It’s been thought that T cells would only move into the brain in the case of a serious problem. New work shows otherwise… | Cell And Molecular Biology
Category: neuroscience – Page 220
Dancing to the dopamine reward threshold: How long-term addiction shifts music perception
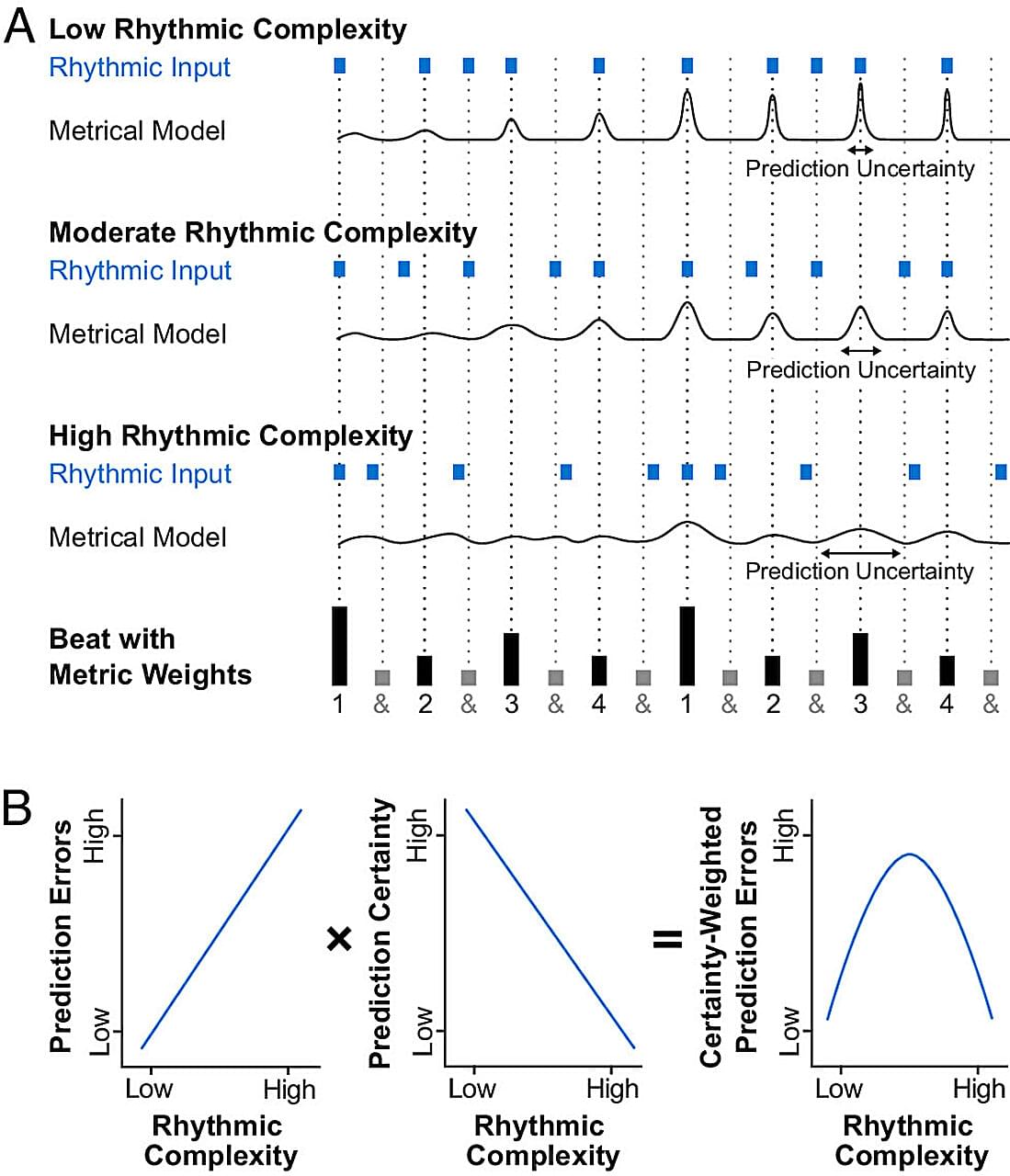
Research led by Aarhus University in Denmark reports that individuals with substance use disorders experience a heightened urge to move in response to music with complex rhythms and harmonies.
Long-term use of cocaine and heroin disrupts dopamine signaling in the brain, depleting receptors and diminishing the effects of non-drug stimuli, such as music, to trigger pleasure.
Prior research has shown that music can activate dopaminergic pathways involved in reward, anticipation, and movement. Groove, the pleasurable urge to move to music, follows an inverted-U pattern in healthy listeners, peaking when rhythms fall into a sweet spot of moderate rhythmic complexity. Most people feel the strongest compulsion to move their bodies to the beat when those beats are neither too simple nor too unpredictable.


Size matters: The link between social groups and human evolution
Humans are social creatures; we live in family groups, socialise with friends, and work with colleagues. Evolutionary psychologist Robin Dunbar’s ‘social brain hypothesis’ suggests that brain size is directly related to social group size in mammals. The bigger the group, the bigger the brain. In this interview with Research Outreach, we find out how Dunbar developed his theory as well as his now famous ‘Dunbar’s number’
Robin Dunbar discusses his eponymous ‘Dunbar’s Number’, primates to people, and why size matters with social groups and evolution.


Inside The New Era of Longevity Supplements
More and more people are investing their time and energy into longevity — it’s not just living longer, but living happier, healthier and staying productive well past what has been considered “old age.” McKinsey reports that up to 60 percent of consumers across health and wellness markets say that healthy aging is a “top” or “very important” priority. The movement has created a boost in the health and wellness businesses, and to get an overview of the longevity supplements space, we spoke with Dr. Luke Winegard, the Chief Operating Officer at Longevity Method.
Entrepreneur: What is driving the current boom in the longevity supplement market? Dr. Luke Winegard: Growing consumer demand for health and wellness products is creating explosive growth in the longevity supplement market. Scientific advancements and increasing health consciousness are driving this trend, with consumers now focused on “healthspan” — not just how long they live, but how well they live. The pursuit of longevity has moved from being a niche interest of visionaries to becoming mainstream in 2025.
What does “healthspan” mean and why is it important? Healthspan refers to the period of life spent in good health, free from chronic diseases and disabilities. Today’s consumers are concerned not just about adding years to their lives, but making those years healthy, productive, and vital. This represents a cultural shift toward proactive self-optimization where maintaining energy, cognitive sharpness, and resilience is just as important as achieving physical goals.
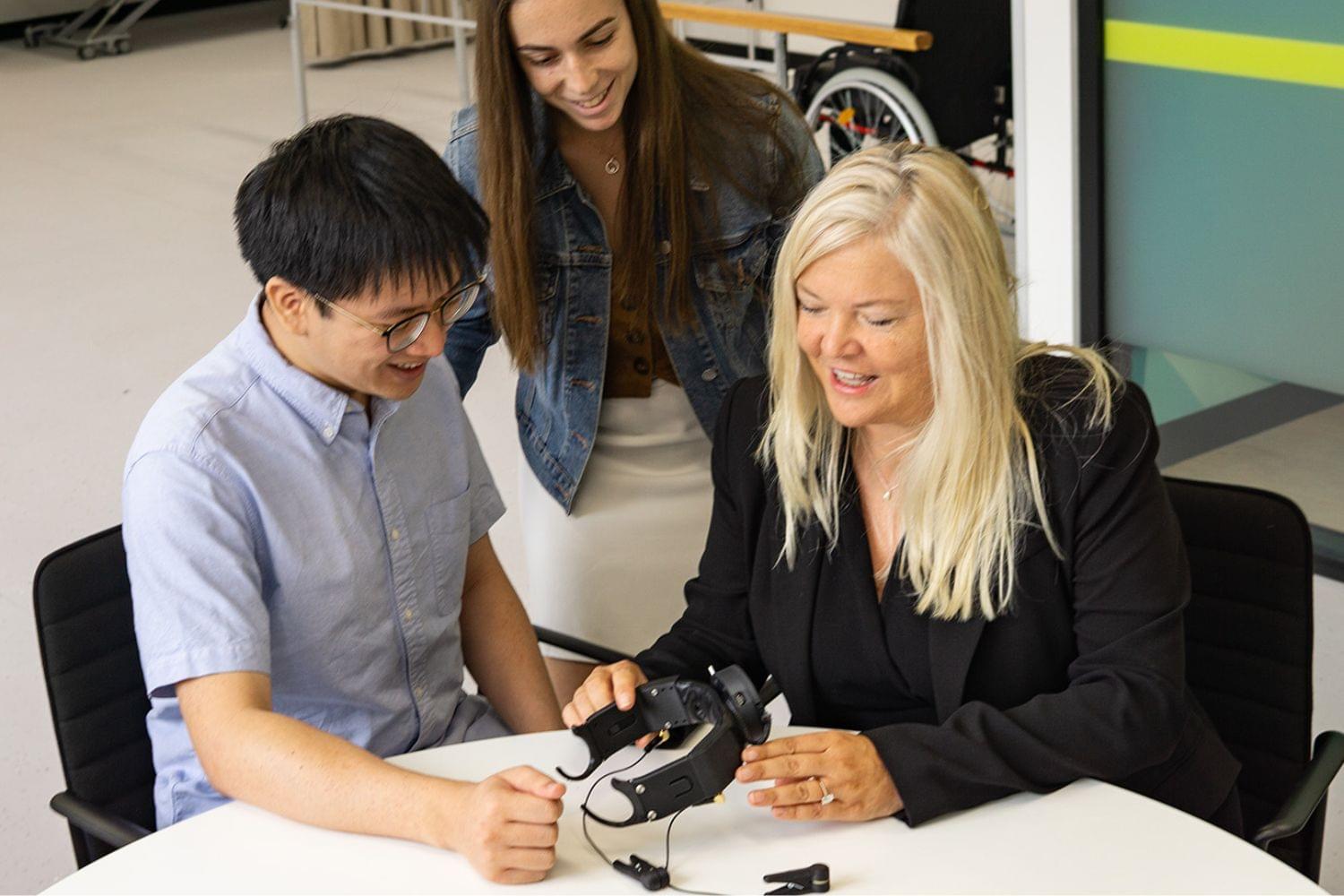

Scientists Taught People to Change Their Own Brainwaves to Feel Less Pain
The brainwaves of people with neuropathic pain show a distinct pattern: more slow theta waves, fewer alpha waves, and more fast, high beta waves, co-lead author Sylvia Gustin, a clinical psychologist and UNSW professor, said in the statement. Her research has investigated changes in the thalamus—a central brain structure that relays sensory and motor signals to the cerebral cortex—associated with nerve pain.
The PainWaive system consists of an electroencephalogram (EEG) headset that records brain activity paired with an app that instructs patients on how to control their brainwaves through neurofeedback games, according to a UNSW statement. Four participants who suffer from corneal neuropathic pain—a condition that causes painful hypersensitivity of the eyes, face, or head—underwent 20 PainWaive sessions over the course of four weeks.
This study offers new hope for drug-free pain treatments, but further trials will need to verify its results.

When less is more: How inhibition shapes learning and spatial memory formation
Nuri Jeong remembers the feeling of surprise she felt during a trip back to South Korea, while visiting her grandmother, who’d been grappling with Alzheimer’s disease.
“I hadn’t seen her in six years, but she recognized me,” said Jeong, a former graduate researcher in the lab of Annabelle Singer in the Wallace H. Coulter Department of Biomedical Engineering at Georgia Tech and Emory University.
“I didn’t expect that. Even though my grandmother struggled to remember other family members that she saw all the time, she somehow remembered me,” Jeong added. “It made me wonder how the brain distinguishes between familiar and new experiences.”

This diet can protect your brain even if started later in life, study suggests
People who follow a MIND diet, even if started later in life, were significantly less likely to develop Alzheimer’s disease or related forms of dementia, according to new research.
The MIND diet stands for “Mediterranean-DASH Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay” and combines many elements of the Mediterranean diet and DASH (“Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension”). It emphasizes brain-healthy foods like leafy greens, berries, nuts and olive oil.
The study, being presented Monday at the American Society for Nutrition’s annual meeting, analyzed data from nearly 93,000 U.S. adults aged 45 to 75 starting in the 1990s.