, but up until recently it hardly played a role in imaging the tiniest structures of our bodies such as cells. “Clinical ultrasound, like the kind used for pregnancy scans, creates real-time images of body parts”, the first author explains. “It allows diagnosis of various diseases, or to monitor a developing baby. However, what is going on at a microscopic level remains hidden.”
Now, a team of scientists managed to image specifically labelled cells in 3D with ultrasound. For the first time, they imaged living cells inside whole organs across volumes the size of a sugar cube. In comparison, current light-based microscopes often require imaging of non-living samples, the author says. “The sample or organ of interest has to be removed and processed, and you lose the ability to track activity of cells over time”
Researchers at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and College of Medicine have discovered a new way that neurons act in neurodegeneration by using human neural organoids—also known as “mini-brain” models—from patients with frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD).
Understanding this new pathway could help researchers find better treatments for FTLD and Alzheimer’s, the two most common forms of dementia that lead to cognitive decline.
Researchers used advanced techniques to study neurons from patients and mice, including growing human neural organoids (mini-brains) that can feature several cell types found in the brain.

Neurons are specialized brain cells responsible for transmitting signals throughout the body. For a long time, scientists believed that once neurons develop from stem cells into a specific subtype, their identity remains fixed, regardless of changes in their surrounding environment.
However, new research from the Braingeneers, a collaborative team of scientists from UC Santa Cruz and UC San Francisco, challenges this long-held belief.
In a study published in iScience, the Braingeneers report that neuronal subtype identity may be more flexible than previously thought. The team used cerebral organoids, 3D models of brain tissue, to investigate how neurons develop and adapt. Their findings offer new insights into how different neuron subtypes influence brain function and may play a role in neurodevelopmental disorders.
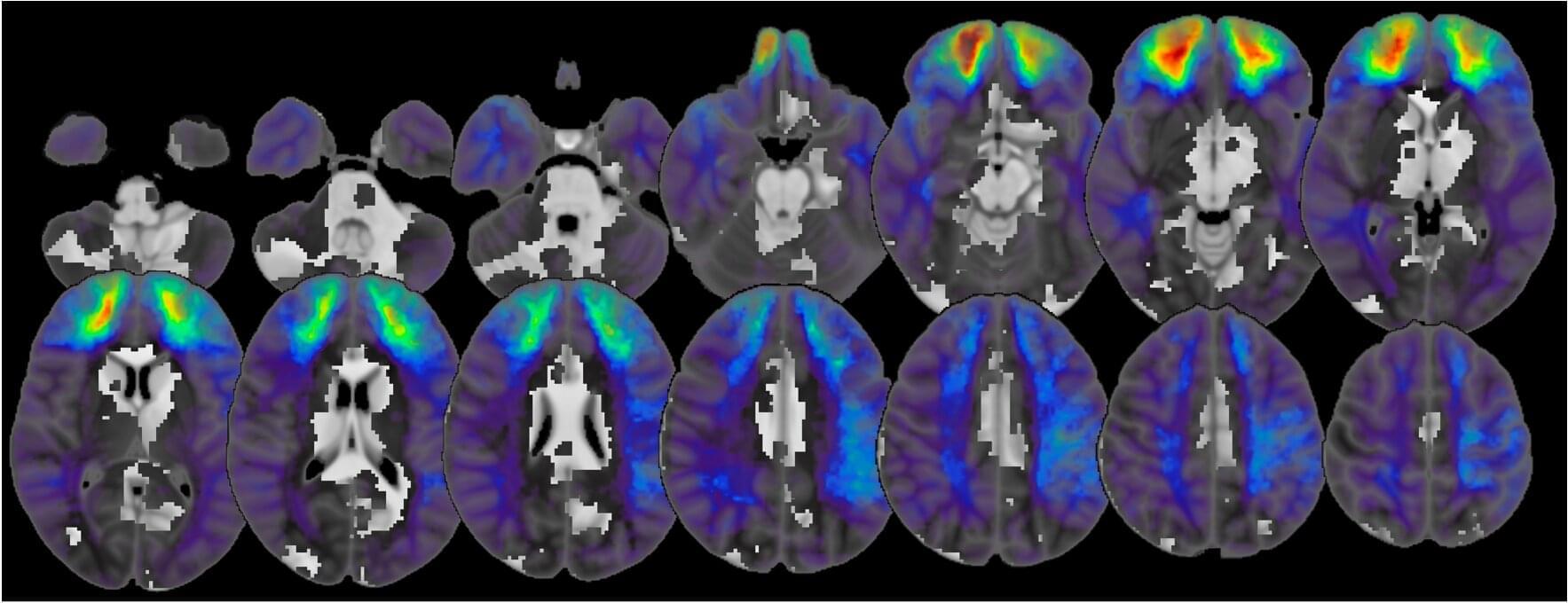
People diagnosed with various mental health disorders can sometimes start engaging in intense political behavior, such as violent protests, civil disobedience and the aggressive expression of political views. So far, however, the link between political behavior and the brain has been rarely explored, as it was not viewed as central to the understanding of mental health disorders.
Researchers at Harvard Medical School, Stanford University School of Medicine and Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine recently carried out a study investigating the neural underpinnings of political behavior. Their findings, published in Brain, unveil the existence of a brain circuit that is associated with the intensity of people’s political involvement, irrespective of their ideology or party affiliation.
“This paper started out as a collaborative effort that focused on learning how to help people better come together and thrive, alongside Stephanie Balters at Stanford,” Shan H. Siddiqi, first author of the paper, told Phys.org.
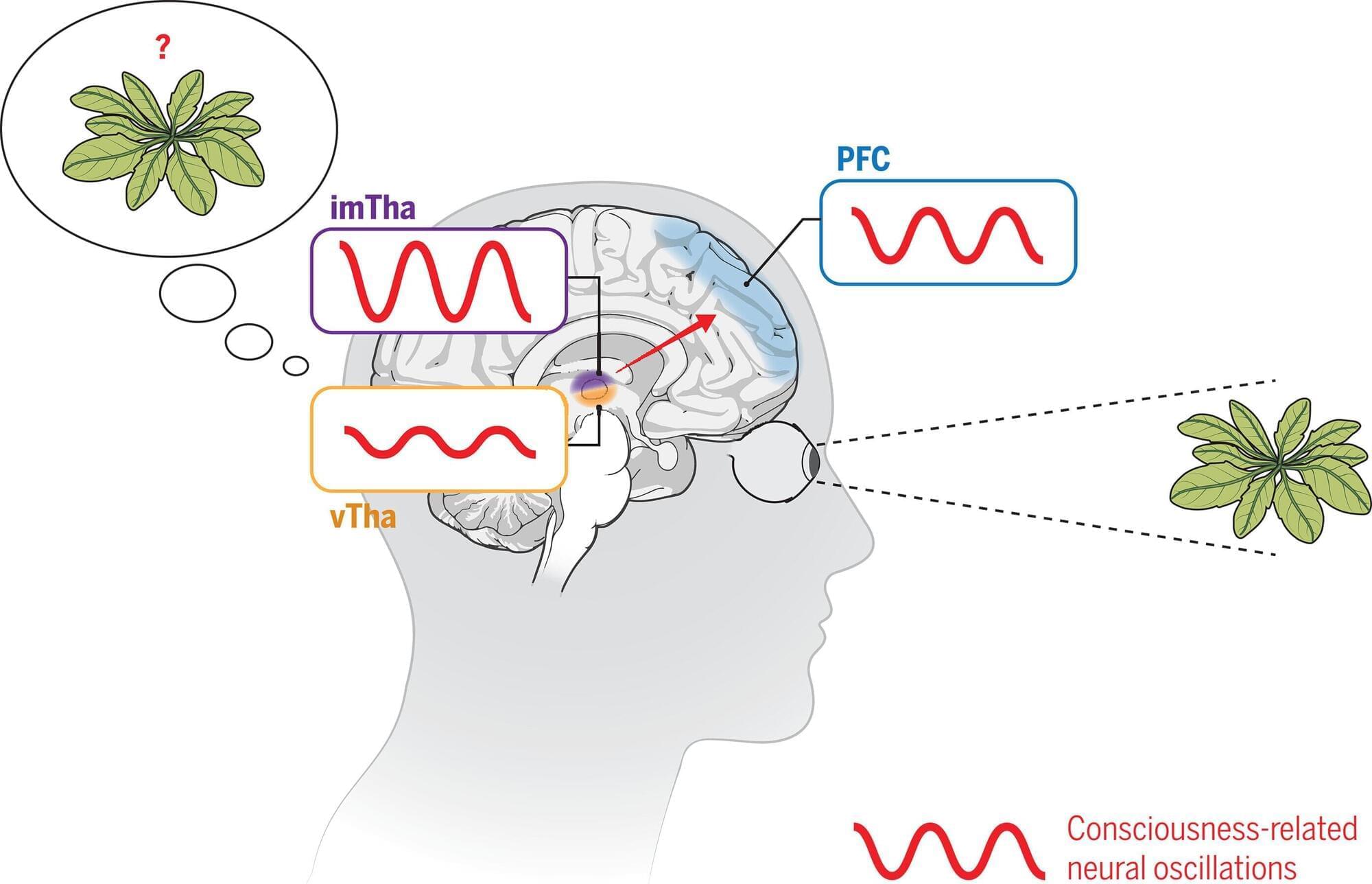
Beijing Normal University-led researchers have identified specific high-order thalamic nuclei that drive human conscious perception by activating the prefrontal cortex. Their findings enhance understanding of how the brain forms conscious experience, offering new empirical support for theories that assign a central role to thalamic structures rather than cortical areas alone.
Consciousness has been described as existing in two distinct forms: the general state of being awake or asleep, and the specific contents of subjective awareness. Most studies investigating the neural basis of perception have focused on the cerebral cortex.
Subcortical structures, including high-order thalamic nuclei, remain comparatively unexplored, ill-accounting for how rapidly shifting sensory information becomes part of conscious experience.
A recent study published in The Journal of Neuroscience has found evidence for a link between breathing patterns and brain activity during anxious states. Researchers found that rats experiencing anxiety-like behavior in a common behavioral test breathed more rapidly and that this change in breathing influenced brain rhythms in a key frontal brain area. The study highlights how shifts in respiration actively shape how the brain functions during emotional experiences.
Scientists have long known that feelings of anxiety can trigger physical changes in the body, including alterations in breathing. Previous research has shown that breathing influences brain activity, particularly in areas involved in processing smells and in the front part of the brain. This connection between breathing and brain function has been especially well-documented in relation to fear, where slow, steady breathing is often linked to freezing behavior in rodents. However, it remained unclear whether breathing plays a similar role in other negative emotional states like anxiety, which tends to involve faster breathing.
To investigate this, researchers set out to understand how breathing affects brain activity in situations that evoke anxiety. They used a widely accepted method for studying anxiety in rodents called the elevated plus maze. This maze is shaped like a plus sign and has two arms that are enclosed and two that are open and exposed. Because rats naturally prefer the safety of enclosed spaces, spending time in the open arms is considered an indication of anxiety-like behavior.