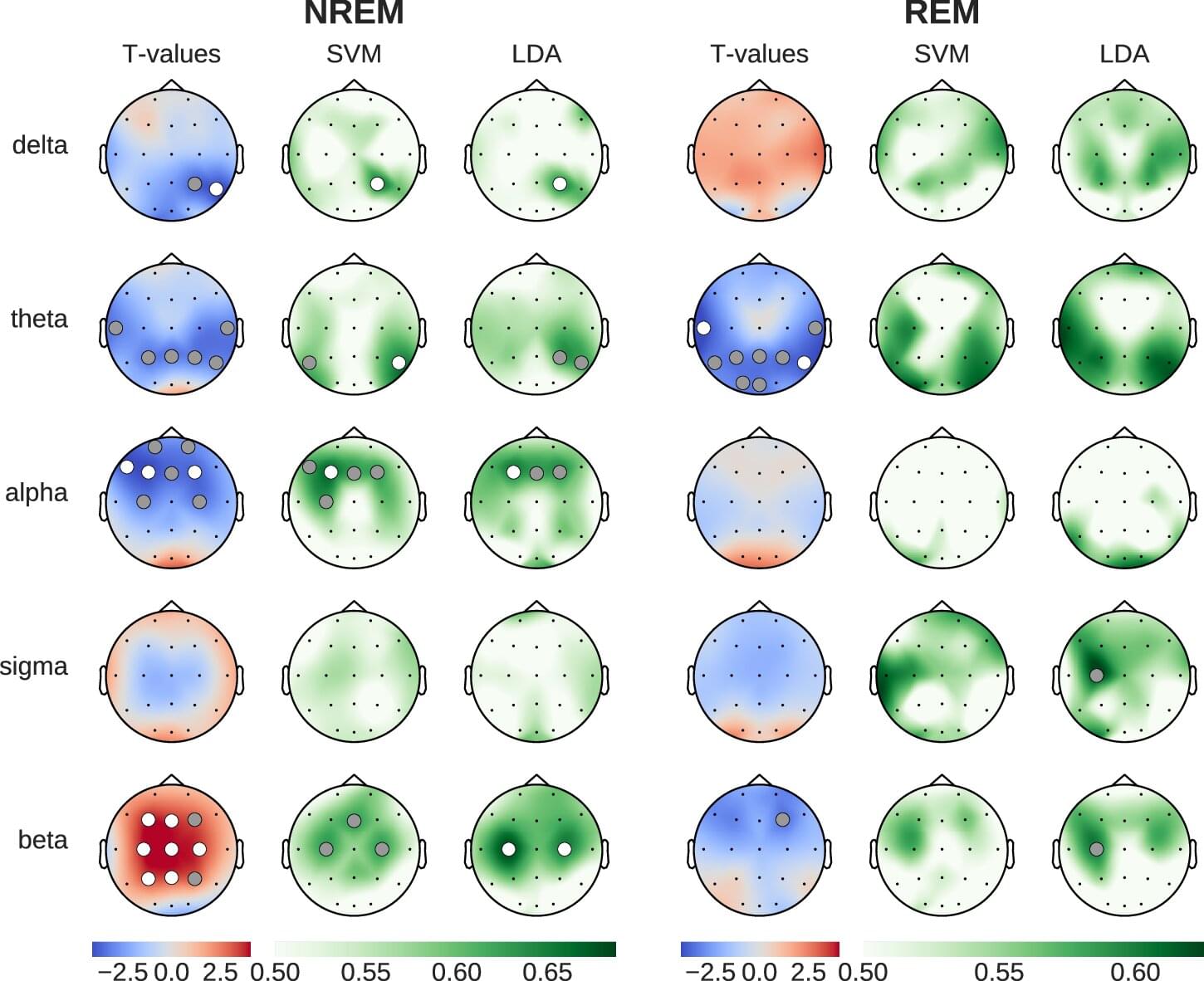
Caffeine is not only found in coffee, but also in tea, chocolate, energy drinks and many soft drinks, making it one of the most widely consumed psychoactive substances in the world.
In a study published in Communications Biology, a team of researchers from Université de Montréal shed new light on how caffeine can modify sleep and influence the brain’s recovery—both physical and cognitive—overnight.
The research was led by Philipp Thölke, a research trainee at UdeM’s Cognitive and Computational Neuroscience Laboratory (CoCo Lab), and co-led by the lab’s director, Karim Jerbi, a psychology professor and researcher at Mila–Quebec AI Institute.