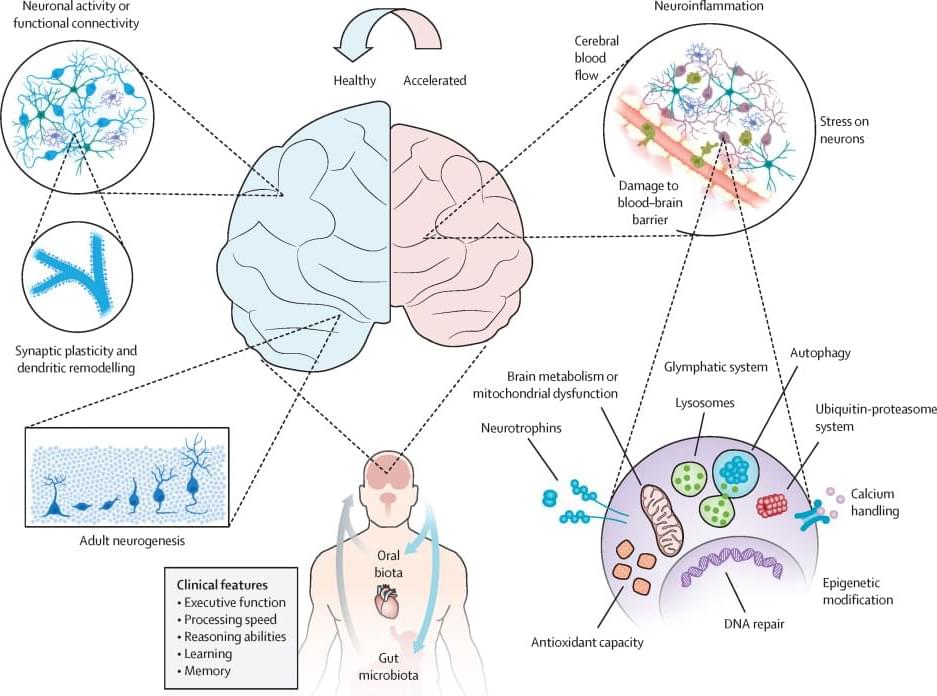
In this episode of the Neural Implant Podcast, we’re joined by Nathan Piland, CEO of Nunex, a consulting firm that specializes in helping MedTech companies navigate the complex journey from concept to commercialization. With over two decades of experience across regulatory strategy, product development, and market access, Nathan shares invaluable insights into the critical steps for MedTech startups and established companies looking to succeed in today’s competitive landscape. Tune in as we discuss the unique challenges of the neurotech industry, strategic consulting for MedTech ventures, and how Nunex is helping companies grow and scale through a holistic, tailored approach.
Top 3 Takeaways: